如果你也在 怎样代写光学Optics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
光学是研究光的行为和属性的物理学分支,包括它与物质的相互作用以及使用或探测它的仪器的构造。光学通常描述可见光、紫外光和红外光的行为。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写光学Optics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写光学Optics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写光学Optics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的光学Optics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
物理代写|光学代写Optics代考|Lyotropic Liquid Crystals
Lyotropic liquid crystals are obtained when an appropriate concentration of material is dissolved in some solvent. The most common systems are those formed by water and amphiphilic molecules (molecules that possess a hydrophilic part that interacts strongly with water and a hydrophobic part that is water insoluble) such as soaps, detergents, and lipids. Here the most important variable controlling the existence of the liquid crystalline phase is the amount of solvent (or concentration). There are quite a number of phases observed in such water-amphiphilic systems, as the composition and temperature are varied; some appear as spherical micelles, and others possess ordered structures with 1-, 2-, or 3 – $\mathrm{D}$ positional order.
Examples of these kinds of molecules are soaps (Figure 1.8) and various phospholipids like those present in cell membranes. Lyotropic liquid crystals are of interest in biological studies [7].
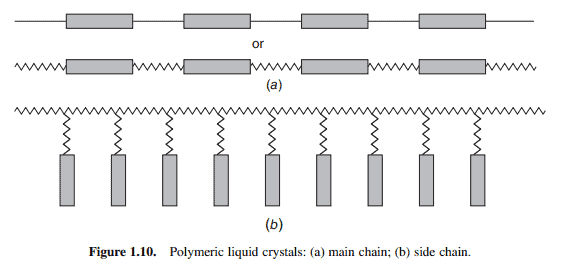
Polymeric liquid crystals are basically the polymer versions of the monomers discussed in Section 1.1. A good account of polymeric liquid crystals may be found in [9]. There are three common types of polymers, as shown in Figure $1.9 \mathrm{a}-\mathrm{c}$, which are characterized by the degree of flexibility. The vinyl type (Figure $1.9 \mathrm{a}$ ) is the most flexible, the Dupont Kevlar polymer (Figure 1.9b) is semirigid, and the polypeptide chain (Figure $1.9 \mathrm{c}$ ) is the most rigid. Mesogenic (or liquid crystalline) polymers are classified in accordance with the molecular architectural arrangement of the mesogenic monomer. Main-chain polymers are built by linking rigid mesogenic groups in a manner depicted schematically in Figure $1.10$; the link may be a direct bond or some flexible spacer. Liquid crystal side-chain polymers are formed by pendant side attachment of mesogenic monomers to a conventional polymeric chain, as depicted in Figure 1.10b.
物理代写|光学代写Optics代考|Thermotropic Liquid Crystals: Smectic, Nematic, Cholesteric
Although the molecular structures of thermotropic liquid crystals are quite complicated, they are often represented as “rigid rods” that interact with one another to form distinctive ordered structures (or phases) as a function of ascending temperature: crystals, smectic, nematic, cholesteric (including blue-phase), and the isotropic liquid phase. In smectic liquid crystals, there are several subclassifications in accordance with the positional and directional arrangement of the molecules.
As explained in greater detail in the following chapters, these mesophases are defined and characterized by many physical parameters such as long- and shortrange order, orientational distribution functions, and so on. Here we continue to use the rigid-rod model and pictorially describe these phases in terms of their molecularr arrangement.
Figure 1.11a depicts the collective arrangement of the rodlike molecules in the nematic phase schematically. These molecules are, however, directionally correlated; they are aligned in a general direction défined by a unit vector $n$, the so-called director axis, which may be regarded as the crystal axis. Nevertheless, the molecules are positionally random and exhibit flow very much like liquids; X-ray diffraction from nematics does not exhibit any diffraction peak.
Although individual molecules of nematic liquid crystal (NLC), cholesteric liquid crystal (CLC), and blue-phase liquid crystal (BPLC) may be polar, i.e. carry a permanent dipole, they tend to self-assemble themselves in such a manner that bulk liquid crystals are centrosymmetric, cf. Figure 1.12; their physical properties are the same in the $+\hat{n}$ and the optically uniaxial $-\hat{n}$ directions.
