如果你也在 怎样代写金融数学Financial Mathematics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
金融数学是将数学方法应用于金融问题。(有时使用的同等名称是定量金融、金融工程、数学金融和计算金融)。它借鉴了概率、统计、随机过程和经济理论的工具。传统上,投资银行、商业银行、对冲基金、保险公司、公司财务部和监管机构将金融数学的方法应用于诸如衍生证券估值、投资组合结构、风险管理和情景模拟等问题。依赖商品的行业(如能源、制造业)也使用金融数学。 定量分析为金融市场和投资过程带来了效率和严谨性,在监管方面也变得越来越重要。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写金融数学Financial Mathematics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写金融数学Financial Mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写金融数学Financial Mathematics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的金融数学Financial Mathematics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
数学代考|金融数学代考Financial Mathematics代写|Consumers
The population consists of overlapping generations of finitely-lived agents who are identical in every respect except for their health type. Agents live for a maximum of two periods, termed ‘youth’ (superscript $y$ ) and ‘old age’ (o). At birth each agent learns her health status as proxied by the survival probability, $\mu$. This is where the difference between health types comes in: unhealthy agents have a higher risk of dying, and therefore a shorter expected life span (which equals $1+\mu$ periods). We assume that cohorts are sufficiently large such that there is no aggregate uncertainty and probabilities and frequencies coincide. For example, the fraction of young agents of type $\mu$ who die after the first period equals exactly $1-\mu$. Note that from the perspective of an individual agent, lifetime uncertainty is resolved at the start of the second period. When still alive, the agent will live for exactly one additional period.
Labour supply is exogenous. During youth the agent is fully employed while during old age labour supply is only a fraction $\lambda$ of the unit time endowment as a result of mandatory retirement $(0<\lambda<1)$. The expected lifetime utility of a representative agent of health type $\mu$ who is born in period $t$ is given by: $$ \mathbb{E} \Lambda_{t}(\mu) \equiv U\left(C_{t}^{y}(\mu)\right)+\mu \beta U\left(C_{t+1}^{o}(\mu)\right), $$ where $C_{t}^{y}(\mu)$ and $C_{t+1}^{o}(\mu)_{\text {are }}$ consumption during youth and old age, respectively, $\beta$ is a parameter capturing pure time preference $(0<\beta<1)$, and $U(\cdot)$ is the felicity function: $$ U(x) \equiv \frac{x^{1-1 / \sigma}-1}{1-1 / \sigma}, \quad \sigma>0 .
$$
This functional form is chosen for analytical convenience and it implies a constant intertemporal substitution elasticity, $\sigma$. We assume that the agent does not have a bequest motive such that she does not derive any utility from wealth that remains after her death.
数学代考|金融数学代考Financial Mathematics代写|Demography
Let $\mathrm{h}(\mu)$ denote the probability density function of health types in a given cohort upon its arrival. Then the distribution of agents in the cohort born at time $t$ can be written as:
$$
L_{t}(\mu) \equiv h(\mu) L_{t},
$$
$\int_{\mu_{l}}^{\mu_{h}} h(\mu) d \mu=\int_{\mu_{l}}^{\mu_{h}} d H(\mu)=1$ where $\mathrm{H}(\mu)$ is the cumulative density function. The density of $\mu$-type agents alive at time $t$ is given by $P_{t}(\mu) \equiv$ $\mu L_{t-1}(\mu)+L_{t}(\mu)$. Assuming that newborn cohorts evolve according to $L_{t}=$ $(1+n) L_{t-1}$ (with $\left.n>-1\right)$ we thus find that:
$$
P_{t}(\mu)=\frac{1+\mu+n}{1+n} L_{t}(\mu) .
$$
The total population alive in period $t$ is obtained by aggregating over health types:
$$
P_{t} \equiv \int_{\mu_{t}}^{\mu_{\phi}} P_{t}(\mu) d \mu=\frac{1+\bar{\mu}+n}{1+n} L_{t},
$$
where $\bar{\mu} \equiv \int_{\mu \mu}^{\mu_{h}} \mu h(\mu) d \mu$ is the average survival rate in the population as a whole.
