如果你也在 怎样代写工程统计engineering statistics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
工程统计结合了工程和统计,使用科学方法分析数据。工程统计涉及有关制造过程的数据,如:部件尺寸、公差、材料类型和制造过程控制。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写工程统计engineering statistics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写工程统计engineering statistics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写工程统计engineering statistics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的工程统计engineering statistics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|工程统计代写engineering statistics代考|GENERAL BETA DISTRIBUTION
General three-parameter beta distribution is given by
$$
f_{x}(a, b, c)=(x / c)^{a-1}(1-x / c)^{b-1} / c B(a, b) .
$$
The four-parameter beta distribution follows from (4.1) using $y=(x-a) /(b-a)$ as
$$
f(x ; a, b, c, d)=\frac{\Gamma(c+d)}{\Gamma(c) \Gamma(d)(b-a)^{c+d-1}}(x-a)^{c-1}(b-x)^{d-1}
$$
This could also be written as
$$
f(x ; a, b, c, d)=\frac{\Gamma(c+d)}{\Gamma(c) \Gamma(d)(b-a)}[(x-a) /(b-a)]^{c-1}[1-(x-a) /(b-a)]^{d-1},
$$
which can be transformed to Beta-I using $y=(x-a) /(b-a)$. This has mean $(a d+b c) /(c+$ $d)$, and variance $\sigma^{2}=c d(b-a)^{2} /\left[(c+d+1)(c+d)^{2}\right]$. The location parameters are “a”, “b” and scale parameters are $\mathrm{c}$ and $\mathrm{d}$. Coefficient of skewness is $2 c d(d-c) /\left[(c+d)^{2}(c+\right.$ $\left.d)^{(3)}\left[c d /\left((c+d)(c+d)^{(2)}\right)\right]\right]$ where $(c+d)^{(k)}$ is raising Pochhammer notation with $(c+$ $d)^{(3)}=(c+d)(c+d+1)(c+d+2)$. The mode is $\frac{a(d-1)+b(c-1)}{(c+d-2)}$ for $c$ not 1 and $d$ not 1 . The beta-geometric (discrete) distribution is defined in terms of CBF as
$$
f(x ; a, b)=B(a+1, x+b-1) / B(a, b), \quad \text { for } \mathrm{x}=1,2,3, \ldots
$$
This satisfies the recurrence relation $(a+b+x-1) p_{x}(a, b)=(x+b-2) p_{x-1}(a, b)$ with $p_{0}=B(a+1, b-1) / B(a, b)$. A change of origin transformation $Y=X-1$ results in the PMF $f(x ; a, b)=B(a+1, x+b) / B(a, b)$, for $\mathrm{x}=0,1,2, \ldots$
统计代写|工程统计代写engineering statistics代考|GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
The shear strength parameters in geotechnical engineering (cohesive force $c$, and internal friction angle $\phi$ ) are crucial in accurate reliability analysis. The risk assessment accuracy can then be modeled using a joint distribution of $c$ and $\phi$. Data scarcity may lead to inaccurate estimates of the probability of failure. Either a truncated normal, half-normal, truncated lognormal ${ }^{4}$ or a beta distribution (with range $[a, b]$ ) is assumed for the above parameters. As there are multiple parameters (like cohesive force, internal friction angle, unit weight of soils) involved, one approach is to approximate the joint distribution by a univariate distribution. This is called the “copula-approach,” or “copula modeling technique.” As the shear strength parameter is more important to achieve high accuracy, marginal distribution of it using the beta law can improve the accuracy of reliability analysis. Restricting attention to only the shear-strength (c) and internal friction angle $(\phi)$, the bivariate CDF $F(c, \phi)$ can be expressed in terms of individual marginal distributions and a copula function as
$$
F(c, \phi)=C\left(F_{1}(c), F_{2}(\phi) ; \theta\right),
$$
where $C O$ denotes the copula. Take partial derivative $\partial^{2} / \partial c \partial \phi$ to get
$$
f(c, \phi)=c\left(F_{1}(c), F_{2}(\phi) ; \theta\right) f_{1}(c) f_{2}(\phi),
$$
where $f_{1}(c)$ and $f_{2}(\phi)$ are the marginal PDFs. Some geotechnical processes are multi-modal (exhibit two or more distinct peaks) in which case linear combination of appropriate uni-modal distributions are used in reliability analysis under uncertainties.
