如果你也在 怎样代写产业经济学Industrial Economics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
产业经济学是关于公司、行业和市场的研究。它研究各种规模的公司–从当地的角落商店到沃尔玛或乐购这样的跨国巨头。它还考虑了一系列的行业,如发电、汽车生产和餐馆。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写产业经济学Industrial Economics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的产业经济学Industrial Economics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Continue to Deepen Supply-Side Reform and Stimulate New Vitality of Industrial Growth
The supply-side reform’s emphasis on decisive roles of market in resource allocation aims to release new demands and create new supplies; on the one hand, market is supposed to release overcapacity and create new economic growth points, and on the other, the use is made of innovation to form effective supplies with higher quality and stimulate new demands. The supply-side reform is a specific remedy for the currently existing economic issues in China, a new method for China’s economic reform and an effective action to vitalize industrial growth.
Firstly, we need to focus on release of excess capacity and elimination of “zombie” enterprises. The existing excess capacity, “zombie” and loss-making enterprises and low-efficiency or even inefficient assets are consuming huge quantity of resources and hinder transformation and upgrading of industrial structure. The Central Economic Working Conference stated expressly that top priority of supply-side structural reform in 2016 would be given to active and prudent dissolution of excess capacity and release of valuable resource elements from enterprises featuring severely excess capacity and limited space for growth and the “zombie” enterprises so as to improve effective supply and create new productivity by straightening out the supply side. To dissolve excess capacity, the Central Government, local government, authorities and enterprises must exercise strict control over incremental productive capacity. In particular, the local government is not supposed to increase investment blindly for local economic development or follow the suit simply because of huge potential in emerging industrials; instead, it should solve this problem at its source. The existing excess productive capacities may be dissolved by carrying out structural optimization or adjustment, promoting enterprise reorganization and M\&A, improving inventory warning mechanism and perform real-time monitoring over change in business inventories. Further solutions include: creating external demands and encouraging “go out” of China’s industrial capital to promote capacity output under the opportunity of the Belt and Road Initiative, accelerating reform of liberalization of production elements, breaking the government-led distribution mode of land and resources, giving full play to the regulating roles of market mechanism, and guiding allocation of capital and labor in all industrial sectors so as to dissolve excess capacity. As excess capacity is a systematic and long-term issue requiring both short-term administrative intervention and long-term governance according to the law, we need to improve the system of policy, laws and regulations for dissolution of excess capacity, and give full play to fiscal, financial and tax roles in the de-capacity process; accelerate consolidation, reorganization or bankruptcy of “zombie” enterprises or low-efficiency and inefficient assets, and make reasonable relocation of personnel and disposal of assets; actively guide upstream and downstream industrial organizations of the “zombie” enterprises to transform into high value added segments, or accept merging and reorganization of competitive industrial enterprises; and perfect the delisting mechanism of “zombie” enterprises to make adjustment and optimization of industrial structure, providing that the ecological equilibrium of these industrial organizations are maintained.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Expand Effective Demands and Further Exploit
Firstly, we need to make endeavors to promote supply-side reform, but it does not necessarily mean the quit of demand management; instead, implementation of the supply-side reform requires appropriate enlargement of aggregate demands; the supply-side reform and the demand management should promote and cooperate with each other. Since 2015 , obstructions have emerged in economic growth measures through expansion of investment and net export volume. The stabilizing and rising consumer goods market is unable to drive industrial growth, but the explosion of various emerging industries due to implementation of the innovation-driven strategy has brought about new possibilities for consumption and investment; as a result, the scale effect was replaced by consumption upgrading and investment efficiency in promoting industrial growth. In addition, the implementation of various regional strategies has provided unprecedented demand space for consumption and trade. In the second quarter of 2016 , more effective demands were exploited to promote industrial growth.
