如果你也在 怎样代写金融中的随机方法Stochastic Methods in Finance这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
随机建模是金融模型的一种形式,用于帮助做出投资决策。这种类型的模型使用随机变量预测不同条件下各种结果的概率。随着现代经济学、金融学实证研究的发展,金融中的随机方法Stochastic Methods in Finance作为一种数学工具具有越来越重要的应用价值。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写金融中的随机方法Stochastic Methods in Finance方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写金融中的随机方法Stochastic Methods in Finance方面经验极为丰富,各种代写金融中的随机方法Stochastic Methods in Finance相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的金融中的随机方法Stochastic Methods in Finance及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|金融中的随机方法作业代写Stochastic Methods in Finance代考|A 10-Year P&C ALM Problem
We present results for a test problem modelling a large $P \& C$ company assumed to manage a portfolio worth 10 billion $€$ (bln) at $t_{0}$. The firm’s management has set a first-year operating profit of 400 million $€(\mathrm{mln})$ and wishes to maximize in expectation the company realized and unrealized profits over 10 years. Company figures have been disguised for confidentiality reasons, though preserving the key elements of the original ALM problem. We name the P\&C company Danni Group.
The following tree structure is assumed in this case study. The current implementable decision, corresponding to the root node, is set at 2 January 2010 (Table 5.4).
Within the model the $P \& C$ management will revise its strategy quarterly during the first year to minimize the expected shortfall with respect to the target.
Initial conditions in the problem formulation include average first-year insurance premiums $R(t)$ estimated at $4.2$ bln $€$, liability reserves $\Lambda(0)$ equal to $6.5$ bln $€$, and expected insurance claims $L(t)$ in the first year of $2.2$ bln $€$. The optimal investment policy, furthermore, is constrained by the following upper and lower bounds relative to the current portfolio value:
- Bond portfolio upper bound: $85 \%$
- Equity portfolio upper bound: $20 \%$
- Corporate portfolio upper bound: $30 \%$
- Real estate portfolio upper bound: $25 \%$
- Desired turnover at rebalanced dates: $\leq 30 \%$
- Cash lower bound: $5 \%$
The results that follow are generated through a set of software modules combining MATLAB $7.4 \mathrm{~b}$ as the main development tool, GAMS $21.5$ as the model generator and solution method provider, and Excel 2007 as the input and output data collector running under a Windows XP operating system with $1 \mathrm{~GB}$ of RAM and a dual processor.
The objective function (5.1) of the P\&C ALM problem considers a tradeoff between short-, medium-, and long-term goals through the coefficients $\lambda_{1}=$ $0.5, \lambda_{2}=0.2$, and $\lambda_{3}=0.3$ at the 10-year horizon. The first coefficient determines a penalty on profit target shortfalls. The second and the third coefficients are associated, respectively, with a medium-term portfolio value decision criterion and long-term terminal wealth. Rebalancing decisions can be taken at decision epochs from time 0 up to the beginning of the last stage; no decisions are allowed at the horizon.
统计代写|金融中的随机方法作业代写Stochastic Methods in Finance代考|Optimal Investment Policy Under P&C Liability Constraints
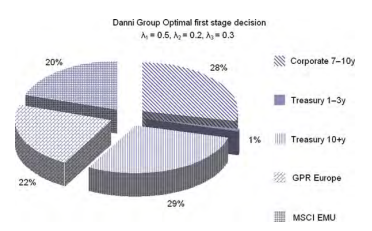
The optimal portfolio composition at time 0 , current time, the only one under full uncertainty regarding future financial scenarios, is displayed in Fig. 5.5.
Relying on a good liquidity buffer at time 0 the insurance manager will allocate wealth evenly across the asset classes with a similar portion of long Treasury and corporate bonds. As shown in Fig. $5.6$ the optimal strategy will then progressively
reduce holdings in equity and corporate bonds to increase the investment in Treasuries. A non-negligible real estate investment is kept throughout the 10 years. The allocation in the real estate index remains relatively stable as a result of the persistent company liquidity surplus. Real estate investments are overall preferred to equity investments due to higher expected returns per unit volatility estimated from the 1999 to 2009 historical sample. The optimal investment policy is characterized by quarterly rebalancing decisions during the first year with limited profit-taking operations allowed beyond the first business year. The 3 -year objective is primarily associated with the medium-term maximization of the portfolio asset value; the strategy will maximize unrealized portfolio gains specifically from long Treasury bonds, real estate, and corporate bonds. Over the 10 years the portfolio value moves along the average scenario from the initial 10 bln $€$ to roughly $14.3$ bln $€$.
