如果你也在 怎样代写产业经济学Industrial Economics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
产业经济学是关于公司、行业和市场的研究。它研究各种规模的公司–从当地的角落商店到沃尔玛或乐购这样的跨国巨头。它还考虑了一系列的行业,如发电、汽车生产和餐馆。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写产业经济学Industrial Economics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的产业经济学Industrial Economics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Factors Influencing Cyclical Variation of Industrial Economics
The cyclical fluctuation of industrial economics in the future will be subject to factors such as global economic recovery and changes in both national and international demands, and will therefore lead to cyclical variations of industrial economics. Various uncertainties will likely result in drastic fluctuation in the future industrial economics.
(1) Sluggish global economy recovery and significant global trade slow down
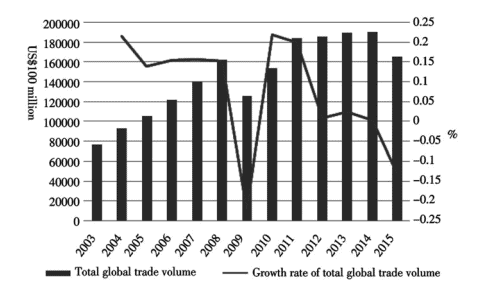
Since the year of 2008 , the growth of global international trade slowed down under the influence of financial crisis. Despite various incentive policies that simulated economic growth in 2010 and 2011 , the zero or even negative growth trend remained unchanged (see Fig. 2.4).
Economic differentiation continued in main economies of the world. The American economy saw a steady recovery and assumed a trend of slight growth. The European economy was recovering from European debt crisis and moving towards stabilization. The emerging economies witnessed obvious internal differentiation; India maintained a steady economic growth while Russia and Brazil suffered a negative growth. On the whole, the international economic situation has slightly improved, but the global economic growth still featured a too slow, fragile and unbalanced recovery. The US dollars appreciation and continuous decline of international oil price added more uncertainties to global financial markets and global economic recovery, such as intensification of global trade protection,expansion of exchange rate fluctuations, local economic upheaval and geopolitical tensions. Continuous changes of the world economic pattern have brought about huge risks and impact on China’s foreign trade and restriction on China’s external demands. In addition, the “Road and Belt” strategy involves many sensitive regions in Westem Asia and Eastern Europe, so the geopolitical tensions may have adverse effects on China’s overseas investment under the background of the Belt and Road Initiative and to some extent compromise industrial growth that should be stimulated by the Belt and Road Initiative.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Challenges facing China’s industrial
In the international trade pattern, China’s industrial goods took up an increasingly high proportion. In 2003 , China’s industrial goods only took up $5.7 \%$ of global goods trade, but the proportion rose to $13.8 \%$ in 2015 , steadily increasing in more than ten years. Under the influence of shrinking global trade, China’s export growth rate slowed down and trade scale also withered, but China’s trade competitiveness witnessed a rising trend year by year; it is predicted that the rising trend of trade proportion will persist in $2016 .$
The comparative advantages of China’s industrial development are under various threats and interruptive risks. The competitive advantages of China’s industrial enterprises have over years depended on low-cost advantages based on low-level production factors. With the loss of demographic dividend, the rise of domestic factor cost, the intensification of resource and environment pressure and the expansion of economic scale, however, this low-cost advantage is diminishing little by little and the dividend in trade that uses low cost as the main competitiveness basically comes to an end. In addition, new advantages based on the high-level product factors can hardly be established in a short time and may interrupt competitive advantages, resulting in depression of industrial goods export, slowdown of economic growth rate and decline of enterprises’ international competitiveness. In contrast, some emerging economies, such as Southeast Asian and African countries, have lower labor cost than China, and the comparative advantages of labor force in these countries have come into market, tending to supersede China’s traditional advantages. In addition, the advanced manufacturing technology, information technology, biotechnology and energy technology spread quickly over the world and are widely used by developed countries to exploit potential markets and realize “backflow of manufacturing industry” and “reindustrialization”. The “backflow of manufacturing industry” and “reindustrialization” strategy of developed countries has enabled them to slow down overseas transfer of their manufacturing industries, especially the high-end manufacturing industries. The development of China’s hi-tech industries depends largely on the international market, so it will be more difficult for China to borrow technologies from developed countries; instead, China will rely on its financing cost, logistics cost and tax cost as well as the technological gap.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|The effect of regional collaborative strategy
In March 2015, the Vision and Actions on Jointly Building the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21 st-Century Maritime Silk Road was issued jointly by the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Ministry of Commerce to promote construction of the Belt and Road Initiative. In April 2015, the Coordinated Development Program for Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region was adopted at the meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. In October 2015, China’s 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020) on National Economic and Social Development, adopted at the Fifth Plenary Session of the 18th Communist Party of China $(\mathrm{CPC})$ Central Committee, proposed formation of the lengthwise and crosswise economic axial belt along the coast, the river and the line guided by the Belt and Road Initiative construction, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei coordinated development and Yangtze River Economic Belt construction and based on the overall strategy of regional development, and formation of city clusters including the northeast region, the central plains region, the middle reaches of the Yangtze River region, the Chengdu-Chongqing region and the central Shaanxi region through prior development of such city clusters as Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta.