Secondly, we need to expand and upgrade consumption. On the one hand, we should focus on development of new technologies and new products, encourage innovation of commercial forms, create new demands by means of new supply, and direct consumers towards intelligent, green and healthy consumption. As the “imitative” consumption period comes to an end, individualized and diversified demand has become the mainstream consumption pattern; therefore, in addition to effort in new commercial forms, we need to make efforts on improvement product quality and grade to accommodate consumers’ individualized demands of products, and push consumption towards some new industries. On the other hand, we need to expand consumers’ demands by virtue of inter-regional collaboration strategies. As China’s economy develops, the consumption potentialities in central and western regions have been exploited to some extent. The current inter-regional collaboration strategy plays an important role in promoting consumption in the underdeveloped central and western regions. The “Yangtze River Economic Belt” is a significant action of China’s combination of regional coordination and opening up in the new period. This is an unprecedented policy that links together the eastern, central and western regions, and also a solid step to promote construction of inland economic belts. The western region of China is covered by the Belt and Road Initiative while the developed eastern region will take active part in the strategy by economic ties with central and western regions, and will promote inter-regional interactions through market force. All these will further exploit the consumption potentialities in the central and western regions. Meanwhile, “people foremost” is core to the new-type urbanization; more and more production factors such as rural population, information, capital and technologies that are flooding into cities will generate huge aggregation effect and scale effect in these cities to achieve better development of production factors market, especially the labor market; besides, rural laborers will get better paid in cities and will also improve incomes of urban residents and promote upgrading of consumption structure. Therefore, urbanization is an important means to expand consumption and promote consumption upgrading while the construction of the “Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei integration” and “Yangtze River Economic Belt” provides infinite opportunity for new-type urbanization. The inter-regional connection of public services, social insurance system and transportation will become the main market for future urbanization. To stimulate consumption, we need to make the best of inter-regional collaborative strategy to drive urbanization in the central and western regions; besides, we need to take active measures to optimize consumption environment, standardize market competition to facilitate transition of market competition from quantitative expansion and price competition to quality and differentiation competition, promote service-oriented development of manufacturing enterprises, protect consumers’ rights and interests, accelerate infrastructure construction in the field of consumer goods, and implement the “broadband China” strategy.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|International Industries in the First Half of 2016
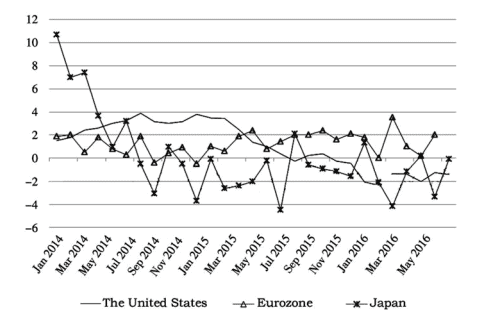
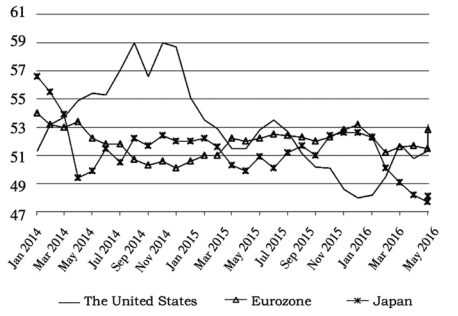
In the first half of 2016 , the world economy was still subject to a deep adjustment period after the financial crisis. Global manufacturing PMI index dropped from $50.1 \%$ in April to $50 \%$ in May 2016 . The industrial economics of major economies recovered slowly in a zigzag way and unevenly in main countries and regions, indicated significant uncertainty in industrial economics operation. In general, developed economies recovered faster than emerging economies did.
