如果你也在 怎样代写数据可视化Data visualization这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
数据可视化是将信息转化为视觉背景的做法,如地图或图表,使数据更容易被人脑理解并从中获得洞察力。数据可视化的主要目标是使其更容易在大型数据集中识别模式、趋势和异常值。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写数据可视化Data visualization方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写数据可视化Data visualization代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写数据可视化Data visualization相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的数据可视化Data visualization及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|数据可视化代写Data visualization代考|Other Data Visualization Design Issues
Data visualizations should be easy to view and interpret by the audience. Charts and tables should reveal insights to the audience, while minimizing the cognitive load required of the audience. We can minimize cognitive load by using preattentive attributes and Gestalt principles as well as by increasing the data-ink ratio in our data visualizations. We can also minimize cognitive load by minımizing the eye travel required by the audience.
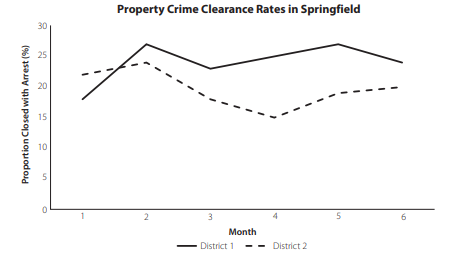
Consider the Ollice of Budget and Performance Improvement for the City of Springfield. This city office would like to compare the performance of the two police districts located in its city. One performance metric used by the city is clearance rate, which is the fraction of reported crimes that result in an arrest. Figure $3.25$ compares the clearance rates for property crimes in Springfield’s District 1 and District 2 over the last 6 months.A
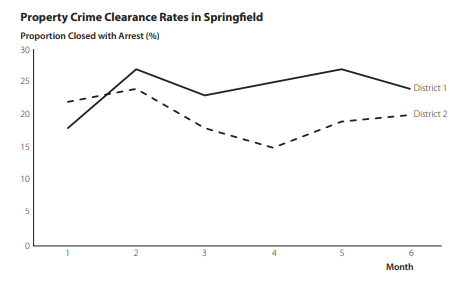
Figure $3.25$ has several characteristics that increase the required eye travel for the audience. Many of these characteristics are typical of default charts created in Excel. First, the legend is located at the bottom of the chart. This requires the audience members to look at the legend at the bottom of the chart and then move their eyes up to the lines to match the line type from the legend with the correct line in the chart. We can greatly reduce the eye travel required of the audience by moving the legend closer to the lines or, even better, by directly labeling each line in the chart. Second, Excel also typically inserts vertical-axis title text as rơated 90 dégrees from thé chart titlé ănd hoorizontăl-axis title. This requires thé audiencế’s eyes to move all around the chart to read the horizontal-axis title, the vertical-axis title, and the chart title. It is better to align the titles within a chart as much as possible so the audicnce can look at only a few places to quickly interpret the chart. The steps below demonstrate how we can improve Figure $3.25$ to reduce the amount of eye travel required by the audience.
Step 1. Click anywhere on the chart in the file ClearanceRatesChart
Click the Chart Elements button $+$
Deselect the check box for Legend
Step 2. Double-click the last data point on the line in the chart for the District 1 data to select only that data point
Right-click the selected data point and select Add Data Label (this will add a data label with the value of this data point which is “24”)
Change the “24” in this data label to District $l$ and change the font to
Calibri $10.5$
Step 3. Double-click the last data point on the line in the chart for the District 2 data to select only that data point
Right-click the selected data point and select Add Data Label (this will add a data label with the value of this data point, which is ” $20 “$ “) Change the ” $20 “$ in this data label to District 2 and change the font to Calibri $10.5$
Step 4. Click the vertical-axis title “Proportion Closed with Arrest (क)” Press the Delete key
统计代写|数据可视化代写Data visualization代考|Choosing a Font for Text
Text is an important part of any data visualization. It is used to label axes, fill in table values, and call out important aspects of the visualization to the audience. Because text is such an important part of a data visualization, the font that is used to display the text is also an important consideration. Most data visualization software tools, including Excel, allow the user to choose from dozens, and even hundreds, of font options for displaying text.
