如果你也在 怎样代写tensorflow这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
TensorFlow是一个用于机器学习和人工智能的免费和开源的软件库。它可以用于一系列的任务,但特别关注深度神经网络的训练和推理。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写tensorflow方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写tensorflow代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写tensorflow相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的tensorflow及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
机器学习代写|tensorflow代写|Data representation and features
Data is a first-class citizen of machine learning. Computers are nothing more than sophisticated calculators, so the data we feed our machine-learning systems must be mathematical objects such as scalars, vectors, matrices, and graphs.
The basic theme in all forms of representation is features, which are observable properties of an object:
“Vectors have a flat and simple structure, and are the typical embodiments of data in most real-world machine-learning applications. A scalar is a single element in the vector. Vectors have two attributes: a natural number representing the dimension of the vector, and a type (such as real numbers, integers, and so on). Examples of 2D vectors of integers are $(1,2)$ and $(-6,0)$; similarly, a scalar could be 1 or the character $a$. Examples of $3 \mathrm{D}$ vectors of real numbers are (1.1, $2.0,3.9) \mathrm{~ a n d ~ (}$ same type. In a program that uses machine learning, a vector measures a property of the data, such as color, density, loudness, or proximity-anything you can describe with a series of numbers, one for each thing being measured.
- Moreover, a vector of vectors is a matrix. If each feature vector describes the features of one object in your dataset, the matrix describes all the objects; each item in the outer vector is a node that’s a list of features of one object.
- Graphs, on the other hand, are more expressive. A graph is a collection of objects (nodes) that can be linked with edges to represent a network. A graphical structure enables representing relationships between objects, such as in a friendship network or a navigation route of a subway system. Consequently, they’re tremendously harder to manage in machine-learning applications. In this book, our input data will rarely involve a graphical structure.
Feature vectors are practical simplifications of real-world data, which can be too complicated to deal with. Instead of attending to every little detail of a data item, using a feature vector is a practical simplification. A car in the real world, for example, is much more than the text used to describe it. A car salesman is trying to sell you the car, not the intangible words spoken or written. Those words are abstract concepts, similar to the way that feature vectors are summaries of the data.
机器学习代写|tensorflow代写|Distance metrics
If you have feature vectors of cars you may want to buy, you can figure out which two cars are most similar by defining a distance function on the feature vectors. Comparing similarities between objects is an essential component of machine learning. Feature vectors allow us to represent objects so that we may compare them in a variety of ways. A standard approach is to use the Euclidian distance, which is the geometric interpretation you may find most intuitive when thinking about points in space.
Suppose that we have two feature vectors, $x=\left(x_{1}, x_{2}, \ldots, x_{n}\right)$ and $y=\left(y_{1}, y_{2}, \ldots, y_{n}\right)$. The Euclidian distance $|x-y|$ is calculated with the following equation, which scholars call the $L .2$ norm.
$$
\sqrt{\left(x_{1}+y_{1}\right)^{2}+\left(x_{2}-y_{2}\right)^{2}+\ldots+\left(x_{n}-y_{n}\right)^{2}}
$$
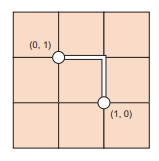
The Euclidian distance between $(0,1)$ and $(1,0)$ is
$$
\begin{aligned}
&|(0,1)-(1,0)| \
&|(-(1,1))| \
&\sqrt{(-1)^{2}+1^{2}} \
&=\sqrt{2}=1.414 \ldots
\end{aligned}
$$
That function is only one of many possible distance functions, however. The L0, L1, and L-infinity norms also exist. All these norms are valid ways to measure distance. Here they are in more detail:
- The LO norm counts the total nonzero elements of a vector. The distance between the origin $(0,0)$ and vector $(0,5)$ is 1 , for example, because there’s only one nonzero element. The Lo distance between $(1,1)$ and $(2,2)$ is 2 , because neither dimension matches up. Imagine that the first and second dimensions represent username and password, respectively. If the Lo distance between a login attempt and the true credentials is 0 , the login is successful. If the distance is 1 , either the
username or password is incorrect, but not both. Finally, if the distance is 2 , neither username nor password is found in the database.
The $L 1$ norm, shown in figure $1.8$, is defined as $\sum x_{n}$. The distance between two vectors under the Ll norm is also referred to as the Manhattan distance. Imagine living in a downtown area like Manhattan, where the streets form a grid. The shortest distance from one intersection to another is along the blocks. Similarly, the Ll distance between two vectors is along the orthogonal directions. The distance between $(0,1)$ and $(1,0)$ under the Ll norm is 2. Computing the Ll distance between two vectors is the sum of absolute differences at each dimension, which is a useful measure of similarity.
机器学习代写|tensorflow代写|Supervised learning
By definition, a supervisor is someone higher up in the chain of command. When we’re in doubt, our supervisor dictates what to do. Likewise, supervised learning is all about learning from examples laid out by a supervisor (such as a teacher).
A supervised machine-learning system needs labeled data to develop a useful understanding, which we call its model. Given many photographs of people and their recorded corresponding ethnicities, for example, we can train a model to classify the ethnicity of a never-before-seen person in an arbitrary photograph. Simply put, a model is a function that assigns a label to data by using a collection of previous examples, called a training dataset, as reference.
A convenient way to talk about models is through mathematical notation. Let $x$ be an instance of data, such as a feature vector. The label associated with $x$ is $f(x)$, often referred to as the ground truth of $x$. Usually, we use the variable $y=f(x)$ because it’s quicker to write. In the example of classifying the ethnicity of a person through a photograph, $x$ can be a 100-dimensional vector of various relevant features, and $y$ is one of a couple of values to represent the various ethnicities. Because $y$ is discrete with few
values, the model is called a classifier. If $y$ can result in many values, and the values have a natural ordering, the model is called a regressor.