A weak recovery continued in developed countries, such as European countries and the United States. The American economy operated fairly well. Due to trade and government investment in consumption that offset slump in consumption, the year-on-year growth rate of American economy was modified to rise by $1.1 \%$, higher than the desired value and the last modified value. The American people’s confidence in economy was enhanced by the constantly recovering labor market, the higher employment rate and lower price index. The bounce-off of consumer spending in the second quarter will further promote American GDP growth. In addition, the American industrial production improved markedly. The overall production index (seasonally adjusted) entered year-on-year positive growth status, and the manufacturing PMI has climbed above the threshold since March 2016 , which kept ascending on a monthly basis in the first half year and hit a new high in June, so its manufacturing industry was expected to flourish; due to external environment’s influence, however, the American trade volume remained in sharp fluctuations, for which there was still large space for improvement. The Eurozone economy recovered slowly, with first quarter’s GDP growth rate higher than was expected. The Eurozone industrial production also recovered persistently. The manufacturing PMI in June was the highest this year, which indicated a recovering trend of Eurozone industry. Currently, the inflation pressure was slightly alleviated and generally better than market expectation, and the inflation that had lasted for four months eventually carne to an end in June. Eurozone saw a good trend of employment as the unemployment rates kept descending; due to British referendum on departure from the EU and its external environment, however, the Eurozone trade was not as optimistic as expected. Japan suffered a slow economic recovery,
regardless of its first quarter’s GDP growth rate higher than was expected. Other data indicated that Japanese economy remains flat and that continual fluctuations occurred in its industrial output, e.g. PMI in March stayed below the threshold, inflation risk remained and import/export trade volume kept shrinking.
Among major emerging economies, Brazil’s economy and industrial production continued shrinking, but the shrinking amplitude slowed down dramatically; despite a slight decline in the second quarter, Brazil’s PMI remained below the threshold in the first half of 2016 , with a rising unemployment rate and inflation. In the first quarter, South Africa’s economic growth rate went down significantly; the growth rate of industrial production fluctuated drastically; though the PMI began recovering up to the threshold in March, there was still uncertainty in its economic recovery as its inflation deteriorated and foreign trade fluctuated obviously. In comparison, India’s economy recovered more steadily, regardless of its sluggish industrial growth. In the first quarter of 2016 , India’s GDP grew $7.95 \%$ year on year, higher than the average of all quarters in 2015 , indicating a better recovering trend of India’s economy. Since the year of 2016 , India’s PMI maintained above the threshold; the decreasing amplitude of its foreign trade kept going down and improving steadily. Due to the declining international oil price, Russia’s economy continued with the downturn; industrial production remained sluggish, regardless of a slightly positive turnabout. In the first half of 2016 , Russia’s PMI basically remained below the threshold; the unemployment rate went up somewhat, but the inflation went down markedly and foreign trade improved to some extent. It was clear that as compared with developed economies, major emerging economies were faced with a more difficult problem in economic recovery. In the first half of 2016 , the general economic situation of developed economies seemed much better than aforesaid emerging economies.
