如果你也在 怎样代写商业建模Business Modeling这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
商业建模是一种风格化的模式,描述了公司如何创造并向客户提供价值,以及他们如何为此获得回报。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写商业建模Business Modeling方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写商业建模Business Modeling代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写商业建模Business Modeling相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的商业建模Business Modeling及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
商科代写|商业建模代写Business Modeling代考|Related Work
We consider rule expressions defined in relation algebra as a starting point for determining rule styles. We create an ontology for business rules that contains the necessary components to be displayed in the interface. The focus is on how the mapped business rules can be displayed in the interface. The Ampersand tool [6] displays errors directly when detecting business rule violations. The rule modality determines whether the user may or may not proceed without resolving the violation. If the user may proceed, a violation message appears in a yellow box as a warning. If the violation may not even be temporary, then the message box is red.
Ampersand classifies rules by the method of enforcement, which can be an axiom, invariant rule, process rule or automated rule [6]. The syntax of a rule in Ampersand contains a purpose, meaning, message, violation text and expression of the rule in relation algebra. The purpose and meaning are used to inform the end user why a rule exists and what it means. The message and violation text contain information to be displayed on screen when the rule is violated. The violation text can contain references to the concepts and relations that cause the violation, whereas the message informs the user without explicitly mentioning the affected instance. We use the message of a rule in our research for displaying rule violations. For process and automated rules, a role is defined that should maintain the business rule.
Another Ampersand feature is limiting input values to a composition of relations. This feature prevents users from selecting values that would trigger a violation. While Ampersand displays violations on screen, it does not change the style of a field when a rule states that this field should be mandatory. The limitation of input values for an input field based on a composition of relations must be configured separately, as the composition is not derived from business rules specified by a business engineer. In earlier work, we use Ampersand to demonstrate how relation algebra implementations of business rules apply to IT alignment [4].
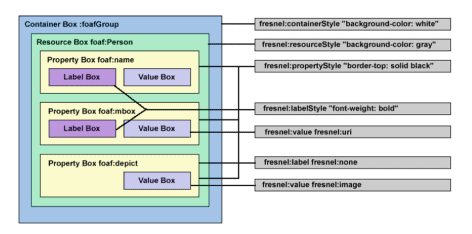
Fresnel displays RDF data in a human readable form on semantic browsers [11]. CSS [1] has a significant influence on Fresnel: CSS does for XML and HTML what Fresnel does for RDF. For example, the CSS concepts of selectors and the formatting model are also important to Fresnel. A CSS selector specifies components of XML and HTML documents so it can apply a given style to them. The formatting model for CSS is the HTML document display, with familiar document structure components such as paragraphs, along with a more abstract box model. A CSS rule has a selector and a style declaration. A CSS declaration can say which type of formatting model component the selected document content appears in. A CSS declaration also defines the more familiar aspects of CSS visual style for selected content, such as font size.
While CSS has its own syntax, Fresnel code consists of RDF triples, which conform to the RDFS-defined ontology for Fresnel. Fresnel has two main concepts: lenses and formats, both of which correspond roughly to the CSS rule. Lenses determine which properties of RDF (Resource Description Format) data to show and in what order. Formats determine how to display, typically using CSS.
商科代写|商业建模代写Business Modeling代考|Methodology
The remaining sections evaluate our proposed model for rule styles by demonstration. We implement business rules retrieved from $E U$-Rent [10]. Our prototype uses and, where needed, extends an OWL-defined ontology for EU-Rent [12] and an Ampersand implementation for EU-Rent [5]. Each demonstration has this structure:
- Explanation of the rule and desired behavior of the rule style
- Demonstration in Ampersand
- Encoding in the Semantic Web
- Proposed Fresnel implementation
- Example of the rule style output in Semantic MediaWiki.
Our ontology for alethic and deontic business rules is derived from how Ampersand captures business rules with the rule syntax [6]. We made the rule types in our ontology explicit as OWL restrictions. The ontology can be extended with additional subclasses and properties relevant for each rule type. A business rule is created as subclass of a new general violation class. The rules contain class restrictions modelled as equivalent classes that are asserted by as style in Fresnel with Fresnel Violations. A property for the violation message of the business rules captures the message to be displayed for the violation.
The message annotation is also similar in Ampersand. The main difference is that Ampersand can also integrate classes and properties (or concepts and relations) in the message using the keyword VIOLATION, whereas our message is an annotation property that only contains text. A comparison of syntax used in Ampersand and our Violation ontology is listed in Table 2. This paper’s code fragments use bold font to emphasis specific aspects in the syntax of the various languages. In Ampersand, bold font indicates where the logic is defined, while the rest is names and strings. The Fresnel code fragments have our own extensions displayed in bold.