Not all data visualization experts agree on the preferred type of font to use for text in data visualizations, and often this choice may depend on the needs of the audience or on other design elements of the data visualization. However, most experts agree that some font types are generally preferred for text in a data visualization over others, for example, sans-serif fonts (fonts that do not contain serifs) are generally preferred over serif fonts (fonts that do contain serifs) for text in a data visualization. Serif’s refer to the small end-of-stroke features that are visual in the characters created using serif fonts. Figure $3.27$ illustrates the difference between sansserif and serif fonts. Common serif fonts include Times, Times New Roman, and Courier. Common sans-serif fonts include Arial, Calibri, Myriad Pro and Verdana.
In general, serif fonts are preferred for printed work and sans-serif fonts are preferred for text displayed digitally. Sans-serif fonts are also often more legible than serif fonts at small sizes. Because data visualizations are often viewed in both print form and digitally, and because data visualizations often contain fonts of many different sizes, sans-serif fonts are generally preferred over serif fonts for text in data visualizations. In this textbook, all charts provided in Excel use the sans-serif font Calibri because it is the default font in Excel. Most printed charts in the textbook use the sans-serif font Myriad Pro because it is legible at many different sizes and it works well for both print and digital work. However, other sans-serif fonts, such as Arial and Verdana, are also usually acceptable for data visualization purposes.
统计代写|数据可视化代写Data visualization代考|Wrong Type of Visualization
The best type of chart or table to use for data visualization strongly depends on the audience that will view the visualization as well as the insights or story that is to be told through the visualization. Throughout this textbook, we provide best practices for designing effective data visualizations, but many of the decisions related to which chart to use and some aspects of the design will depend on the situation and goal of the visualization. In this section, we use the concepts presented in this chapter to discuss several situations for which one type of visualization is preferred over another. However, we must keep in mind that the most effective visualization depends on the needs of the audience and the message we are trying to convey.
If the goal of the visualization is to convey precise numerical values, then it is often preferable to use a table rather than a chart. Because it is more difficult for an audience to make relative comparisons on the preattentive attribute of shape than on the preattentive attribute of length, bar or column charts are generally preferred over pie charts. However, there are cases for which the most appropriate type of visualization depends on the goal of the visualization and is not always obvious.
Consider the case of Stanley Consulting Group, a company that provides analytics consulting to nonprofit companies. Stanley Consulting Group has offices in Hartford, Stamford, and Providence. Each office has a similar number of consultants and similar performance expectations. Stanley Consulting Group would like to compare the performance of each office. It is mostly interested in comparing each office’s performance relative to the quarterly goal, and in identifying trends over time at each location.