产业经济学代考
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Continue to Deepen Supply-Side Reform and Stimulate New Vitality of Industrial Growth
供给侧改革强调市场在资源配置中的决定性作用,旨在释放新需求,创造新供给;市场一方面要释放过剩产能,创造新的经济增长点,另一方面要利用创新形成更高质量的有效供给,激发新的需求。供给侧改革是解决当前我国经济存在问题的具体办法,是我国经济改革的新途径,是振兴产业增长的有效举措。
一是要着力释放过剩产能,淘汰“僵尸”企业。现有产能过剩、“僵尸”、亏损企业、低效甚至低效资产正在消耗大量资源,阻碍产业结构转型升级。中央经济工作会议明确提出,2016年供给侧结构性改革的首要任务是积极稳妥化解过剩产能,释放产能严重过剩、增长空间有限的企业和“僵尸企业”的宝贵资源要素。 ”企业通过理顺供给侧来提高有效供给,创造新的生产力。化解过剩产能,中央、地方政府、当局和企业必须严格控制增量生产能力。尤其是地方政府不应该因为新兴产业的巨大潜力而盲目地增加投资以促进地方经济发展或效仿。相反,它应该从源头上解决这个问题。通过结构优化调整,推进企业重组并购,完善库存预警机制,实时监测企业库存变化,化解现有过剩产能。进一步的解决方案包括:在“一带一路”倡议下,创造外部需求,鼓励中国产业资本“走出去”,促进产能输出,加快推进生产要素自由化改革,打破政府主导的土地资源配置模式,充分发挥市场机制的调节作用,引导资本和劳动力在各产业领域配置,化解过剩产能。产能过剩是一个系统性、长期性的问题,既需要短期行政干预,也需要长期依法治理,需要健全化解过剩产能的政策法规体系,充分发挥去产能的作用。在去产能过程中扮演财政、金融和税收角色;加快“僵尸”企业或低效低效资产的整合、重组或破产,合理安置人员和资产处置。积极引导“僵尸”企业上下游产业组织向高附加值领域转型,或接受优势产业企业兼并重组。完善“僵尸”企业退市机制,在保持这些产业组织生态平衡的前提下,调整优化产业结构。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Expand Effective Demands and Further Exploit
一是着力推进供给侧改革,但这并不一定意味着需求管理的退出;相反,供给侧改革的实施需要适当扩大总需求;供给侧改革和需求管理要相互促进、相互配合。2015年以来,通过扩大投资和净出口,经济增长措施出现障碍。消费品市场企稳回升,无法带动产业增长,但创新驱动战略实施带来的各类新兴产业爆发,为消费和投资带来了新的可能;结果,促进产业增长的规模效应被消费升级和投资效率所取代。此外,各项区域战略的实施,为消费和贸易提供了前所未有的需求空间。2016年二季度,更多有效需求带动产业增长。
其次,要扩大和升级消费。一方面,着力发展新技术、新产品,鼓励创新商业形态,以新供给创造新需求,引导消费者走向智能、绿色、健康消费。随着“模仿”消费期的结束,个性化、多元化需求成为主流消费模式;因此,除了要在新的商业形态上发力外,还要着力提升产品的品质和档次,以适应消费者对产品的个性化需求,推动消费向一些新的产业方向发展。另一方面,我们需要通过跨区域的合作战略来扩大消费者的需求。随着中国经济的发展,中西部地区的消费潜力得到了一定程度的挖掘。当前的跨区域合作战略对促进中西部欠发达地区的消费发挥了重要作用。“长江经济带”是新时期中国区域协调与对外开放相结合的重大举措。这是一项前所未有的东中西部联动政策,也是推动内陆经济带建设迈出的坚实一步。中国西部地区被“一带一路”覆盖,东部发达地区将通过与中西部地区的经济联系积极参与战略,并以市场力量促进区域间的互动。这些都将进一步挖掘中西部地区的消费潜力。同时,“以人为本”是新型城镇化的核心;越来越多的农村人口、信息、资金、技术等生产要素涌入城市,将在这些城市产生巨大的聚集效应和规模效应,实现生产要素市场特别是劳动力市场的更好发展;此外,农村劳动力将在城市获得更好的报酬,也将提高城镇居民的收入,促进消费结构升级。所以,城镇化是扩大消费、促进消费升级的重要手段,“京津冀一体化”和“长江经济带”建设为新型城镇化提供了无限机遇。公共服务、社会保障体系和交通的跨区域衔接将成为未来城镇化的主要市场。刺激消费,用好区域协同战略,推动中西部地区城镇化;采取积极措施优化消费环境,规范市场竞争,促进市场竞争从数量扩张、价格竞争向质量竞争、差异化竞争转变。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|International Industries in the First Half of 2016