This paper’s Semantic Web definitions of this same type of rule are usually as OWL equivalent classes of OWL restrictions, as the code fragments in the upcoming sections show. Items that violate of the rule get inferred as an instance of the rule’s assigned class. The benefit of using this method is that is guides exchange of rule expressions between relation algebra and OWL, provided that the RDFS classes and properties have equivalents in the concepts and relations in Ampersand. In each demonstration, we show Semantic Web code. We use bold font for URLs that we make, either as extensions to existing ontologies, or as our own example triples. The restriction that determines whether an instance will be inferred is listed under the header equivalent class. Constructs that the Violation ontology introduces have the namespace prefix “fresvio:”.
商科代写|商业建模代写Business Modeling代考|User Task Lists
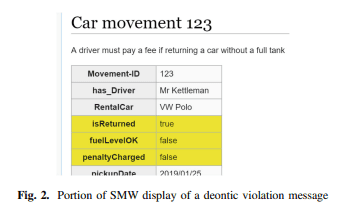
This section’s implementation shows a list of violations of the EU-Rent rule that prohibits a rental period from exceeding 90 days. While an alethic rule would prevent any initial car rental reservation from lasting more than 90 days, one can extend reservations during rental, and renters can return cars late. Therefore, an open car rental can become overdue and thus trigger a rule violation. Process lists inform the user of this kind of rule violation. Since neither relation algebra nor the Semantic Web perform math, we simply add a data property to the RDFS ontology code, and a relation in relation algebra representation, each of which indicate overextended rentals. For Ampersand, an example for computing the maximum rental days is made [5].
This rule is post-justified, and thus deontic, and similar to the process rule in Ampersand. The Ampersand tool displays existing process rule violations as a list (see Fig. 3). Clicking on the warning message shows the elements causing the violation. Clicking on one presents a form to amend information about the element. This can be viewed as a process list. The rule in Ampersand is expressed as follows:
RULE max90Days : I [Carmovement] I- -longerthang0days
MESSAGE
“There are car rentals open for more than 90 days”
As before, we define this on the Semantic Web as an OWL restriction. A data property states whether the car movement exceeds the 90 -day maximum. We verify the rule with an example with a Car Movement individual whose property isOverdue is true, which then infers it as a CarMovementopenoverdue.
Our goal is to show all instances of class CarMovementopenoverdue in a table overview, similar to how Ampersand displays a process list. Our Fresnel code defines a
lens that selects the URL for the class. This lens displays the message and then all objects linked by the inverse property for rdf : type, which thus infers all movements violating this rule. The Fresnel lens code is:
vioRent:CarMovementopenoverduelns a fresnel: Lens ; fresnel:instanceLensDomain $\quad$ VioRent: CarMovementopenOverdue ; fresnel:purpose fresnel:defaultLens; fresnel: showProperties $\quad$ ( fresvio:message fresvio:hasinstance ) .
