如果你也在 怎样代写贝叶斯统计这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
贝叶斯统计学是一个使用概率的数学语言来描述认识论的不确定性的系统。在 “贝叶斯范式 “中,对自然状态的相信程度是明确的;这些程度是非负的,而对所有自然状态的总相信是固定的。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写贝叶斯统计方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写贝叶斯统计代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写贝叶斯统计相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的贝叶斯统计及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|贝叶斯统计代写beyesian statistics代考|Air pollution in the eastern US
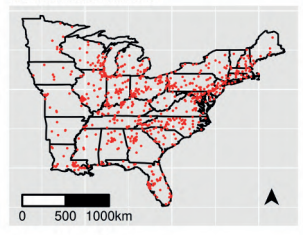
This example is taken from Sahu and Bakar (2012b), where we consider modeling the daily maximum 8-hour average ozone concentration data obtained from 691 monitoring sites in the eastern US, as shown in Figure $1.3$. These pollution monitoring sites are made up of 646 urban and suburban monitoring sites known as the National Air Monitoring Stations/State and Local Air Monitoring Stations (NAMS/SLAMS) and 45 rural sites monitored by the Clean Air Status and Trends Network (CASTNET).
We analyze daily data for $T=153$ days in every year from May to September since this is the high ozone season in the US. We consider these data for the 10 year period from 1997 to 2006 that allows us to study trend in ozone concentration levels. Thus, we have a total of $1,057,230$ observations and among them approximately $10.44 \%$ are missing, which we assume to be at random, although there are some annual variation in this percentage of missingness.
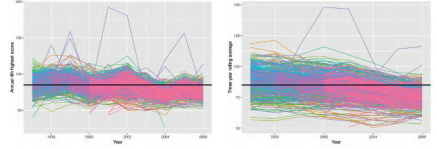
The main purpose of the modeling exercise here is to assess compliance with respect to the primary ozone standard which states that the 3 -year rolling average of the annual 4 th highest daily maximum 8-hour average ozone concentration levels should not exceed $85 \mathrm{ppb}$, see e.g., Sahu et al. (2007). Figure $1.4$ plots the 4 th highest maximum and their 3 -year rolling averages with a superimposed horizontal line at 85 . As expected, the plot of the rolling averages is smoother than the plot of the annual 4th highest maximum values. The plots show that many sites are compliant with respect to the standard, but many others are not. In addition, the plot of the 3 -year rolling averages shows a very slow downward trend. Both the plots show the presence of a few outlier sites which are perhaps due to site-specific issues in air pollution, for example, due to natural disasters such as forest fires. This data set is analyzed in Section 8.3.
统计代写|贝叶斯统计代写beyesian statistics代考|Hubbard Brook precipitation data
Measuring total precipitation volume in aggregated space and time is important for many environmental and ecological reasons such as air and water quality, the spatio-temporal trends in risk of flood and drought, forestry management and town planning decisions.
The Hubbard Brook Ecosystem Study (HBES), located in New Hampshire, USA and established in 1955 , continuously observes many environmental outcome variables such as temperature, precipitation volume, nutrient volumes in water streams. HBES is based on the 8,000 -acre Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest (see e.g. https://hubbardbrook.org/) and is a valuable source of scientific information for policy makers, members of the public, students and scientists. Of-interest here is a spatio-temporal data set on weekly precipitation volumes collected from 22 rain-gauges from 1997 to $2015 .$
Taken from Hammond et al. (2017), this example studies long-term trends in chlorophyll (chl) levels in the ocean, which is a proxy measure for phytoplankton (marine algae). Phytoplankton is at the bottom of food chain and provides the foundation of all marine ecosystem. The abundance of phytoplankton affects the supply of nutrients and light exposure. Global warming can potentially affect the phytoplankton distribution and abundance, and hence it is of much scientific interest to study long-term trends in chl which influences the abundance of phytoplankton.
Figure $1.6$ shows a map of the 23 ocean regions of interest where we have observed satellite-based measurements. The main modeling objective here is to study long-term trends in chl levels in these 23 oceanic regions. Section $8.5$ assesses these trend values.
统计代写|贝叶斯统计代写beyesian statistics代考|Atlantic ocean temperature and salinity data set
This example is taken from Sahu and Challenor (2008) on modeling deep ocean temperature data from roaming Argo floats. The Argo float program, see for example, http://www.argo.ucsd.edu, is designed to measure the temperature and salinity of the upper two kilometers of the ocean globally. These floats record the actual measurements which are in contrast to satellite data, such as the ones used in the ocean chlorophyll example in Section 1.3.5, which provide less accurate observations with many missing observations. Each Argo float is programmed to sink to a depth of one kilometer, drifting at that depth for about 10 days. After this period the float sinks a further kilometer to a depth of two kilometers and adjusting its buoyancy rises to the surface, measuring temperature and conductivity (from which salinity measurements are derived) on the way. Once at the surface, the data and the position of the float are transmitted via a satellite. This gives scientists access to near realtime data. After transmitting the data the float sinks back to its ‘resting’ depth
of one kilometer and drifts for another ten days before measuring another temperature and salinity profile at a different location. Argo data are freely available via the international Argo project office, see the above-mentioned website.