Let’s denote a model’s prediction of $x$ as $g(x)$. Sometimes, you can tweak a model to change its performance dramatically. Models have parameters that can be tuned by a human or automatically. We use the vector to represent the parameters. Putting it all together, $g(x \mid)$ more completely represents the model, read ” $g$ of $x$ given.”
tensorflow代考
机器学习代写|tensorflow代写|Data representation and features
数据是机器学习的一等公民。计算机只不过是复杂的计算器,因此我们提供给机器学习系统的数据必须是数学对象,例如标量、向量、矩阵和图形。
所有表示形式的基本主题是特征,它们是对象的可观察属性:
“向量具有扁平而简单的结构,是大多数现实世界机器学习应用中数据的典型体现。标量是向量中的单个元素。向量有两个属性:表示向量维度的自然数和类型(如实数、整数等)。整数的二维向量的例子是(1,2)和(−6,0); 同样,标量可以是 1 或字符一个. 示例3D实数向量为 (1.1,2.0,3.9) 一个nd (同类型。在使用机器学习的程序中,向量测量数据的属性,例如颜色、密度、响度或接近度——任何你可以用一系列数字描述的东西,每个被测量的东西一个。
- 此外,向量的向量是矩阵。如果每个特征向量描述数据集中一个对象的特征,则矩阵描述所有对象;外部向量中的每个项目都是一个节点,它是一个对象的特征列表。
- 另一方面,图表更具表现力。图是对象(节点)的集合,可以与边链接以表示网络。图形结构能够表示对象之间的关系,例如在友谊网络或地铁系统的导航路线中。因此,它们在机器学习应用程序中非常难以管理。在本书中,我们的输入数据很少涉及图形结构。
特征向量是现实世界数据的实际简化,可能太复杂而无法处理。使用特征向量不是关注数据项的每一个小细节,而是一种实际的简化。例如,现实世界中的汽车远不止用于描述它的文字。汽车推销员试图向您推销汽车,而不是口头或书面的无形文字。这些词是抽象概念,类似于特征向量是数据摘要的方式。
机器学习代写|tensorflow代写|Distance metrics
如果您有可能想要购买的汽车的特征向量,您可以通过在特征向量上定义距离函数来确定哪两辆车最相似。比较对象之间的相似性是机器学习的重要组成部分。特征向量允许我们表示对象,以便我们可以以多种方式比较它们。一种标准方法是使用欧几里得距离,这是您在考虑空间中的点时可能会发现的最直观的几何解释。
假设我们有两个特征向量,X=(X1,X2,…,Xn)和是=(是1,是2,…,是n). 欧几里得距离|X−是|计算公式如下,学者称大号.2规范。
(X1+是1)2+(X2−是2)2+…+(Xn−是n)2
欧几里得距离(0,1)和(1,0)是
|(0,1)−(1,0)| |(−(1,1))| (−1)2+12 =2=1.414…
然而,该函数只是许多可能的距离函数之一。L0、L1 和 L-infinity 范数也存在。所有这些规范都是测量距离的有效方法。在这里他们更详细:
- LO 范数计算向量的总非零元素。原点之间的距离(0,0)和矢量(0,5)是 1 ,例如,因为只有一个非零元素。之间的 Lo 距离(1,1)和(2,2)是 2 ,因为两个维度都不匹配。想象一下,第一维和第二维分别代表用户名和密码。如果登录尝试和真实凭据之间的 Lo 距离为 0 ,则登录成功。如果距离为 1 ,则
用户名或密码不正确,但两者都不正确。最后,如果距离为 2 ,则在数据库中找不到用户名和密码。
这大号1范数,如图1.8, 定义为∑Xn. Ll范数下的两个向量之间的距离也称为曼哈顿距离。想象一下住在像曼哈顿这样的市区,街道形成一个网格。从一个路口到另一个路口的最短距离是沿着街区。类似地,两个向量之间的 Ll 距离沿正交方向。之间的距离(0,1)和(1,0)在 Ll 范数下是 2。计算两个向量之间的 Ll 距离是每个维度上的绝对差之和,这是一种有用的相似性度量。
机器学习代写|tensorflow代写|Supervised learning
根据定义,主管是指挥链中更高级别的人。当我们有疑问时,我们的主管会指示我们该怎么做。同样,监督学习就是从主管(例如老师)布置的示例中学习。
有监督的机器学习系统需要标记数据来形成有用的理解,我们称之为模型。例如,给定许多人的照片及其记录的相应种族,我们可以训练一个模型来对任意照片中从未见过的人的种族进行分类。简单地说,模型是一个函数,它通过使用先前示例的集合(称为训练数据集)作为参考来为数据分配标签。
谈论模型的一种方便方法是通过数学符号。让X是数据的一个实例,例如特征向量。关联的标签X是F(X),通常被称为基本事实X. 通常,我们使用变量是=F(X)因为写起来更快。在通过照片对一个人的种族进行分类的例子中,X可以是各种相关特征的 100 维向量,并且是是代表不同种族的几个价值观之一。因为是是离散的,很少
值,该模型称为分类器。如果是可以产生许多值,并且这些值具有自然顺序,该模型称为回归器。
让我们表示一个模型的预测X作为G(X). 有时,您可以调整模型以显着改变其性能。模型具有可以由人工或自动调整的参数。我们使用向量来表示参数。把这一切放在一起,G(X∣)更完整地代表模型,阅读“G的X给的。”
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。