商业建模代考
商科代写|商业建模代写Business Modeling代考|Related Work
我们将关系代数中定义的规则表达式视为确定规则样式的起点。我们为业务规则创建一个本体,其中包含要在界面中显示的必要组件。重点是如何在界面中显示映射的业务规则。Ampersand 工具 [6] 在检测业务规则违规时直接显示错误。规则模式确定用户是否可以在不解决违规的情况下继续。如果用户可以继续,则会在黄色框中显示一条违规消息作为警告。如果违规甚至不是暂时的,则消息框为红色。
&符号通过执行方法对规则进行分类,可以是公理、不变规则、过程规则或自动规则[6]。Ampersand 中规则的语法包含关系代数中规则的目的、含义、消息、违规文本和表达式。目的和含义用于告知最终用户规则存在的原因及其含义。消息和违规文本包含违反规则时要在屏幕上显示的信息。违规文本可以包含对导致违规的概念和关系的引用,而消息会通知用户而没有明确提及受影响的实例。我们在研究中使用规则信息来显示违反规则的情况。对于流程和自动化规则,定义了一个应该维护业务规则的角色。
另一个&符号功能是将输入值限制为关系的组合。此功能可防止用户选择会触发违规的值。虽然 & 符号在屏幕上显示违规,但当规则声明该字段应为必填时,它不会更改字段的样式。基于关系组合的输入字段的输入值限制必须单独配置,因为组合不是从业务工程师指定的业务规则派生的。在早期的工作中,我们使用 & 来演示业务规则的关系代数实现如何应用于 IT 对齐 [4]。
Fresnel 在语义浏览器 [11] 上以人类可读的形式显示 RDF 数据。CSS [1] 对 Fresnel 有重大影响:CSS 对 XML 和 HTML 的作用就像 Fresnel 对 RDF 的作用一样。例如,选择器的 CSS 概念和格式化模型对 Fresnel 也很重要。CSS 选择器指定 XML 和 HTML 文档的组件,因此它可以将给定的样式应用于它们。CSS 的格式化模型是 HTML 文档显示,具有熟悉的文档结构组件(例如段落)以及更抽象的框模型。CSS 规则有一个选择器和一个样式声明。CSS 声明可以说明所选文档内容出现在哪种类型的格式化模型组件中。CSS 声明还定义了所选内容的 CSS 视觉样式更熟悉的方面,例如字体大小。
虽然 CSS 有自己的语法,但 Fresnel 代码由 RDF 三元组组成,符合 RDFS 定义的 Fresnel 本体。菲涅耳有两个主要概念:镜头和格式,两者都大致对应于 CSS 规则。镜头确定要显示 RDF(资源描述格式)数据的哪些属性以及显示顺序。格式决定如何显示,通常使用 CSS。
商科代写|商业建模代写Business Modeling代考|Methodology
其余部分通过演示评估我们提出的规则样式模型。我们实现从和在-租金 [10]。我们的原型使用并在需要时扩展了用于 EU-Rent [12] 的 OWL 定义的本体和用于 EU-Rent [5] 的 & 符号实现。每个演示都有这样的结构:
- 规则说明和规则样式的期望行为
- & 符号中的演示
- 语义网中的编码
- 建议的菲涅耳实施
- Semantic MediaWiki 中的规则样式输出示例。
我们的 alethic 和 deontic 业务规则本体源自 Ampersand 如何使用规则语法 [6] 捕获业务规则。我们将本体中的规则类型明确表示为 OWL 限制。可以使用与每个规则类型相关的附加子类和属性来扩展本体。业务规则被创建为新的一般违规类的子类。规则包含建模为等效类的类限制,这些类限制在 Fresnel with Fresnel Violations 中由 as 样式声明。业务规则的违规消息的属性捕获要为违规显示的消息。
Ampersand 中的消息注释也类似。主要区别在于,Ampersand 还可以使用关键字 VIOLATION 在消息中集成类和属性(或概念和关系),而我们的消息是仅包含文本的注释属性。表 2 中列出了 Ampersand 和我们的 Violation 本体中使用的语法比较。本文的代码片段使用粗体字来强调各种语言语法中的特定方面。在与符号中,粗体表示逻辑的定义位置,其余的是名称和字符串。菲涅耳代码片段有我们自己的扩展,以粗体显示。
这篇论文的语义网对这种相同类型的规则的定义通常与 OWL 限制的 OWL 等价类一样,正如后面几节中的代码片段所示。违反规则的项目被推断为规则指定类的实例。使用这种方法的好处是指导关系代数和 OWL 之间的规则表达式的交换,前提是 RDFS 类和属性在与符号中的概念和关系中具有等价物。在每个演示中,我们都会展示语义 Web 代码。我们对我们制作的 URL 使用粗体字体,或者作为现有本体的扩展,或者作为我们自己的示例三元组。确定是否将推断实例的限制列在标题等效类下。Violation 本体引入的构造具有命名空间前缀“fresvio:”。
商科代写|商业建模代写Business Modeling代考|User Task Lists
本节的实施显示了违反 EU-Rent 规则的列表,该规则禁止租赁期超过 90 天。虽然 alethic 规则会阻止任何初始汽车租赁预订持续超过 90 天,但可以在租赁期间延长预订,并且租户可以延迟还车。因此,开放式汽车租赁可能会过期,从而引发违规行为。进程列表会通知用户这种违反规则的行为。由于关系代数和语义 Web 都不执行数学运算,我们只需在 RDFS 本体代码中添加一个数据属性,以及一个关系代数表示中的关系,每个都表示过度租用。对于 & 符号,计算了最大租赁天数的示例 [5]。
这条规则是后对齐的,因此是道义的,类似于 & 中的过程规则。Ampersand 工具将现有的流程规则违规显示为列表(参见图 3)。单击警告消息会显示导致违规的元素。单击一个会显示一个表单以修改有关元素的信息。这可以看作是一个进程列表。Ampersand 中的规则表示如下:
RULE max90Days : I [Carmovement] I- -longerthang0days
MESSAGE
“有租车营业时间超过 90 天”
和以前一样,我们在语义 Web 上将其定义为 OWL 限制。数据属性说明汽车移动是否超过 90 天的最大值。我们用一个例子来验证规则,其中一个 Car Movement 个体的属性 isOverdue 为真,然后将其推断为 CarMovementopenoverdue。
我们的目标是在表格概览中显示 CarMovementopenoverdue 类的所有实例,类似于 Ampersand 显示进程列表的方式。我们的菲涅耳代码定义了一个
为班级选择 URL 的镜头。该镜头显示消息,然后显示由 rdf : type 的逆属性链接的所有对象,从而推断出所有违反此规则的运动。菲涅尔透镜代码为:
vioRent:CarMovementopenoverduelns a fresnel: Lens ;菲涅耳:instanceLensDomainVioRent: CarMovementopenOverdue ; 菲涅尔:目的菲涅尔:defaultLens;菲涅尔:showProperties(fresvio:消息fresvio:hasinstance)。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
