如果你也在 怎样代写数学建模math modelling这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
数学建模指的是对现实世界的情景创建一个数学表示,以进行预测或提供洞察力的过程。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写数学建模math modelling方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写数学建模math modelling代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写数学建模math modelling相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的数学建模math modelling及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
数学代写|数学建模代写math modelling代考|Algebra Thinking in Problem Solving
Although American students are struggling with many aspects of mathematics, the National Mathematics Advisory Panel has identified “algebra as a central concern” (National Mathematics Advisory Panel, 2008, p. xiii). Interestingly, American students tend to enjoy school mathematics during the early elementary grades. However, they begin to experience difficulty in and come to dislike mathematics after fourth grade when learning becomes more abstract or symbolic and involves more algebraic thinking (Cai, Lew, Morris, Moyer, Ng, \& Schmittau, 2004). In particular, students with learning disabilities or difficulties in mathematics (LDM) are falling further behind their normal achieving peers as they move from elementary to secondary schools. A majority are essentially failing the secondary math curriculum. According to the Panel, mathematics achievement in the U.S. decreases significantly in the late middle grades when students are expected to learn algebra, which raises the essential question: How can students, including those with LP, “be best prepared for entry into algebra?”(Panel, p. xiii). No doubt, the Panel’s report underscores the importance of algebra-readiness instruction.
The purpose of this curriculum book is to present a Conceptual Model-Based Problem Solving (COMPS) approach to the teaching of elementary mathematics problem solving. It emphasizes the teaching of big ideas in mathematics problem solving and making connections between mathematical ideas including the connection between arithmetic and algebra learning.
In this chapter, I will first briefly characterize algebraic thinking in problem solving. Next, I will present a framework for mathematical modeling. Then, I will introduce the COMPS approach that emphasizes mathematical modeling involving algebraic thinking and readiness. Finally, I will provide a brief review of relevant research in word problem solving with students with LDM, and illustrate the distinctive features of COMPS and its advantages with the support of scientificbased research.
数学代写|数学建模代写math modelling代考|Mathematical Modeling
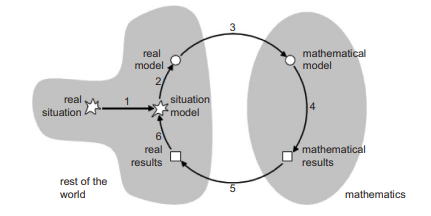
Recently, Blum and Leiss (2005) provided a framework for modeling (see Figure $\mathrm{Cl}-1$ ). In this modeling cycle, one must (1) read and understand the task, (2) structure the task and develop a real situational model, (3) connect it to and/or represent it with a relevant mathematical model; (4) solve and obtain the mathematical results, (5) interpret the math results in real problem context; and (6) validate the results (either end the task or re-modify the math model if it does not fit the situation). In light of research in mathematics education, many students have difficulties in making the transition from a real situational model to a mathematical model; and it is a weak area in students’ mathematical understanding (Blomhøj, 2004).
In short, modeling involves translation or representation of a real problem situation into a mathematical expression or model. Mathematical models are an essential part of all areas of mathematics including arithmetic and should be introduced to all age groups including elementary students (Mevarech \& Kramarski, 2008). It should be noted that engaging students in the modeling process does not necessarily mean engaging students in the discovery or invention of mathematical models or complex notational systems; however, according to Lesh, Doerr, Carmona, and Hjalmarson (2003), it does mean that when such models or systems are given to the students, “the central activities that students need to engage in is the unpacking of the meaning of the system” (p. 216), representation of the real problem situation in a mathematical expression or model, and the flexible use of the model to solve real world problems.