2016年上半年,世界经济仍处于金融危机后的深度调整期。全球制造业 PMI 指数从50.1%四月至50%2016 年 5 月。主要经济体产业经济回升缓慢,主要国家和地区呈现曲折态势,反映产业经济运行存在较大不确定性。总体而言,发达经济体的复苏速度快于新兴经济体。
欧洲国家和美国等发达国家继续疲软复苏。美国经济运行良好。由于贸易和政府对消费的投资抵消了消费的下滑,美国经济的同比增长率被修正为上升1.1%, 高于期望值和最后修改的值。劳动力市场不断回暖,就业率上升,物价指数走低,增强了美国民众对经济的信心。第二季度消费者支出的反弹将进一步推动美国GDP增长。此外,美国工业生产明显改善。整体生产指数(经季调)进入同比正增长状态,制造业采购经理人指数自2016年3月以来突破临界点,上半年环比持续攀升,6月再创新高,因此其制造业有望蓬勃发展;但受外部环境影响,美国贸易额仍大幅波动,仍有较大提升空间。欧元区经济复苏缓慢,一季度GDP增速高于预期。欧元区工业生产也持续复苏。6 月份制造业 PMI 创今年以来最高,预示着欧元区工业的复苏趋势。目前,通胀压力略有缓解,总体好于市场预期,持续四个月的通胀终于在6月份结束。欧元区就业趋势良好,失业率持续下降;然而,受英国脱欧公投及外部环境影响,欧元区贸易不如预期乐观。日本经济复苏缓慢,欧元区工业生产也持续复苏。6 月份制造业 PMI 创今年以来最高,预示着欧元区工业的复苏趋势。目前,通胀压力略有缓解,总体好于市场预期,持续四个月的通胀终于在6月份结束。欧元区就业趋势良好,失业率持续下降;然而,受英国脱欧公投及外部环境影响,欧元区贸易不如预期乐观。日本经济复苏缓慢,欧元区工业生产也持续复苏。6 月份制造业 PMI 创今年以来最高,预示着欧元区工业的复苏趋势。目前,通胀压力略有缓解,总体好于市场预期,持续四个月的通胀终于在6月份结束。欧元区就业趋势良好,失业率持续下降;然而,受英国脱欧公投及外部环境影响,欧元区贸易不如预期乐观。日本经济复苏缓慢,通胀压力略有缓解,总体好于市场预期,持续四个月的通胀终于在6月份结束。欧元区就业趋势良好,失业率持续下降;然而,受英国脱欧公投及外部环境影响,欧元区贸易不如预期乐观。日本经济复苏缓慢,通胀压力略有缓解,总体好于市场预期,持续四个月的通胀终于在6月份结束。欧元区就业趋势良好,失业率持续下降;然而,受英国脱欧公投及外部环境影响,欧元区贸易不如预期乐观。日本经济复苏缓慢,
不管其一季度GDP增速是否高于预期。其他数据显示,日本经济持平,工业产出持续波动,如 3 月份 PMI 低于临界点,通胀风险依然存在,进出口贸易量持续萎缩。
主要新兴经济体中,巴西经济和工业生产继续萎缩,但萎缩幅度明显放缓;2016年上半年巴西PMI虽小幅回落,但仍处于临界点以下,失业率和通胀持续上升。一季度,南非经济增速明显回落;工业生产增速大幅波动;尽管PMI在3月份开始回升至临界点,但由于通胀恶化,外贸波动明显,经济复苏仍存在不确定性。相比之下,尽管工业增长乏力,印度经济复苏更为稳健。2016年第一季度,印度GDP增长7.95%同比,高于2015年各季度平均水平,表明印度经济回暖态势较好。2016年以来,印度PMI保持在临界点之上;外贸降幅继续收窄,稳中有升。由于国际油价下跌,俄罗斯经济持续低迷;尽管略有好转,工业生产仍然低迷。2016年上半年,俄罗斯PMI基本保持在临界点以下;失业率有所上升,但通胀明显回落,对外贸易有所改善。显然,与发达经济体相比,主要新兴经济体面临的经济复苏难题更加严峻。2016年上半年,
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