The optimal portfolio strategy is not affected by the liquidity constraints from the technical side as shown in Table $5.5$. Danni Group has a strong liquidity buffer generated by the core insurance activity, but only sufficient on its own to reach the target profit set at the end of the first business year.
At the year I horizon the investment manager seeks to minimize the profit target shortfall while keeping all the upside. Indeed a $1.1$ billion $€$ gross profit is achieved prior to the corporate tax payment corresponding to roughly $750 \mathrm{mln}$ $€$ net profit. Thanks to the safe operational environment, no pressure is put on the investment side in terms of income generation and the investment manager is free to focus on the maximization of portfolio value at the 3-year horizon. Over the final 7-year stage the portfolio manager can be expected to concentrate on both realized and unrealized profit maximization, contributing to overall firm business growth, as witnessed in Table $5.5$ and Fig. 5.6. Empirical evidence suggests that P\&C optimal portfolio strategies, matching liabilities average life time, tend to concentrate on assets with limited duration (e.g. 1-3 years). We show below that such a strategy without an explicit risk capital constraint would penalize the portfolio terminal value.
统计代写|金融中的随机方法作业代写Stochastic Methods in Finance代考|Dynamic Asset Allocation with λ1 = 1
Remaining within a dynamic framework in the objective function (5.1) of the $P \& C$ ALM problem we set $\lambda_{1}=1$, with thus $\lambda_{2}=\lambda_{3}=0$ over the 10 -year horizon. The optimal policy will in this case be driven by the year 1 operating profit target, carrying on until the end of the decision horizon.
Diving a different view from Fig. 5.6, we display in Figs. $5.7$ and $5.8$ the optimal strategies in terms of the portfolio’s time-to-maturity structure in each stage. Relative to the portfolio composition in Fig. $5.8$ which corresponds to giving more weight to medium- and long-term objectives, the portfolio in Fig. $5.7$ concentrates from stage 1 on fixed income assets with lower duration. During the first year it shows an active rebalancing strategy and a more diversified portfolio. At the 9-month horizon part of the portfolio is liquidated and the resulting profit will minimize at the year 1 horizon the expected shortfall with respect to the target. Thereafter the strategy, suggesting a buy and hold management approach, will tend to concentrate on those assets that would not expire within the 10 -year horizon.
Consider now Fig. 5.8, recalling that no risk capital constraints are included in the model. The strategy remains relatively concentrated on long bonds and assets without a contractual maturity. Nevertheless the portfolio strategy is able to achieve the first target and heavily overperform over the 10 years. At $T=10$ years the first portfolio in this representative scenario is worth roughly $12.1$ billions $€$, while the second achieves a value of $14.2$ billions $€$.The year 1 horizon is the current standard for insurance companies seeking an optimal risk-reward trade-off typically within a static, one-period, framework. The above evidence suggests that over the same short-term horizon, a dynamic setting would in any case induce a more active strategy and, furthermore, a 10 -year extension of the decision horizon would not jeopardize the short-medium-term profitability of the P\&C shareholder while achieving superior returns in the long term.
金融中的随机方法代写
统计代写|金融中的随机方法作业代写Stochastic Methods in Finance代考|A 10-Year P&C ALM Problem
我们展示了一个测试问题的结果,它对一个大型模型进行了建模磷&C公司假定管理价值 100 亿美元的投资组合€€(bln) 在吨0. 公司管理层设定第一年营业利润为4亿€€(米一世n)并希望最大限度地期望公司在 10 年内实现和未实现的利润。尽管保留了原始 ALM 问题的关键要素,但出于保密原因对公司数据进行了伪装。我们将 P\&C 公司命名为 Danni Group。
在本案例研究中假设以下树结构。当前可执行的决策,对应于根节点,设置为 2010 年 1 月 2 日(表 5.4)。
在模型内磷&C管理层将在第一年每季度修订其战略,以尽量减少与目标相关的预期缺口。
问题表述中的初始条件包括平均首年保费R(吨)估计在4.2月€€, 负债准备金Λ(0)等于6.5月€€,以及预期的保险索赔大号(吨)在第一年2.2月€€. 此外,最佳投资政策受以下相对于当前投资组合价值的上限和下限的约束:
- 债券组合上限:85%
- 股票投资组合上限:20%
- 企业投资组合上限:30%
- 房地产投资组合上限:25%
- 重新平衡日期的期望营业额:≤30%
- 现金下限:5%
下面的结果是通过一组结合MATLAB的软件模块生成的7.4 b作为主要的开发工具,GAMS21.5作为模型生成器和求解方法提供者,Excel 2007 作为输入和输出数据收集器,在 Windows XP 操作系统下运行1 G乙RAM 和双处理器。
P\&C ALM 问题的目标函数 (5.1) 通过系数考虑了短期、中期和长期目标之间的权衡λ1= 0.5,λ2=0.2, 和λ3=0.3在 10 年的范围内。第一个系数确定对利润目标不足的惩罚。第二和第三个系数分别与中期投资组合价值决策标准和长期终端财富相关联。可以在从时间 0 到最后阶段开始的决策时期进行再平衡决策;不允许在地平线上做出任何决定。
统计代写|金融中的随机方法作业代写Stochastic Methods in Finance代考|Optimal Investment Policy Under P&C Liability Constraints
图 5.5 显示了当前时间 0 时的最优投资组合构成,这是未来金融情景中唯一完全不确定的投资组合。
依靠时间 0 的良好流动性缓冲,保险经理将在资产类别中平均分配财富,并持有类似比例的长期国债和公司债券。如图所示。5.6最优策略将逐渐
减持股票和公司债券,增加对国债的投资。在整个 10 年中保持着不可忽略的房地产投资。由于公司流动性持续过剩,房地产指数的配置保持相对稳定。由于从 1999 年到 2009 年的历史样本估计的每单位波动率的预期回报较高,房地产投资总体上优于股权投资。最佳投资政策的特点是在第一年进行季度再平衡决策,在第一年之后允许有限的获利了结操作。3 年目标主要与投资组合资产价值的中期最大化有关;该策略将最大化未实现的投资组合收益,特别是来自长期国债、房地产、和公司债券。在 10 年中,投资组合价值从最初的 100 亿美元沿着平均情景移动€€大致地14.3月€€.
最优组合策略不受技术面流动性约束的影响,如表所示5.5. Danni Group 拥有由核心保险业务产生的强大流动性缓冲,但仅靠其自身就足以达到第一财年末设定的目标利润。
在我眼中的那一年,投资经理力求将利润目标缺口最小化,同时保持所有上涨空间。确实一个1.1十亿€€毛利是在缴纳企业税之前实现的,大致相当于750米一世n €€净利。得益于安全的运营环境,投资方在创收方面没有压力,投资经理可以在 3 年内专注于投资组合价值的最大化。在最后 7 年阶段,可以预期投资组合经理将专注于已实现和未实现的利润最大化,为公司的整体业务增长做出贡献,如表所示5.5和图 5.6。经验证据表明,P\&C 最优投资组合策略,匹配负债平均寿命,往往集中在有限期限(例如 1-3 年)的资产上。我们在下面展示了这种没有明确风险资本约束的策略会惩罚投资组合的终值。
统计代写|金融中的随机方法作业代写Stochastic Methods in Finance代考|Dynamic Asset Allocation with λ1 = 1
保持在目标函数(5.1)的动态框架内磷&C我们设置的 ALM 问题λ1=1, 因此λ2=λ3=0在 10 年的范围内。在这种情况下,最优政策将由第 1 年的营业利润目标驱动,一直持续到决策期限结束。
潜水与图 5.6 不同的视图,我们显示在图 5.6 中。5.7和5.8根据投资组合在每个阶段的到期时间结构的最优策略。相对于图 1 中的投资组合构成。5.8这对应于给予中长期目标更多的权重,图 3 中的投资组合。5.7从第 1 阶段开始,专注于期限较短的固定收益资产。在第一年,它显示出积极的再平衡策略和更加多元化的投资组合。在 9 个月范围内,部分投资组合被清算,由此产生的利润将在第 1 年范围内最小化与目标相关的预期缺口。此后,建议采取买入并持有管理方法的策略将倾向于专注于那些不会在 10 年内到期的资产。
现在考虑图 5.8,回顾模型中没有包含风险资本约束。该策略仍然相对集中于长期债券和没有合同到期的资产。尽管如此,投资组合策略还是能够实现第一个目标,并且在 10 年内表现出色。在吨=10年这个代表性场景中的第一个投资组合价值大约12.1数十亿€€,而第二个达到的值14.2数十亿€€. 第 1 年范围是保险公司寻求最佳风险回报权衡的当前标准,通常是在静态的单周期框架内。上述证据表明,在相同的短期范围内,动态环境无论如何都会引发更积极的战略,此外,决策范围延长 10 年不会危及公司的中短期盈利能力。 P\&C 股东,同时实现长期超额回报。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