We consider the data observed in the North Atlantic ocean between the latitudes $20^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ north and longitudes $10^{\circ}$ and $50^{\circ}$ west. Figure $1.7$ shows the locations of the Argo floats in the deep ocean. The figure shows the moving nature of Argo floats in each of the 12 months. The primary modeling objective here is to construct an annual map of temperature at the deep ocean along with its uncertainty. The time points at which the data are observed are not equi-lagged, and we do not assume this in our modeling endeavor. Modeling required to produce an annual temperature map of the North Atlantic ocean is performed in Section 8.6.
贝叶斯统计代写
统计代写|贝叶斯统计代写beyesian statistics代考|Air pollution in the eastern US
这个例子取自 Sahu 和 Bakar(2012b),我们考虑对从美国东部 691 个监测点获得的每日最大 8 小时平均臭氧浓度数据进行建模,如图1.3. 这些污染监测站点由 646 个城市和郊区监测站点组成,称为国家空气监测站/州和地方空气监测站 (NAMS/SLAMS),以及由清洁空气状况和趋势网络 (CASTNET) 监测的 45 个农村站点。
我们分析每日数据吨=153每年 5 月到 9 月的几天,因为这是美国的臭氧高发季节。我们考虑从 1997 年到 2006 年的 10 年期间的这些数据,这使我们能够研究臭氧浓度水平的趋势。因此,我们一共有1,057,230观察和其中大约10.44%缺失,我们假设它是随机的,尽管这个缺失百分比每年都有一些变化。
此处建模练习的主要目的是评估对主要臭氧标准的遵守情况,该标准规定年度第 4 高日最高 8 小时平均臭氧浓度水平的 3 年滚动平均值不应超过85ppb,参见例如,Sahu 等人。(2007 年)。数字1.4绘制第 4 个最高最大值及其 3 年滚动平均值,并在 85 处叠加水平线。正如预期的那样,滚动平均值的图比年度第四高最大值的图更平滑。这些图显示许多站点都符合该标准,但许多其他站点不符合。此外,3 年滚动平均值的图显示出非常缓慢的下降趋势。这两个图都显示了一些异常站点的存在,这可能是由于空气污染中的特定站点问题,例如,由于森林火灾等自然灾害。该数据集在第 8.3 节中进行分析。
统计代写|贝叶斯统计代写beyesian statistics代考|Hubbard Brook precipitation data
由于空气和水质、洪水和干旱风险的时空趋势、林业管理和城市规划决策等许多环境和生态原因,测量聚合空间和时间的总降水量非常重要。
哈伯德布鲁克生态系统研究 (HBES) 位于美国新罕布什尔州,成立于 1955 年,持续观察许多环境结果变量,例如温度、降水量、水流中的营养物量。HBES 基于 8,000 英亩的 Hubbard Brook 实验森林(参见例如 https://hubbardbrook.org/),是政策制定者、公众、学生和科学家的宝贵科学信息来源。这里感兴趣的是从 1997 年到 22 个雨量计收集的每周降水量的时空数据集2015.
取自 Hammond 等人。(2017 年),这个例子研究了海洋中叶绿素 (chl) 水平的长期趋势,这是浮游植物(海藻)的替代指标。浮游植物处于食物链的底部,是所有海洋生态系统的基础。浮游植物的丰度影响营养物质的供应和光照。全球变暖可能会影响浮游植物的分布和丰度,因此研究影响浮游植物丰度的 chl 的长期趋势具有很大的科学意义。
数字1.6显示了我们观察到的基于卫星的测量结果的 23 个感兴趣的海洋区域的地图。这里的主要建模目标是研究这 23 个海洋区域中 chl 水平的长期趋势。部分8.5评估这些趋势值。
统计代写|贝叶斯统计代写beyesian statistics代考|Atlantic ocean temperature and salinity data set
此示例取自 Sahu 和 Challenor(2008 年)对漫游 Argo 浮标的深海温度数据进行建模。Argo 漂浮计划,例如 http://www.argo.ucsd.edu,旨在测量全球海洋上层两公里的温度和盐度。这些浮标记录了与卫星数据形成对比的实际测量结果,例如第 1.3.5 节中海洋叶绿素示例中使用的数据,这些数据提供了不太准确的观测结果,并且存在许多缺失的观测值。每个 Argo 浮标都被编程为下沉到一公里的深度,在该深度漂流约 10 天。在这段时间之后,浮子再下沉一公里到两公里的深度,并调整其浮力上升到表面,在途中测量温度和电导率(从中得出盐度测量值)。一旦到达地面,浮标的数据和位置就会通过卫星传输。这使科学家可以访问近乎实时的数据。传输数据后,浮子下沉到其“静止”深度
一公里,再漂移十天,然后在不同位置测量另一个温度和盐度分布。Argo 数据可通过国际 Argo 项目办公室免费获得,请参见上述网站。
我们考虑在纬度之间的北大西洋观测到的数据20∘和60∘北和经度10∘和50∘西方。数字1.7显示了 Argo 浮标在深海中的位置。该图显示了 Argo 浮标在 12 个月中每个月的移动性质。这里的主要建模目标是构建深海温度及其不确定性的年度地图。观察数据的时间点不是等滞后的,我们在建模工作中不假设这一点。生成北大西洋年度温度图所需的建模在第 8.6 节中进行。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
