如果你也在 怎样代写量子计算Quantum computer这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
量子计算机是利用量子物理学的特性来存储数据和进行计算的机器。这对于某些任务来说是非常有利的,它们甚至可以大大超过我们最好的超级计算机。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写量子计算Quantum computer方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写量子计算Quantum computer代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写量子计算Quantum computer相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的量子计算Quantum computer及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
物理代写|量子计算代写Quantum computer代考|Introducing the Bell state
So, now you have the ability to toss one or more quantum coins and get a probabilistic outcome. That is all well and good, and we could picture ourselves doing some gambling with this new tool of ours, betting money against the outcome of a coin toss. But with a $50 / 50$ outcome, the possibility of earning any real money is limited, unless, of course, we tweak the odds (that is, we cheat).
So how do you cheat in coin tossing? Well, knowing the outcome beforehand would be a clever way. And it turns out this is possible using a quantum phenomenon called entanglement.
By entangling two qubits, we connect them in a way so that they can no longer be described separately. In the most basic sense, if you have two entangled qubits and measure one of them as $|0\rangle$, the result of measuring the other one will be $|0\rangle$ as.
So, how do we use this to cheat in coin tossing? Well, we create two qubits, entangle them, and then we separate them (turns out this is the tricky part to do physically, but we will ignore that for now). You bring one qubit into the gambling den, and your friend keeps the other qubit outside the room.
When it is time to do a coin toss, you run your quantum circuit, entangle the qubits, and then your friend measures the qubit that they keep outside the room. They then sneakily, through some means (such as Bluetooth earphones, semaphoring, or telepathy), tell you what their measurement was, $|0\rangle$ or $|1\rangle$. You will then instantly know what your qubit is, before you measure it, and can bet money on that outcome. After measuring, you will find that you were indeed right, and cash in your winnings.
So, how is this done quantum programmatically? We will introduce a new gate, controlled-NOT $(\mathrm{CX})$.
物理代写|量子计算代写Quantum computer代考|More ways to quantum-cheat – tweaking the odds
In the previous recipe, we used a quantum phenomenon called entanglement to cheat with our coin tossing. Admittedly, this might be complicated to set up, and people do tend to get suspicious of coin tossers with an earpiece who are obviously listening for information before catching and revealing the coin (measuring the qubit).
But there are more ways to skin a cat. Remember our discussion of qubits and quantum gates. By manipulating the qubit using gates, we could adjust the state of the qubit before we measure it. The closer the vector is to either $|0\rangle$ or $|1\rangle$, the higher the probability of that specific outcome when you measure.
In this recipe, we will use a rotation gate, the Ry gate, to increase the probability of getting a tails outcome when we toss our coin.
Getting ready
The sample code for this recipe can be found here: https://github.com/ PacktPublishing/Quantum-Computing-in-Practice-with-Qiskit-andIBM-Quantum-Experience/blob/master/Chapter04/ch4_r6_coin_toss_ rot.py .
How to do it…
Set up your code like the previous example and then add a Ry gate to rotate the qubit:
- Import the classes and methods that we need:
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, Aer, execute
from qiskit.tools.visualization import plot_histogram
from IPython.core.display import display
from math import pi - Set up our quantum circuit with one qubit and one classical bit and create the quantum circuit based on the registers:
$$
q c=\text { QuantumCircuit }(1,1)
$$
物理代写|量子计算代写Quantum computer代考|Adding more coins – straight and cheating
Up until now, our recipes have been mainly of the 1- or 2-qubit sort. With our simulator, there is nothing stopping us from adding more qubits to our circuits at will, with the caveat that each additional qubit will require more and more processing power from the system on which your simulator runs. For example, the IBM Quantum Experience qasm_simulator runs on an IBM POWER9 $9^{\mathrm{m}}$ server and maxes out at around 32 qubits.
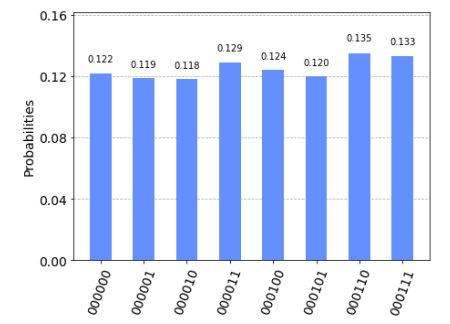
In this recipe, we will create two 3 -qubit quantum programs, one multi-coin toss, and one new entangled state called GHZ (for Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state).