Government
In the absence of annuity markets we have to make an assumption about how the accidental bequests left by the dead are redistributed among the agents who are still alive. We therefore introduce a government sector which collects the bequests and uses them to finance lump-sum income transfers $Z_{t}$ to the young. ${ }^{3}$ The government budget constraint is given by:
$$
\left(1+r_{t}\right) \int_{\mu t_{t}}^{\mu_{t}}(1-\mu) L_{t-1}(\mu) S_{t-1}(\mu) d \mu=L_{t} \mathrm{Z}_{t} .
$$
That is, the total amount of accidental bequests (left-hand side) equals the sum of income transfers (right-hand side).
数学代考|金融数学代考Financial Mathematics代写|Production
0The production side of this closed economy features a large number of perfectly competitive firms who produce a homogeneous commodity. The technology is represented by the following Cobb-Douglas production function:
$$
Y_{t}=\Omega_{0} K_{t}^{\varepsilon} N_{t}^{1-\varepsilon}, \quad 0<\varepsilon<1, $$ where $Y_{t}$ is total output, $\Omega_{0}>0$ is an exogenously given index of general factor productivity, $\mathrm{K}{\mathrm{t}}$ is the aggregate capital stock, and $N{t} \equiv L_{t}+\bar{\mu} \lambda L_{t-1}$ is the labour force. By defining $y_{t} \equiv Y_{t} / N_{t}$ and $k_{t} \equiv K_{t} / N_{t}$ we can write the intensive-form production function as:
$$
y_{t}=\Omega_{0} k_{t}^{\varepsilon} .
$$
Profit-maximizing behaviour of firms yields the following factor demand equations:
$$
\begin{aligned}
r_{t}+\delta &=\varepsilon \Omega_{0} k_{t}^{\varepsilon-1}, \
w_{t} &=(1-\varepsilon) \Omega_{0} k_{t}^{\varepsilon},
\end{aligned}
$$
where $\delta$ is the constant rate of depreciation of the capital stock $(0<\delta<1)$. The general model without annuities is fully characterized by the following fundamental difference equation:
$$
k_{t+1}=\phi_{1}^{T Y}\left(r_{t+1}\right)\left[w_{t}+Z_{t}\right]-\phi_{2}^{T Y}\left(r_{t+1}\right) \frac{\lambda w_{t+1}}{1+r_{t+1}},
$$
where $\phi_{1}^{T \gamma}\left(r_{t+1}\right)$ and $\phi_{2}^{T \gamma}\left(r_{i+1}\right)$ are given by:
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\phi_{1}^{T \gamma}\left(r_{t+1}\right) \equiv \frac{1}{1+n+\lambda \bar{\mu}} \int_{\mu_{t}, \nu}^{\mu_{t}}\left[1-\Phi\left(\mu, 1+r_{t+1}\right)\right] h(\mu) d \mu . \
&\phi_{2}^{T \gamma}\left(r_{t+1}\right) \equiv \frac{1}{1+n+\lambda \bar{\mu}} \int_{\mu_{k i t}}^{\mu_{\mu}} \Phi\left(\mu, 1+r_{t+1}\right) h(\mu) d \mu .
\end{aligned}
$$
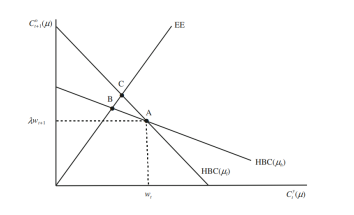
Equation (19) is obtained by imposing equilibrium in the savings market and using the cohort size evolutions described in Sect. 2.2. At time $t$ the predetermined capital intensity, $\mathrm{k}{\mathrm{t}}$, pins down $\mathrm{r}{\mathrm{t}}, \mathrm{w}{\mathrm{t}}$, and $\mathrm{Z}{\mathrm{t}}$, so that (19) in combination with (17) and (18) constitutes an implicit function determining $\mathrm{k}{\mathrm{t}+1}, \mathrm{r}{\mathrm{t}+1}$, and $\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{t}+1}$.