Cholesteric liquid crystals, often also called chiral nematic liquid crystals, resemble nematic liquid crystals except that the molecules assembled in a helical manner, as depicted in Figure 1.11. This property results from the addition of chiral agents to nematic constituents in the starting mixture. Owing to the spatially (helical) varying refractive index, CLCs possess special optical properties such as photonic bandgaps for transmission of circularly polarized lights. More details on CLC as well as cholesteric BPLCs obtained by increasing the concentration of the chiral constituent $[10]$ in the starting mixture are presented in Chapter 4 .
光学代考
物理代写|光学代写Optics代考|Lyotropic Liquid Crystals
当适当浓度的材料溶解在某种溶剂中时,获得溶致液晶。最常见的系统是由水和两亲分子(具有与水强烈相互作用的亲水部分和不溶于水的疏水部分的分子)形成的系统,例如肥皂、洗涤剂和脂质。这里控制液晶相存在的最重要变量是溶剂的量(或浓度)。随着成分和温度的变化,在这种水-两亲系统中观察到相当多的相;一些表现为球形胶束,而另一些则具有有序结构,具有 1-、2- 或 3-D位置顺序。
这类分子的例子有肥皂(图 1.8)和各种磷脂,例如存在于细胞膜中的磷脂。溶致液晶在生物学研究中很受关注 [7]。
聚合物液晶基本上是 1.1 节中讨论的单体的聚合物版本。在 [9] 中可以找到对聚合物液晶的一个很好的说明。共有三种常见的聚合物类型,如图所示1.9一个−C,其特点是灵活性的程度。乙烯基型(图1.9一个) 是最柔韧的,Dupont Kevlar 聚合物(图 1.9b)是半刚性的,而多肽链(图1.9C) 是最严格的。介晶(或液晶)聚合物根据介晶单体的分子结构排列进行分类。主链聚合物是通过以图 1 中示意性描述的方式连接刚性介晶基团来构建的1.10; 链接可能是直接键或一些柔性垫片。如图 1.10b 所示,液晶侧链聚合物通过介晶单体与常规聚合物链的侧向连接形成。
物理代写|光学代写Optics代考|Thermotropic Liquid Crystals: Smectic, Nematic, Cholesteric
尽管热致液晶的分子结构相当复杂,但它们通常被表示为“刚性棒”,它们相互作用形成独特的有序结构(或相)作为温度升高的函数:晶体、近晶型、向列型、胆甾型(包括蓝相)和各向同性液相。在近晶液晶中,根据分子的位置和方向排列有几个亚类。
正如以下章节中更详细解释的那样,这些中间相由许多物理参数定义和表征,例如长程和短程有序、取向分布函数等。在这里,我们继续使用刚杆模型,并根据它们的分子排列来形象地描述这些相。
图 1.11a 示意性地描绘了向列相中棒状分子的集体排列。然而,这些分子是方向相关的。它们在由单位向量定义的一般方向上对齐n,即所谓的导向轴,可以看作是晶轴。然而,分子的位置是随机的,并且非常像液体一样流动。向列相的 X 射线衍射不显示任何衍射峰。
尽管向列型液晶 (NLC)、胆甾型液晶 (CLC) 和蓝相液晶 (BPLC) 的单个分子可能是极性的,即带有永久偶极子,但它们倾向于以这样的方式自我组装液晶是中心对称的,参见。图 1.12;它们的物理性质在+n^和光学单轴−n^方向。
胆甾型液晶,通常也称为手性向列液晶,类似于向列液晶,只是分子以螺旋方式组装,如图 1.11 所示。这种性质是由于将手性试剂添加到起始混合物中的向列成分所致。由于空间(螺旋)变化的折射率,CLC 具有特殊的光学特性,例如用于传输圆偏振光的光子带隙。通过增加手性成分浓度获得的 CLC 以及胆甾型 BPLC 的更多详细信息[10]在第 4 章中介绍了起始混合物。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