Instead of doing this by creating two separate files, we will take a look at a new command, reset (). As the name implies, using the reset () command with a qubit sets it back to its original state of $|0\rangle$, ready to start a new quantum computing round. In this example, we use reset () to run two quantum programs in a row, writing to two sets of three classical registers, measuring twice per run.
量子计算代考
物理代写|量子计算代写Quantum computer代考|Introducing the Bell state
所以,现在你有能力投掷一个或多个量子硬币并获得概率结果。这一切都很好,我们可以想象自己用我们的这个新工具做一些赌博,赌钱来对抗抛硬币的结果。但是用一个50/50结果,赚取任何真钱的可能性是有限的,当然,除非我们调整赔率(即我们作弊)。
那么如何在抛硬币中作弊呢?好吧,事先知道结果将是一个聪明的方法。事实证明,这可以通过一种称为纠缠的量子现象来实现。
通过纠缠两个量子比特,我们以某种方式将它们连接起来,这样它们就不能再被单独描述了。从最基本的意义上说,如果你有两个纠缠的量子比特并将其中一个测量为|0⟩,测量另一个的结果将是|0⟩作为。
那么,我们如何利用它来欺骗抛硬币呢?好吧,我们创建两个量子比特,将它们纠缠在一起,然后将它们分开(事实证明,这是物理上很难做到的部分,但我们现在将忽略它)。你将一个量子比特带入赌场,而你的朋友将另一个量子比特留在房间外。
当需要掷硬币的时候,你运行你的量子电路,纠缠量子比特,然后你的朋友测量他们放在房间外的量子比特。然后他们偷偷地通过某种方式(如蓝牙耳机、信号或心灵感应)告诉你他们的测量值是多少,|0⟩或者|1⟩. 然后,您将在测量之前立即知道您的量子比特是什么,并可以在该结果上押注金钱。经过测量,你会发现你确实是对的,并兑现你的奖金。
那么,这是如何以量子编程方式完成的呢?我们将介绍一个新的门,受控-NOT(CX).
物理代写|量子计算代写Quantum computer代考|More ways to quantum-cheat – tweaking the odds
在前面的秘籍中,我们使用了一种称为纠缠的量子现象来欺骗我们的抛硬币。诚然,这可能设置起来很复杂,而且人们确实倾向于怀疑带有听筒的硬币投掷者,他们显然在捕捉和揭示硬币(测量量子比特)之前正在听信息。
但是还有更多的方法可以给猫剥皮。记住我们对量子比特和量子门的讨论。通过使用门操作量子比特,我们可以在测量之前调整量子比特的状态。向量越接近|0⟩或者|1⟩,当您测量时,该特定结果的概率越高。
在这个秘籍中,我们将使用一个旋转门,即 Ry 门,以增加我们抛硬币时得到反面结果的概率。
准备
可以在此处找到此配方的示例代码:https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Quantum-Computing-in-Practice-with-Qiskit-andIBM-Quantum-Experience/blob/master/Chapter04/ch4_r6_coin_toss_rot。 py 。
怎么做……
像前面的例子一样设置你的代码,然后添加一个 Ry 门来旋转量子比特:
- 导入我们需要的类和方法:
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, Aer, execute
from qiskit.tools.visualization import plot_histogram
from IPython.core.display import display
from math import pi - 用一个量子位和一个经典位建立我们的量子电路,并根据寄存器创建量子电路:
qC= 量子电路 (1,1)
物理代写|量子计算代写Quantum computer代考|Adding more coins – straight and cheating
到目前为止,我们的配方主要是 1 或 2 量子位类型。使用我们的模拟器,没有什么能阻止我们随意向我们的电路添加更多的量子比特,但需要注意的是,每个额外的量子比特都需要运行模拟器的系统提供越来越多的处理能力。例如,IBM Quantum Experience qasm_simulator 在 IBM POWER9 上运行9米服务器,最大约 32 个量子位。
在这个秘籍中,我们将创建两个 3-qubit 量子程序、一个多硬币抛掷和一个称为 GHZ(Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger 状态)的新纠缠态。
我们不会通过创建两个单独的文件来执行此操作,而是看一下新命令 reset()。顾名思义,使用带有 qubit 的 reset() 命令将其设置回其原始状态|0⟩,准备开始新一轮的量子计算。在这个例子中,我们使用 reset() 连续运行两个量子程序,写入两组三个经典寄存器,每次运行测量两次。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