金融数学代考
数学代考|金融数学代考Financial Mathematics代写|Consumers
人口由重叠的几代有限寿命的代理人组成,除了他们的健康类型外,他们在各方面都是相同的。代理人最多活两个时期,称为“青年”(上标是)和“老年”(o)。在出生时,每个智能体都会以生存概率为代表了解她的健康状况,μ. 这就是健康类型之间的差异所在:不健康的代理人死亡风险更高,因此预期寿命更短(等于1+μ期)。我们假设群组足够大,以至于不存在总体不确定性,并且概率和频率重合。例如,类型的年轻代理的比例μ在第一个时期之后死亡的人正好等于1−μ. 请注意,从单个代理的角度来看,生命周期的不确定性在第二阶段开始时得到解决。当还活着时,代理将再活一段时间。
劳动力供给是外生的。在青年时期,代理人充分就业,而在老年时期,劳动力供应只是一小部分λ因强制退休而获得的单位时间养老(0<λ<1). 健康类型代表剂的预期寿命效用μ谁出生在经期吨是(谁)给的:
和Λ吨(μ)≡在(C吨是(μ))+μb在(C吨+1○(μ)),在哪里C吨是(μ)和C吨+1○(μ)是 分别在青年和老年消费,b是一个捕获纯时间偏好的参数(0<b<1), 和在(⋅)是幸福函数:
在(X)≡X1−1/σ−11−1/σ,σ>0.
选择这种函数形式是为了分析方便,它意味着恒定的跨期替代弹性,σ. 我们假设代理人没有遗赠动机,因此她不会从她死后剩余的财富中获得任何效用。
数学代考|金融数学代考Financial Mathematics代写|Demography
让H(μ)表示给定队列到达时健康类型的概率密度函数。然后是时间出生的队列中的代理人分布吨可以写成:
大号吨(μ)≡H(μ)大号吨,
∫μlμHH(μ)dμ=∫μlμHdH(μ)=1在哪里H(μ)是累积密度函数。的密度μ型特工当时还活着吨是(谁)给的磷吨(μ)≡ μ大号吨−1(μ)+大号吨(μ). 假设新生儿队列根据大号吨= (1+n)大号吨−1(和n>−1)因此,我们发现:
磷吨(μ)=1+μ+n1+n大号吨(μ).
期内总人口数吨通过聚合健康类型获得:
磷吨≡∫μ吨μφ磷吨(μ)dμ=1+μ¯+n1+n大号吨,
在哪里μ¯≡∫μμμHμH(μ)dμ是整个人口的平均存活率。
政府
在没有年金市场的情况下,我们必须假设死者意外留下的遗产如何在仍然活着的代理人之间重新分配。因此,我们引入了一个政府部门,负责收集遗赠并使用它们为一次性收入转移提供资金从吨给年轻人。3政府预算约束由下式给出:
(1+r吨)∫μ吨吨μ吨(1−μ)大号吨−1(μ)小号吨−1(μ)dμ=大号吨从吨.
也就是说,意外遗赠的总额(左侧)等于收入转移的总和(右侧)。
数学代考|金融数学代考Financial Mathematics代写|Production
0这种封闭经济的生产方面有大量完全竞争的公司生产同质商品。该技术由以下 Cobb-Douglas 生产函数表示:
是吨=Ω0ķ吨eñ吨1−e,0<e<1,在哪里是吨是总产量,Ω0>0是一般要素生产率的外生给定指数,ķ吨是总资本存量,并且ñ吨≡大号吨+μ¯λ大号吨−1是劳动力。通过定义是吨≡是吨/ñ吨和ķ吨≡ķ吨/ñ吨我们可以将密集形式的生产函数写为:
是吨=Ω0ķ吨e.
企业的利润最大化行为产生以下要素需求方程:
r吨+d=eΩ0ķ吨e−1, 在吨=(1−e)Ω0ķ吨e,
在哪里d是资本存量的恒定折旧率(0<d<1). 没有年金的一般模型完全由以下基本差分方程表征:
ķ吨+1=φ1吨是(r吨+1)[在吨+从吨]−φ2吨是(r吨+1)λ在吨+11+r吨+1,
在哪里φ1吨C(r吨+1)和φ2吨C(r一世+1)由以下给出:
φ1吨C(r吨+1)≡11+n+λμ¯∫μ吨,νμ吨[1−披(μ,1+r吨+1)]H(μ)dμ. φ2吨C(r吨+1)≡11+n+λμ¯∫μķ一世吨μμ披(μ,1+r吨+1)H(μ)dμ.
方程 (19) 是通过在储蓄市场中施加均衡并使用第 19 节中描述的队列规模演变来获得的。2.2. 当时吨预定的资本密集度,ķ吨, 固定r吨,在吨, 和从吨, 使得 (19) 与 (17) 和 (18) 结合构成一个隐式函数确定ķ吨+1,r吨+1, 和在吨+1.
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
