如果你也在 怎样代写机器学习Machine Learning这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
机器学习是人工智能(AI)和计算机科学的一个分支,主要是利用数据和算法来模仿人类的学习方式,逐步提高其准确性。
机器学习是不断增长的数据科学领域的一个重要组成部分。通过使用统计方法,算法被训练来进行分类或预测,在数据挖掘项目中发现关键的洞察力。这些洞察力随后推动了应用程序和业务的决策,最好是影响关键的增长指标。随着大数据的不断扩大和增长,市场对数据科学家的需求将增加,需要他们协助确定最相关的业务问题,随后提供数据来回答这些问题。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写机器学习Machine Learning方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写机器学习方面经验极为丰富,各种代写机器学习Machine Learning相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的机器学习Machine Learning及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Classification
In classification, we try to assign a label to a test instance, e.g., we try to predict if the animal in a picture is a “cat” or a “dog”. In other words, we assign a new observation to a specific category. The learning algorithm that assigns the instance to a category is called classifier. Classification answers questions such as: “is that bank client going to repay the loan?”, “will the user who clicked on an ad buy?”, “who is the person in the Facebook picture?”. Classification predicts a discrete target label $y$. If there are two labels such as “spam” / “not spam”, we have a binary classification problem, if there are more labels, we have a multiclass classification problem, e.g., assigning blood samples to the blood types “A”, “B”, “AB” and “O”.
A classifier learns a function $f$ that maps an input $x$ to an output $y$, as shown in equation 4.1. Sometimes, the function $f$ is referred to as classifier instead of the algorithm that implements the classifier.
$$
y=f(x)+\varepsilon
$$
where
$f=$ Function that maps $x$ to $y$, learned from labeled training data
$x=$ Input, independent variable
$\varepsilon$ is the irreducible error that stems from noise and randomness in the training data and that, as the name suggests, cannot be reduced during training. It can be reduced in some cases through more data preprocessing steps, however, $\varepsilon$ is a theoretical limit of the performance of the learning algorithm.
Typical classifiers include Bayesian models, decision trees, support vector machines and artificial neural networks.
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Artificial neural networks
Artificial neural networks are inspired by the human nervous system. They encompass a large number of different models and learning methods. Here, we cover some of the widely-used models inorder to show their principal functioning.
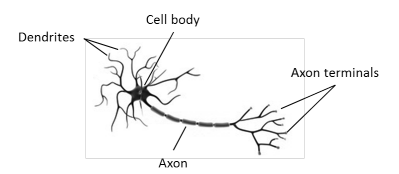
A typical neuron, as found in the human body, looks as depicted in Figure 4.1. It consists of dendrites that receive electrochemical stimulation from upstream neurons through synapses located in different places on the dendrites. Presynaptic cells release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft in response to spikes of electrical activity known as action potentials. The neurotransmitter stimulates the receiving neuron which, in turn, creates an action potential. The action potential is transmitted along the cell membrane down the axon to the axon terminals where it triggers the release of neurotransmitters. The neuron is said to “fire”.
The dendrites can receive signals from more than one upstream neuron. Each neuron is typically connected to thousands of other neurons. It is estimated that there are about 100 trillion $\left(10^{14}\right)$ synapses within the human brain [25]. Also, synaptic connections are not static. They can strengthen and weaken over time as a result of increasing or decreasing activity, a process called synaptic plasticity. Neurologists have discovered that the human brain learns by changing the strength of the synaptic connection between neurons upon repeated stimulation by the same impulse [37]. When two neurons frequently interact, they form a bond that allows them to transmit the signal more easily and accurately (Hebb’s rule). Strong input to a postsynaptic cell causes it to traffic more receptors for neurotransmitters to its surface, amplifying the signal it receives from the presynaptic cell. This phenomenon, known as long-term potentiation (LTP), occurs following persistent, high-frequency stimulation of the synapse. For instance, when we learn a foreign language, we repeat new words until we do not have to concentrate on the translation anymore. We subconsciously use the correct foreign language words. The repeating of the words results in the strengthening of the synaptic connections and formation of a bond between the neurons involved in language speaking. The strengthening and weakening of synaptic connections is imitated in artificial neural networks by linearly combining the input signals with weights. The weights are usually represented in a weight matrix $W$. Learning in an artificial neural network consists of modifying the weight matrix until the generative model represents the training data well [25].
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Bayesian models
Bayesian models are based on Bayes theorem. Generally speaking, the Bayes classifier minimizes the probability of misclassification. It is a model that draws its inferences from the posterior distribution. Bayesian models utilize a prior distribution and a likelihood, which are related by Bayes’ theorem. Bayes rule decomposes the computation of a posterior probability into the computation of a likelihood and a prior probability [30]. It calculates the posterior probability $P(c \mid x)$ from $P(c), P(x)$ and $P(x \mid c)$, as shown in equation 4.7.
$$
P(c \mid x)=\frac{P(x \mid c) P(c)}{P(x)}
$$
where $P(c \mid x)=$ Posterior probability of class $c$ (target) given predictor $P(x \mid c)=$ Likelihood which is the probability of predictor given class $c$
$$
\begin{array}{ll}
P(c) & =\text { Prior probability of class } c \
P(x) & =\text { Prior probability of predictor } x
\end{array}
$$
The probability in Bayesian models is expressed as a degree of belief in an event that can change in the evidence of new information. The Bayes rule tells us how to do inference about hypotheses from data where uncertainty in inferences is expressed using a probability. Learning and prediction can be seen as forms of inference. Calculating $P(x \mid c)$ is not easy when $x=v_{1}, v_{2}, \ldots v_{n}$ is large and requires a lot of computing power. However, Bayesian methods have become popular in recent years due to the advent of more powerful computers.