数学代写|数学建模代写math modelling代考|Theoretical Framework: Conceptual Model-based Problem Solving
Contemporary approaches to story problem solving have emphasized the conceptual understanding of a story problem before attempting any solution that involves selecting and applying an arithmetic operation for solution (Jonassen, 2003). Because problems with the same problem schema share a common underlying structure and hence require similar solutions (Chen, 1999; Gick \& Holyoak, 1983), students need to learn to understand the structure of the mathematical relationships in word problems and should develop this understanding through creating and working with a meaningful representation of the problem (Brenner et al., 1997) as well as mathematical modeling (Hamson, 2003).
The representation that models the underlying mathematical relations in the problem, that is, the conceptual model, facilitates solution planning and accurate problem solving. The conceptual model should drive the development of a solution plan that involves selecting and applying appropriate arithmetic operations. According to Lesh, Landau, \& Hamilton (1983), a conceptual model is defined as an adaptive structure consisting of the following primary components: (a) a within concept network of relations; (b) a between-concept system that links and combines within-concept networks; (c) a system of representations (e.g., written symbols, pictures, and concrete materials); and (d) systems of modeling processes. The first two components address students’ understanding of the idea or underlying structure of the concept. The third component concerns different representation systems, and the fourth component deals with modifying the situation to fit the existing model or changing existing model to make it applicable to a given situation. Based on Lesh et al. (1983), in applied problem solving, important translation and /or modeling processes include (a) simplifying the original problem situation by ignoring irrelevant information in the problem, and (b) “establishing a mapping between the problem situation and the conceptual models used to solve the problem” (p. 9).
Building on metaanalysis (e.g., Xin \& Jitendra, 2009) and cross-cultural curriculum evaluation (e.g., Xin, 2007), as well as empirical studies of intervention strategies (Xin, 2008; Xin et al., 2011; Xin, Wiles, \& Lin, 2008; Xin \& Zhang,2009), I have developed the Conceptual Model-based Problem Solving (COMPS) program that is consistent with the theoretical framework of mathematical modeling and conceptual models (e.g., Blomhøj, 2004; Lesh et al., 1983). One distinguishable difference between the COMPS approach and prior research in word problem solving by students with LD (e.g., schema-based instruction $[\mathrm{SBI}])$ is that the former focuses on representing the word problem in a defined mathematical