如果你也在 怎样代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
宏观经济学是经济学的一个分支,涉及整个经济或总体经济的结构、绩效、行为和决策。宏观经济研究的两个主要领域是长期经济增长和短期商业周期。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的宏观经济学Macroeconomics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|The Unemployment Rate and Its Weaknesses
The classical approach discussed in the previous section considers that, given the adjustment of real wages, the economy will always be in full employment (at the level of GDP of full employment), although unemployment is an obvious phenomenon in the real world. How can we understand this apparent contradiction?
To begin with, it is important to note that part of unemployment corresponds to the normal rotation in the labor market, which lies behind the natural rate of unemployment. This unemployment rate is associated with the time it takes to bring together an employer who offers a job with an individual who seeks work according to his professional skills.
This time varies with the institutional characteristics of labor markets, such as social protection laws (e.g., a minimum wage law) and the bargaining power of labor unions, all of which raise hiring and dismissal costs, making the process of wage determination less flexible. The natural rate of unemployment prevails even in an economy where wages are completely flexible, but in general, the more flexible the process of wage determination, the lower this rate will be. Minimum wages, for example, although intended to guarantee a minimum standard of living for dependent workers, if higher than the market wage, can be a source of unemployment. This is particularly true in countries where the minimum wage is above the productivity of workers.
Markets where labor flows freely, that is, markets in which there are very few obstacles to hiring or firing workers, have lower unemployment rates than those in which strict regulations remain in place. The World Bank has developed an index that measures various aspects of the functioning of labor markets around the world. According to this index, countries such as the United States, Singapore, and Hong Kong have highly flexible labor markets, while countries such as Spain and France (among other European countries) have more rigid labor markets, notwithstanding the recent efforts of President Macron to increase flexibility.
Latin American countries also tend to show greater rigidities, as in the case of Argentina and Venezuela, where minimum wages have tended to be above the productivity of their workers. This has led to double-digit unemployment rates over the last few decades. Excessive labor regulations, in the end, lead workers to employment in the informal sector, where working conditions are more precarious. On the other hand, the evidence is mixed in the cases of Chile and Peru, which have a minimum wage closer to worker productivity than other countries in Latin America but still maintain high dismissal costs.
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|WHY AND HOW DO COUNTRIES GROW
The process of economic growth is defined as the sustained increase in the output of a country or region. It is usually measured as the increase in real gross domestic product (GDP) over a period of time, which could be a few years or even decades.
In 1980 , China’s average annual per capita income was close to US $\$ 310$, while a Bolivian national had an average annual income of US $\$ 2,090$ and someone from Venezuela had an income of US $\$ 7,838$ (all figures expressed in purchasing power parity, or PPP, dollars, as explained in chapter 1). That is, the average income of a Chinese citizen was one-seventh that of a Bolivian and one-twenty-fifth that of a Venezuelan.
By 2017, China’s per capita income was about twentyone times the 1980 figure, while Bolivia’s average income had grown slowly and Venezuela’s income had decreased
over the same period. Thus today an average Chinese citizen has more than twice the income of a Bolivian, and also more than the average income of a Venezuelan. What is surprising is that such dramatic changes in the relative living standards of these countries occurred within a relatively short period-only three decades.
Cases of rapid economic growth for some countries and economic stagnation or decline for others are far from isolated. While Chile and Ecuador had similar incomes in 1980 , today an average Chilean lives with more than twice the income of the average Ecuadorean. Similarly, in 1980 South Korea had a per capita income one quarter that of Spain, whereas today a Korean has a slightly higher income than a Spaniard. What are the causes of such differences? Why do some countries grow so much more than others? What should a country do to grow more?
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|Modern Economic Growth
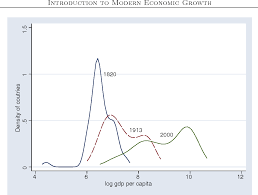
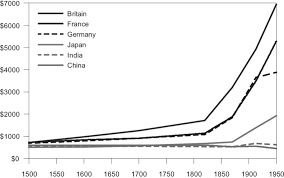
To understand the changes in the material wealth of the world, we must begin by examining development over the centuries. Table 3 shows the evolution of world population and per capita output in the last two thousand years. Note that the real leap forward occurred in the last phase, when the per capita output growth rate increased to almost $1.3$ percent per year and the population grew at more than double its growth rate in the previous stage. This jump
coincides with the Industrial Revolution, when modern economic growth began.
As an economy enters the last stage of growth, it undergoes important changes in its economic structure. As a result, we observe some common patterns in different countries and regions. The characteristics of this common process are the following:
- In growing economies, the relative size of the agricultural sector in the economy tends to decline. Thus, whereas in 1810,70 percent of the US labor force was engaged in agriculture, that figure now stands at barely 1 percent.
- In the early stages of accelerated growth, the industrial sector increases rapidly, peaks, and then its share in
the economy tends to decline. At the same time, the services sector grows steadily and increases its participation in the economy as industry and agriculture reduce theirs.