Figure $3.28$ uses a clustered column chart to compare the performances of the offices in terms of quarterly booked revenue for the previous six quarters. The chart also compares this performance to the quarterly booked revenue goal of $\$ 600,000$ that applies to each office.
This clustered column chart in Figure $3.28$ is not necessarily inappropriate for any obvious reason, but we should try to visualize the same data with other charts to see if we can improve on this design. The steps below show how we can change the clustered column chart shown in Figure $3.28$ to a line chart in Excel.
数据可视化代考
统计代写|数据可视化代写Data visualization代考|Other Data Visualization Design Issues
数据可视化应该易于观众查看和解释。图表和表格应该向观众展示洞察力,同时最大限度地减少观众的认知负担。我们可以通过使用前注意属性和格式塔原则以及增加数据可视化中的数据墨水比率来最小化认知负荷。我们还可以通过最小化观众所需的视线移动来最小化认知负荷。
考虑一下斯普林菲尔德市的预算和绩效改进计划。这个城市办公室想比较位于其城市的两个警察区的表现。该市使用的一个绩效指标是清除率,这是导致逮捕的报告犯罪的比例。数字3.25比较过去 6 个月斯普林菲尔德 1 区和 2 区的财产犯罪清除率。
数字3.25有几个特点,增加了观众所需的眼睛旅行。其中许多特征是 Excel 中创建的默认图表的典型特征。首先,图例位于图表底部。这需要观众查看图表底部的图例,然后将视线向上移到线条上,以使图例中的线条类型与图表中的正确线条相匹配。我们可以通过将图例移近线条,或者更好地直接标记图表中的每条线,从而大大减少观众的视线移动。其次,Excel 通常还插入垂直轴标题文本,与图表标题和水平轴标题成 90 度角。这需要观众的眼睛在图表周围移动以阅读横轴标题、纵轴标题和图表标题。最好将图表中的标题尽可能对齐,这样听众就可以只看几个地方来快速解释图表。下面的步骤演示了我们如何改进 Figure3.25以减少观众所需的视线移动量。
步骤 1. 单击 ClearanceRatesChart 文件中图表上的任意位置
单击图表元素按钮+
取消选中图例步骤 2 的复选框
。双击图表中第 1 区数据线上的最后一个数据点以仅选择该数据点
右键单击选定的数据点并选择添加数据标签(这将添加一个数据标签,该数据点的值为“24”)
将此数据标签中的“24”更改为地区l并将字体更改为
Calibri10.5
步骤 3. 双击 District 2 数据图表中线条上的最后一个数据点以仅选择该数据点
右击选中的数据点,选择添加数据标签(这将添加一个数据标签,其中包含该数据点的值,即“20““)改变”20“在此数据标签中为 District 2 并将字体更改为 Calibri10.5
步骤 4. 单击纵轴标题“Proportion Closed with Arrest (क)”按 Delete 键
统计代写|数据可视化代写Data visualization代考|Choosing a Font for Text
文本是任何数据可视化的重要组成部分。它用于标记轴、填写表格值以及向观众展示可视化的重要方面。因为文本是数据可视化的重要组成部分,所以用于显示文本的字体也是一个重要的考虑因素。大多数数据可视化软件工具,包括 Excel,允许用户从数十种甚至数百种显示文本的字体选项中进行选择。
并非所有数据可视化专家都同意在数据可视化中用于文本的首选字体类型,并且通常这种选择可能取决于观众的需求或数据可视化的其他设计元素。然而,大多数专家同意,在数据可视化中,某些字体类型通常比其他字体更适合文本,例如,无衬线字体(不包含衬线的字体)通常比衬线字体(包含衬线的字体)更受欢迎。数据可视化中的文本。衬线指的是使用衬线字体创建的字符中可见的小笔画结束特征。数字3.27说明无衬线字体和衬线字体之间的区别。常见的衬线字体包括 Times、Times New Roman 和 Courier。常见的无衬线字体包括 Arial、Calibri、Myriad Pro 和 Verdana。
一般来说,衬线字体是印刷作品的首选,而无衬线字体是数字显示文本的首选。无衬线字体通常也比小尺寸的衬线字体更易读。因为数据可视化通常以打印形式和数字形式查看,并且因为数据可视化通常包含许多不同大小的字体,所以对于数据可视化中的文本,无衬线字体通常比衬线字体更受欢迎。在本教材中,Excel 中提供的所有图表都使用无衬线字体 Calibri,因为它是 Excel 中的默认字体。教科书中的大多数印刷图表都使用无衬线字体 Myriad Pro,因为它在许多不同的尺寸下都清晰易读,并且适用于印刷和数字工作。但是,其他无衬线字体(例如 Arial 和 Verdana)通常也可以用于数据可视化目的。
统计代写|数据可视化代写Data visualization代考|Wrong Type of Visualization
用于数据可视化的最佳图表或表格类型在很大程度上取决于将查看可视化的受众以及通过可视化讲述的见解或故事。在这本教科书中,我们提供了设计有效数据可视化的最佳实践,但是与使用哪个图表以及设计的某些方面相关的许多决策将取决于可视化的情况和目标。在本节中,我们使用本章中介绍的概念来讨论几种情况,其中一种可视化类型优于另一种。但是,我们必须记住,最有效的可视化取决于观众的需求和我们试图传达的信息。
如果可视化的目标是传达精确的数值,那么通常最好使用表格而不是图表。因为观众更难对形状的前注意属性进行相对比较,而不是长度的前注意属性,所以条形图或柱形图通常比饼图更受欢迎。但是,在某些情况下,最合适的可视化类型取决于可视化的目标,而且并不总是显而易见的。
以 Stanley Consulting Group 为例,该公司为非营利公司提供分析咨询。斯坦利咨询集团在哈特福德、斯坦福和普罗维登斯设有办事处。每个办公室都有相似数量的顾问和相似的绩效期望。斯坦利咨询集团想比较每个办公室的表现。它最感兴趣的是比较每个办事处相对于季度目标的绩效,并确定每个地点随时间推移的趋势。
数字3.28使用聚类柱形图比较办公室在前六个季度的季度预订收入方面的表现。该图表还将这一表现与季度预定收入目标进行了比较$600,000这适用于每个办公室。
图中的这个簇状柱形图3.28由于任何明显的原因,不一定不合适,但我们应该尝试用其他图表将相同的数据可视化,看看我们是否可以改进这种设计。下面的步骤展示了我们如何改变如图所示的簇状柱形图3.28到 Excel 中的折线图。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