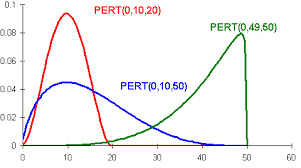
统计代写|工程统计代写engineering statistics代考|BETA DISTRIBUTION IN PERT
The program (or project) evaluation and review technique (PERT) is a diagrammatic tool used in project management. It was first introduced in 1957 for the U.S. Navy’s Polariz nuclear submarine design and construction scheduling project. The project must be comprised of tasks (called
${ }^{4}$ As the soil properties are strictly non-negative, the lognormal is preferred over normal distribution.
activities) with a dependency among them. Each activity is uniquely identified using a start and end dates (or times in micro-projects), and represented by an arrow. Isolated activities that do not have dependency among other activities are excluded from PERT. This implies that the PERT graph is always a directed acyclic graph (DAG) with the project start-date as the start-node (or source), and project finish-date as the end-node (sink) with predecessor and successor events for all intermediate activities. ${ }^{5}$ Its primary purpose is to analyze various activities so as to provide a best and worst estimates on project completion time and costs. In other words, uncertainty is incorporated in a controlled manner so that projects can be scheduled without knowing the precise details and durations of all the activities involved. The information on early-start (ES), early-finish (EF), late-start (LS), late-finish (LF), and expected duration can be obtained for internal nodes (and sink node) so that management can schedule activities in an optimal way (manpower, materials, machines, etc.) to complete a project within constraints. A critical path (which is the path with the longest time to complete) is identified from the source to the sink which identifies all activities with slack. Even internal nodes can be analyzed to understand each completed phase of a complex project, so that management can periodically review the progress within scheduled time and cost expenditures. A similar tool called critical path method (CPM) is also popular in project management. Although PERT and CPM are complementary tools, CPM uses one time and one cost estimation for each activity, so that PERT is more versatile for analysis of milestones in big projects.
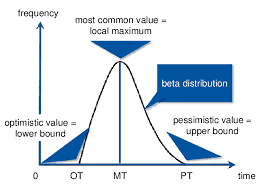
PERT uses four types of time estimates to accomplish an activity. An optimistic-estimate (o) is the minimum possible time required, a pessimistic-estimate (p) is the maximum possible time required, a most-likely time $(\mathrm{m})$ is the best estimate of the time required (mode), and an expected time $(\mathrm{o}+4 \mathrm{~m}+\mathrm{p}) / 6$ is the average (arithmetic mean) time required, with variance $(p-$ $o)^{2} / 36$. Activity duration in PERT networks (used in project planning and implementations) are assumed to follow the beta distribution, in which case more precise estimates are available for expected time as $(2 \mathrm{o}+9 \mathrm{~m}+2 \mathrm{p}) / 13$. It may also be associated with any particular set of PERT estimates. The four-parameter beta distribution is typically used in PERT modeling (especially to model earth-moving activities in construction projects). The PDF is given by
$$
f(x ; a, b, p, q)=(x-c)^{a-1}(d-x)^{b-1} /\left[(d-c)^{a+b-1} B(a, b)\right],
$$
where $c$ (most optimistic completion time) is the lower and $d$ (most pessimistic completion time) is the upper limit on activity duration.
工程统计代考
统计代写|工程统计代写engineering statistics代考|GENERAL BETA DISTRIBUTION
一般的三参数 beta 分布由下式给出
FX(一个,b,C)=(X/C)一个−1(1−X/C)b−1/C乙(一个,b).