- Another pattern in development is urbanization, defined as population concentration in relatively large and dense settlements. In Chile, more than 70 percent of the population lived in rural areas in 1865 . By 1907, the urban population constituted 43 percent of the total, and by 2015,87 percent of the population lived in urban areas. In the entire world in 1880 the urban population was around 8 percent. Worldwide, urbanization surpassed the 50 percent mark for the first time in history at some point around 1990. The growth of cities is a consequence of the decline of agriculture and the growth of industry and the services sector.
宏观经济学代考
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|The Unemployment Rate and Its Weaknesses
上一节讨论的经典方法认为,考虑到实际工资的调整,经济将始终处于充分就业状态(在充分就业的 GDP 水平上),尽管失业在现实世界中是一个明显的现象。我们如何理解这种明显的矛盾?
首先,重要的是要注意,部分失业对应于劳动力市场的正常轮换,这落后于自然失业率。该失业率与将提供工作的雇主与根据其专业技能寻求工作的个人聚集在一起所需的时间有关。
这个时间随着劳动力市场的制度特征而变化,例如社会保护法(例如,最低工资法)和工会的议价能力,所有这些都增加了雇用和解雇成本,从而降低了工资确定过程的灵活性。即使在工资完全灵活的经济体中,自然失业率也很普遍,但一般来说,工资确定过程越灵活,这个失业率就越低。例如,最低工资虽然旨在保证受抚养工人的最低生活水平,但如果高于市场工资,则可能成为失业的来源。在最低工资高于工人生产率的国家尤其如此。
劳动力自由流动的市场,即雇佣或解雇工人几乎没有障碍的市场,其失业率低于仍然存在严格监管的市场。世界银行开发了一个指数,衡量世界各地劳动力市场运作的各个方面。根据该指数,美国、新加坡和香港等国家的劳动力市场高度灵活,而西班牙和法国(以及其他欧洲国家)等国家的劳动力市场更为刚性,尽管马克龙总统最近努力增加灵活性。
拉丁美洲国家也往往表现出更大的刚性,例如阿根廷和委内瑞拉,那里的最低工资往往高于工人的生产力。在过去的几十年中,这导致了两位数的失业率。过度的劳动法规最终导致工人在非正规部门就业,那里的工作条件更加不稳定。另一方面,智利和秘鲁的证据则参差不齐,这两个国家的最低工资比拉丁美洲其他国家更接近工人的生产率,但仍然保持着较高的解雇成本。
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|WHY AND HOW DO COUNTRIES GROW
经济增长的过程被定义为一个国家或地区产出的持续增长。它通常以一段时间内实际国内生产总值(GDP)的增长来衡量,可能是几年甚至几十年。
1980年中国人均年收入接近美国$310,而玻利维亚国民的平均年收入为美国$2,090来自委内瑞拉的人的收入为美国$7,838(所有数字均以购买力平价或 PPP 美元表示,如第 1 章所述)。也就是说,中国公民的平均收入是玻利维亚人的七分之一,委内瑞拉人的二十五分之一。
到2017年,中国人均收入约为1980年的21倍,而玻利维亚的平均收入增长缓慢,委内瑞拉的收入下降
在同一时期。因此,今天中国公民的平均收入是玻利维亚人的两倍多,也超过委内瑞拉人的平均收入。令人惊讶的是,这些国家的相对生活水平发生了如此巨大的变化,发生在相对较短的时期内——仅仅三年。
一些国家经济快速增长和其他国家经济停滞或下滑的案例绝非孤立。虽然智利和厄瓜多尔在 1980 年的收入相似,但如今智利人的平均收入是厄瓜多尔人平均收入的两倍多。同样,1980 年韩国的人均收入是西班牙的四分之一,而今天韩国人的收入略高于西班牙人。造成这种差异的原因是什么?为什么有些国家的增长比其他国家快得多?一个国家应该怎么做才能增长更多?
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|Modern Economic Growth
要了解世界物质财富的变化,我们必须从考察几个世纪以来的发展开始。表 3 显示了过去 2000 年世界人口和人均产出的演变。请注意,真正的飞跃发生在最后一个阶段,当时人均产出增长率上升到几乎1.3年增长率,人口增长率是前一阶段增长率的两倍多。这个跳跃
恰逢工业革命,现代经济增长开始。
随着一个经济体进入增长的最后阶段,它的经济结构发生了重大变化。因此,我们观察到不同国家和地区的一些共同模式。这种通用流程的特点如下:
- 在发展中的经济体中,农业部门在经济中的相对规模趋于下降。因此,尽管在 1810 年,70% 的美国劳动力从事农业,但这个数字现在只有 1%。
- 在加速增长的早期阶段,工业部门快速增长,达到顶峰,然后是其份额
经济趋于衰退。与此同时,随着工业和农业的减少,服务业稳步增长并增加其对经济的参与。
- 另一种发展模式是城市化,定义为人口集中在相对较大和密集的定居点。在智利,1865 年超过 70% 的人口生活在农村地区。到 1907 年,城市人口占总人口的 43%,到 2015 年,87% 的人口居住在城市地区。1880 年,全世界的城市人口约为 8%。在世界范围内,城市化率在 1990 年左右的某个时间点在历史上首次超过 50%。城市的增长是农业衰退以及工业和服务业增长的结果。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