机器学习代写
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Classification
在分类中,我们尝试为测试实例分配标签,例如,我们尝试预测图片中的动物是“猫”还是“狗”。换句话说,我们将新的观察分配给特定的类别。将实例分配给类别的学习算法称为分类器。分类回答诸如“那个银行客户会偿还贷款吗?”、“点击广告的用户会购买吗?”、“Facebook 图片中的人是谁?”等问题。分类预测离散目标标签是. 如果有两个标签,例如“垃圾邮件”/“非垃圾邮件”,我们就有一个二分类问题,如果有更多标签,我们就有一个多类分类问题,例如,将血样分配给血型“A”、“ B”、“AB”和“O”。
分类器学习一个函数F映射输入X到一个输出是,如公式 4.1 所示。有时,函数F被称为分类器,而不是实现分类器的算法。
是=F(X)+e
在哪里
F=映射的函数X到是,从标记的训练数据中学习
X=输入,自变量
e是源于训练数据中的噪声和随机性的不可约误差,顾名思义,在训练期间无法减少。在某些情况下,可以通过更多的数据预处理步骤来减少它,但是,e是学习算法性能的理论极限。
典型的分类器包括贝叶斯模型、决策树、支持向量机和人工神经网络。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Artificial neural networks
人工神经网络受到人类神经系统的启发。它们包含大量不同的模型和学习方法。在这里,我们介绍了一些广泛使用的模型,以展示它们的主要功能。
人体中的典型神经元如图 4.1 所示。它由树突组成,这些树突通过位于树突不同位置的突触从上游神经元接收电化学刺激。突触前细胞响应称为动作电位的电活动尖峰,将神经递质释放到突触间隙中。神经递质刺激接收神经元,进而产生动作电位。动作电位沿着细胞膜沿轴突向下传递到轴突末端,在那里它触发神经递质的释放。神经元被称为“发射”。
树突可以接收来自多个上游神经元的信号。每个神经元通常连接到数千个其他神经元。估计有100万亿左右(1014)人脑内的突触[25]。此外,突触连接不是静态的。由于活动的增加或减少,它们会随着时间的推移而增强和减弱,这一过程称为突触可塑性。神经学家发现,人类大脑通过在同一脉冲的反复刺激下改变神经元之间突触连接的强度来学习 [37]。当两个神经元频繁相互作用时,它们会形成一种结合,使它们能够更轻松、更准确地传递信号(赫布规则)。对突触后细胞的强输入会使其将更多的神经递质受体运送到其表面,从而放大它从突触前细胞接收到的信号。这种现象称为长时程增强 (LTP),发生在持续的高频刺激突触之后。例如,当我们学习一门外语时,我们会重复生词,直到我们不再需要专注于翻译。我们下意识地使用正确的外语单词。单词的重复导致突触连接的加强,并在涉及语言的神经元之间形成联系。通过将输入信号与权重线性组合,在人工神经网络中模仿突触连接的加强和削弱。权重通常用权重矩阵表示 通过将输入信号与权重线性组合,在人工神经网络中模仿突触连接的加强和削弱。权重通常用权重矩阵表示 通过将输入信号与权重线性组合,在人工神经网络中模仿突触连接的加强和削弱。权重通常用权重矩阵表示在. 人工神经网络中的学习包括修改权重矩阵,直到生成模型很好地代表训练数据[25]。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Bayesian models
贝叶斯模型基于贝叶斯定理。一般来说,贝叶斯分类器将错误分类的概率降到最低。它是一个从后验分布中得出推论的模型。贝叶斯模型利用与贝叶斯定理相关的先验分布和可能性。贝叶斯规则将后验概率的计算分解为似然性和先验概率的计算[30]。它计算后验概率磷(C∣X)从磷(C),磷(X)和磷(X∣C),如公式 4.7 所示。
磷(C∣X)=磷(X∣C)磷(C)磷(X)
在哪里磷(C∣X)=类的后验概率C(目标)给定的预测器磷(X∣C)=可能性是给定类别的预测器的概率C磷(C)= 类的先验概率 C 磷(X)= 预测变量的先验概率 X
贝叶斯模型中的概率表示为对可能改变新信息证据的事件的相信程度。贝叶斯规则告诉我们如何从数据中推断假设,其中推断中的不确定性使用概率表示。学习和预测可以看作是推理的形式。计算磷(X∣C)不容易的时候X=v1,v2,…vn很大,需要大量的计算能力。然而,由于更强大的计算机的出现,贝叶斯方法近年来变得流行。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