The new demand space for China’s industrial development provided by the regional coordinated development strategy along with its policy effect has brought indefinite opportunities for China’s industrial development in the next year. Firstly, the strategy has driven the balanced development in these regions. For a long time, Chinese government’s focus on coastal regions for economic development has create many economic hot spots in the eastern regions with most advanced economic development and most sufficient utilization of funds; in contrast, the central and western regions, especially the western regions, saw a rather low fund utilization rate and a narrow extent of opening up to the outside world due to their location, which laid severe restrictions on economic development but indicated potential industrial demands. The formation of city clusters has led to industrial cluster effect and creation of an industrial development pattern in which the growth poles of Beijing and Shanghai will drive economic growth in surrounding provinces, favorable for optimization of urban spatial layout, coordination among industrial sectors and expansion of environmental capacity and ecological space; in particular, the “Yangtze River Economic Belt” covering 11 provinces and cities has linked together the eastern, central and western regions to form a coordinated development belt that allows interaction and cooperation among the eastern and western regions and drives economic development in the western region, has fundamentally changed the location conditions of the western regions as many provinces along the Belt and Road Initiative are located in West China, has broadened the opening-up extent in China’s northwestern and southwestern regions and provided opportunities for these regions to carry out foreign trade and foreign investment activities and achieve leap-forward development.
产业经济学代考
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Factors Influencing Cyclical Variation of Industrial Economics
未来产业经济的周期性波动,将受全球经济复苏、国家和国际需求变化等因素影响,导致产业经济周期性波动。各种不确定性可能导致未来产业经济出现剧烈波动。
(一)全球经济复苏乏力,全球贸易增速明显放缓
2008年以来,受金融危机影响,全球国际贸易增速放缓。尽管 2010 年和 2011 年有各种刺激政策模拟经济增长,但零增长甚至负增长的趋势没有改变(见图 2.4)。
世界主要经济体继续分化。美国经济稳步回升,呈现小幅增长态势。欧洲经济正从欧债危机中复苏并走向企稳。新兴经济体内部分化明显;印度经济保持平稳增长,俄罗斯、巴西则出现负增长。总体来看,国际经济形势略有好转,但全球经济增长仍呈现缓慢、脆弱、不平衡的复苏态势。美元升值和国际油价持续下跌,给全球金融市场和全球经济复苏增加了更多不确定性,如全球贸易保护力度加大、汇率波动扩大、当地经济动荡和地缘政治紧张局势。世界经济格局的不断变化给我国对外贸易带来了巨大的风险和冲击,对我国的外需形成了制约。此外,“一带一路”战略涉及西亚东欧多个敏感地区,地缘政治紧张局势可能对“一带一路”背景下的中国海外投资产生不利影响,并在一定程度上影响产业增长。应该受到“一带一路”倡议的推动。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Challenges facing China’s industrial
在国际贸易格局中,中国工业品占比越来越高。2003年,中国工业品仅占5.7%全球商品贸易,但比例上升至13.8%2015年,十余年稳步增长。在全球贸易萎缩的影响下,中国出口增速放缓,贸易规模萎缩,但中国贸易竞争力呈逐年上升趋势;预计贸易比重上升趋势将持续2016.
中国产业发展的比较优势面临各种威胁和中断风险。多年来,我国工业企业的竞争优势一直依赖于基于低水平生产要素的低成本优势。然而,随着人口红利的丧失、国内要素成本的上升、资源环境压力的加剧和经济规模的扩大,这种低成本优势正在逐渐消失,以低成本作为贸易红利主要竞争力基本告一段落。此外,基于高水平产品要素的新优势难以在短时间内建立起来,可能会中断竞争优势,导致工业品出口低迷,经济增速放缓,企业国际竞争力下降。相比之下,一些新兴经济体,如东南亚和非洲国家,劳动力成本低于中国,这些国家劳动力的比较优势已经进入市场,有取代中国传统优势的趋势。此外,先进制造技术、信息技术、生物技术和能源技术在世界范围内迅速传播,被发达国家广泛用于开发潜在市场,实现“制造业回流”和“再工业化”。发达国家的“制造业回流”和“再工业化”战略,使其制造业海外转移放缓,尤其是高端制造业。中国高技术产业的发展很大程度上依赖于国际市场,中国向发达国家借鉴技术将更加困难;取而代之的是,中国将依赖其融资成本、物流成本和税收成本以及技术差距。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|The effect of regional collaborative strategy
2015年3月,国家发展改革委、外交部、商务部联合印发《关于共建丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路的愿景和行动》,推动建设“一带一路”倡议。2015年4月,中共中央政治局会议通过了《京津冀协同发展纲要》。2015年10月,中共十八届五中全会通过《国民经济和社会发展“十三五”规划(2016-2020年)》(C磷C)中央提出,以“一带一路”建设、京津冀协同发展、长江经济带建设为指导,立足总体战略,形成沿海、沿江、沿线纵横经济轴心带通过优先发展京津冀等城市群,形成东北地区、中原地区、长江中游地区、成渝地区、陕中地区等城市群。河北、长三角、珠三角。
区域协调发展战略及其政策效应为我国工业发展提供了新的需求空间,为明年我国工业发展带来了无限机遇。一是战略带动了这些地区的均衡发展。长期以来,中国政府以沿海地区为重点发展经济,在东部地区形成了许多经济发展最先进、资金使用最充分的经济热点;相比之下,中西部地区,特别是西部地区,由于所处的地理位置,资金利用率较低,对外开放程度较窄,对经济发展的制约较大,但产业需求潜力较大。城市群的形成,带动了产业集群效应,形成了以北京、上海为增长极带动周边省份经济增长的产业发展格局,有利于优化城市空间布局,促进产业协同,扩大产业链。环境容量和生态空间;尤其是覆盖11个省市的“长江经济带”,将东中西部连接起来,形成了东西部互动合作、带动西部经济发展的协调发展带。 ,从根本上改变了西部地区的区位条件,“一带一路”沿线的许多省份都位于中国西部,
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