model (the stage of “mathematical model” as it is presented in Blum and Leiss’s mathematical modeling cycle, see Figure Cl-1), which is expressed in an algebraic equation that directly drives the solution plan. In the next section, I will provide a brief review of intervention research with students with LDM using SBI and more recently Conceptual Model-based Problem Solving (COMPS) in facilitating elementary students’ ability to solve mathematics word problems.
数学建模代写
数学代写|数学建模代写math modelling代考|Algebra Thinking in Problem Solving
尽管美国学生在数学的许多方面都在苦苦挣扎,但国家数学顾问小组已经确定“代数是一个核心问题”(国家数学顾问小组,2008 年,第 xiii 页)。有趣的是,美国学生在小学早期往往喜欢学校数学。然而,当学习变得更加抽象或符号化并涉及更多代数思维时,他们开始在四年级后遇到困难并开始不喜欢数学(Cai, Lew, Morris, Moyer, Ng, \& Schmittau, 2004)。特别是,有学习障碍或数学困难 (LDM) 的学生在从小学升入中学时,进一步落后于正常成绩的同龄人。大多数人基本上没有通过中学数学课程。据专家小组称,美国的数学成绩在中后期学生被要求学习代数时显着下降,这就提出了一个基本问题:学生,包括那些有 LP 的学生,如何才能“为进入代数做好最好的准备?”(Panel,p.十三)。毫无疑问,小组的报告强调了代数准备教学的重要性。
这本课程书的目的是提出一种基于概念模型的问题解决 (COMPS) 方法来教授初等数学问题解决。它强调数学问题解决中大思想的教学,以及数学思想之间的联系,包括算术和代数学习之间的联系。
在本章中,我将首先简要描述问题解决中的代数思维。接下来,我将介绍一个数学建模框架。然后,我将介绍 COMPS 方法,它强调涉及代数思维和准备的数学建模。最后,我将简要回顾一下 LDM 学生在解决文字问题方面的相关研究,并说明 COMPS 的显着特点及其在科学研究支持下的优势。
数学代写|数学建模代写math modelling代考|Mathematical Modeling
最近,Blum 和 Leiss (2005) 提供了一个建模框架(见图Cl−1)。在这个建模周期中,必须(1)阅读和理解任务,(2)构建任务并开发一个真实的情境模型,(3)将其连接到和/或用相关的数学模型表示;(4) 求解并获得数学结果, (5) 在实际问题上下文中解释数学结果;(6) 验证结果(结束任务或重新修改数学模型,如果它不适合这种情况)。从数学教育的研究来看,很多学生在从真实情境模型到数学模型的过渡过程中存在困难;它是学生数学理解的薄弱环节(Blomhøj,2004)。
简而言之,建模涉及将实际问题情况转换或表示为数学表达式或模型。数学模型是包括算术在内的所有数学领域的重要组成部分,应该介绍给包括小学生在内的所有年龄组(Mevarech & Kramarski,2008)。应该注意的是,让学生参与建模过程并不一定意味着让学生参与数学模型或复杂符号系统的发现或发明;然而,根据 Lesh、Doerr、Carmona 和 Hjalmarson(2003 年)的说法,这确实意味着当将此类模型或系统提供给学生时,“学生需要参与的核心活动是对系统意义的解包”(第 216 页),用数学表达式或模型表示实际问题情况,
数学代写|数学建模代写math modelling代考|Theoretical Framework: Conceptual Model-based Problem Solving
当代解决故事问题的方法强调在尝试任何涉及选择和应用算术运算的解决方案之前对故事问题的概念理解(Jonassen,2003)。由于具有相同问题模式的问题具有共同的底层结构,因此需要类似的解决方案(Chen, 1999; Gick \& Holyoak, 1983),学生需要学习理解单词问题中数学关系的结构,并且应该培养这种理解通过创建和处理问题的有意义的表示(Brenner 等,1997)以及数学建模(Hamson,2003)。
对问题中的基本数学关系建模的表示,即概念模型,有助于解决方案规划和准确的问题解决。概念模型应该推动解决方案的制定,包括选择和应用适当的算术运算。根据 Lesh, Landau, \& Hamilton (1983),概念模型被定义为由以下主要组成部分组成的自适应结构: (a) 概念内的关系网络;(b) 连接和组合概念内网络的概念间系统;(c) 表示系统(例如,书面符号、图片和具体材料);(d) 建模过程系统。前两个组件解决学生对概念的想法或基本结构的理解。第三部分涉及不同的表示系统,第四部分处理修改情况以适应现有模型或更改现有模型以使其适用于给定情况。基于 Lesh 等人。(1983),在应用问题解决中,重要的翻译和/或建模过程包括(a)通过忽略问题中的不相关信息来简化原始问题情况,以及(b)“在问题情况和使用的概念模型之间建立映射解决问题”(第 9 页)。
基于元分析(例如,Xin \& Jitendra,2009)和跨文化课程评估(例如,Xin,2007)以及干预策略的实证研究(Xin,2008;Xin 等人,2011;Xin,Wiles , \& Lin, 2008; Xin \& Zhang,2009),我开发了与数学建模和概念模型的理论框架一致的基于概念模型的问题解决 (COMPS) 程序(例如,Blomhøj,2004;Lesh等人,1983 年)。COMPS 方法与 LD 学生解决文字问题的先前研究(例如,基于模式的教学)之间的一个显着区别[小号乙一世])是前者侧重于在定义的数学模型中表示单词问题(在 Blum 和 Leiss 的数学建模周期中呈现的“数学模型”阶段,参见图 Cl-1),它以代数方程表示直接推动解决方案。在下一节中,我将简要回顾使用 SBI 和最近的基于概念模型的问题解决 (COMPS) 对 LDM 学生的干预研究,以促进小学生解决数学应用题的能力。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