四参数 beta 分布遵循 (4.1) 使用是=(X−一个)/(b−一个)作为
F(X;一个,b,C,d)=Γ(C+d)Γ(C)Γ(d)(b−一个)C+d−1(X−一个)C−1(b−X)d−1
这也可以写成
F(X;一个,b,C,d)=Γ(C+d)Γ(C)Γ(d)(b−一个)[(X−一个)/(b−一个)]C−1[1−(X−一个)/(b−一个)]d−1,
可以转换为 Beta-I 使用是=(X−一个)/(b−一个). 这意味着(一个d+bC)/(C+ d), 和方差σ2=Cd(b−一个)2/[(C+d+1)(C+d)2]. 位置参数为“a”、“b”,尺度参数为C和d. 偏度系数为2Cd(d−C)/[(C+d)2(C+ d)(3)[Cd/((C+d)(C+d)(2))]]在哪里(C+d)(ķ)正在提高 Pochhammer 符号(C+ d)(3)=(C+d)(C+d+1)(C+d+2). 模式是一个(d−1)+b(C−1)(C+d−2)为了C不是 1 和d不是 1 。β-几何(离散)分布根据 CBF 定义为
F(X;一个,b)=乙(一个+1,X+b−1)/乙(一个,b), 为了 X=1,2,3,…
这满足递归关系(一个+b+X−1)pX(一个,b)=(X+b−2)pX−1(一个,b)和p0=乙(一个+1,b−1)/乙(一个,b). 原产地变迁是=X−1导致 PMFF(X;一个,b)=乙(一个+1,X+b)/乙(一个,b), 为了X=0,1,2,…
统计代写|工程统计代写engineering statistics代考|GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
岩土工程中的抗剪强度参数(凝聚力C, 和内摩擦角φ) 在准确的可靠性分析中至关重要。然后可以使用联合分布对风险评估准确性进行建模C和φ. 数据稀缺可能导致对失败概率的不准确估计。截断正态、半正态、截断对数正态4或 beta 分布(范围[一个,b]) 假设为上述参数。由于涉及多个参数(如内聚力、内摩擦角、土壤的单位重量),一种方法是通过单变量分布来近似联合分布。这称为“copula 方法”或“copula 建模技术”。由于抗剪强度参数对于获得高精度更为重要,使用β定律对其进行边际分布可以提高可靠性分析的准确性。仅关注剪切强度 (c) 和内摩擦角(φ), 二元 CDFF(C,φ)可以用个体边际分布和 copula 函数表示为
F(C,φ)=C(F1(C),F2(φ);θ),
在哪里C○表示系词。取偏导数∂2/∂C∂φ要得到
F(C,φ)=C(F1(C),F2(φ);θ)F1(C)F2(φ),
在哪里F1(C)和F2(φ)是边缘 PDF。一些岩土工程过程是多模态的(表现出两个或更多不同的峰),在这种情况下,在不确定性下的可靠性分析中使用适当的单模态分布的线性组合。
统计代写|工程统计代写engineering statistics代考|BETA DISTRIBUTION IN PERT
计划(或项目)评估和审查技术(PERT)是用于项目管理的图表工具。它于 1957 年首次用于美国海军的 Polariz 核潜艇设计和建造调度项目。项目必须由任务组成(称为
4由于土壤性质严格非负,因此对数正态分布优于正态分布。
活动)之间存在依赖关系。每个活动都使用开始和结束日期(或微型项目中的时间)唯一标识,并用箭头表示。不依赖于其他活动的孤立活动被排除在 PERT 之外。这意味着PERT图始终是一个有向无环图(DAG),其中项目开始日期作为开始节点(或源),项目完成日期作为结束节点(汇),前任和后继事件为所有中间活动。5其主要目的是分析各种活动,以提供对项目完成时间和成本的最佳和最差估计。换句话说,不确定性以一种受控的方式被纳入,因此可以在不知道所有相关活动的确切细节和持续时间的情况下安排项目。可以获取内部节点(和汇节点)的早开始(ES)、早结束(EF)、晚开始(LS)、晚结束(LF)和预期持续时间的信息,以便管理可以调度以最佳方式(人力、材料、机器等)在约束范围内完成项目的活动。一条关键路径(即完成时间最长的路径)被识别为从源到接收器,它标识了所有具有松弛的活动。甚至可以分析内部节点以了解复杂项目的每个已完成阶段,以便管理层可以在预定时间和成本支出内定期审查进度。一种称为关键路径方法 (CPM) 的类似工具在项目管理中也很流行。虽然 PERT 和 CPM 是互补的工具,但 CPM 对每项活动使用一次和一次成本估算,因此 PERT 在分析大型项目的里程碑时更加通用。
PERT 使用四种类型的时间估计来完成一项活动。乐观估计 (o) 是所需的最小可能时间,悲观估计 (p) 是所需的最大可能时间,最可能的时间(米)是所需时间(模式)的最佳估计,以及预期时间(○+4 米+p)/6是所需的平均(算术平均)时间,有方差(p− ○)2/36. 假设 PERT 网络中的活动持续时间(用于项目规划和实施)遵循 beta 分布,在这种情况下,可以对预期时间进行更精确的估计,因为(2○+9 米+2p)/13. 它也可能与任何特定的PERT估计集相关联。四参数 beta 分布通常用于 PERT 建模(尤其是用于建模建筑项目中的土方活动)。PDF由下给出
F(X;一个,b,p,q)=(X−C)一个−1(d−X)b−1/[(d−C)一个+b−1乙(一个,b)],
在哪里C(最乐观的完成时间)是较低和d(最悲观的完成时间)是活动持续时间的上限。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
