如果你也在 怎样代写贝叶斯网络Bayesian network这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
贝叶斯网络(BN)是一种表示不确定领域知识的概率图形模型,其中每个节点对应一个随机变量,每条边代表相应随机变量的条件概率。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写贝叶斯网络Bayesian network方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写贝叶斯网络Bayesian network代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写贝叶斯网络Bayesian network相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的贝叶斯网络Bayesian network及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|贝叶斯网络代写Bayesian network代考|DBN Structure Modeling
A BN is generally constructed through two major procedures, namely the construction of structure models and the definition of parameter models [46]. In the first step, a set of relevant variables and their possible values should be decided. A network structure can then be set up by connecting these variables into a directed acyclic graph. In the second step, the conditional probability table for each network variable should be defined.
The DBN structure models for the PV systems with centralized, string, and multistring configurations in the presence of intermittent faults are constructed (Fig. 3) according to the PV system configurations given in Fig. 1. Figure 3a demonstrates that the failure of any PV component in a PV system with centralized configuration will cause the failure of the entire PV system. This case signifies that the PV components, including four PV modules #1, #2, #3, and #4 (i.e., PV1, PV2, PV3, and PV4), two DC combiners (Comb1 and Comb2), a DC/DC converter (Conv), and a DC/AC inverter (Inve), are considered a series. Therefore, the network structure is built with two layers using the Netica software tool. The first layer consists of eight nodes representing the status of eight PV components. Each node has three states, i.e., the fault not existing state (NF), intermittent faulty state (IF), and permanent faulty state (PF). The second layer includes one node that depicts the status of PV system. This node has two states, i.e., work and fail, which indicate whether the whole PV system is working or not.
DBNs are an extension of the general BNs that allow the explicit modeling of changes over time. In this process, each time step is called a time slice. Figure 3a indicates that the DBNs of the PV system with centralized configuration consist of two time slices, that is, from $t=0$ to $t=\Delta t$. The nodes PV1, PV2, PV3, PV4, Comb1, Comb2, Conv, and Inve at $t=0$ are extended to PV5, PV6, PV 7, PV8, Comb3, Comb4, Conv1, and Inve1 at $t=\Delta t$, respectively. The number of time slice and the value of $\Delta t$ are determined by the purpose of research and the time the Netica runs. A great number of time slices correspond to a smaller value of $\Delta t$, and, hence, a longer time at which Netica runs. The DBN structure models for the PV systems with string and multistring configurations are similar to that for the PV system with centralized configuration and are produced based on the series and parallel relationship of the PV components, as shown in Fig. 3b, c. The DBN structure model of the complex PV system is given in Fig. 4. The series and parallel relationship among the PV components establishes the conditional probability tables of nodes, which are described in the subsequent section.
统计代写|贝叶斯网络代写Bayesian network代考|Intermittent Fault Modeling
Intermittent faults can hardly be modeled using a directed DBN structural modeling directed. Therefore, this study proposes a method that fuses the Markov model into a DBN model. The developed method has four basic assumptions specified as follows [47-50]:
(1) The PV systems begin with a perfect operation, in which all PV components are functioning correctly.
(2) The transition rates of the PV components, including the failure and repair rates are different, but constant. The lifetimes of these components are exponentially distributed because they are mainly electronic products.
(3) The states of all components are statistically independent.
(4) The PV systems are considered “as good as new” after repairs.
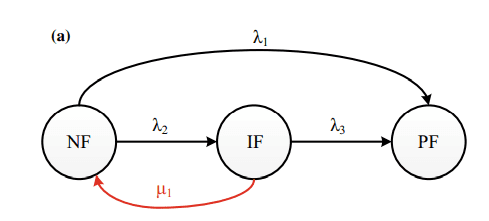
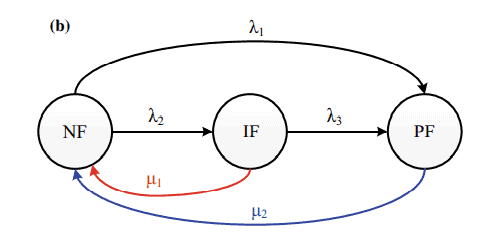
The idea of intermittent and permanent faults can be incorporated in terms of the three-state Markov models as shown in Fig. $5[25,26]$. The model stipulates that the NF state can be converted into a PF and IF states with a failure rate $\lambda_{1}$ and $\lambda_{2}$, respectively. An intermittent fault can lead the components into PF and NF states. Therefore, the IF state can become a PF state with a failure rate of $\lambda_{3}$ and to an NF state with a repair rate of $\mu_{1}$ (autorecovery), as shown in Fig. 5a. If a failed component is repaired once permanent fault occurs, then a repair arc should be added to the state transition diagram. In this case, the PF state can become an NF state with a repair rate of $\mu_{2}$ (manual repair), as shown in Fig. $5 \mathrm{~b}$. When the repair action is not considered, the reliability of the PV system can be calculated. When the repair action is considered, the availability of the PV system can be calculated using the proposed DBN model.
贝叶斯网络代考
统计代写|贝叶斯网络代写Bayesian network代考|DBN Structure Modeling
BN通常通过两个主要程序构建,即结构模型的构建和参数模型的定义[46]。第一步,应确定一组相关变量及其可能值。然后可以通过将这些变量连接到有向无环图中来建立网络结构。第二步,定义每个网络变量的条件概率表。
根据图 1 给出的光伏系统配置,构建了存在间歇性故障的集中式、组串式和多组串配置的光伏系统 DBN 结构模型(图 3)。图 3a 表明任何光伏的故障集中配置的光伏系统中的组件将导致整个光伏系统的故障。这种情况意味着光伏组件,包括四个光伏组件#1、#2、#3 和#4(即 PV1、PV2、PV3 和 PV4),两个 DC 合路器(Comb1 和 Comb2),一个 DC/DC转换器 (Conv) 和 DC/AC 逆变器 (Inve) 被视为串联。因此,使用 Netica 软件工具构建了两层网络结构。第一层由八个节点组成,代表八个 PV 组件的状态。每个节点具有三种状态,即 故障不存在状态(NF)、间歇故障状态(IF)和永久故障状态(PF)。第二层包括一个描述光伏系统状态的节点。该节点有两种状态,即工作和失败,表示整个光伏系统是否工作。
DBN 是通用 BN 的扩展,允许对随时间的变化进行显式建模。在这个过程中,每个时间步称为一个时间片。图 3a 表明集中配置光伏系统的 DBN 由两个时间片组成,即从吨=0至吨=D吨. 节点 PV1、PV2、PV3、PV4、Comb1、Comb2、Conv 和 Inve 在吨=0扩展到 PV5、PV6、PV 7、PV8、Comb3、Comb4、Conv1 和 Inve1吨=D吨, 分别。时间片的数量和值D吨由研究目的和 Netica 运行时间决定。大量的时间片对应于较小的值D吨,因此,Netica 的运行时间更长。组串和多串配置光伏系统的DBN结构模型与集中配置光伏系统相似,是根据光伏组件的串联和并联关系生成的,如图3b、c所示。复杂光伏系统的DBN结构模型如图4所示。光伏组件之间的串联和并联关系建立了节点的条件概率表,将在下一节中描述。
统计代写|贝叶斯网络代写Bayesian network代考|Intermittent Fault Modeling
间歇性断层很难使用有向的 DBN 结构建模来建模。因此,本研究提出了一种将马尔科夫模型融合到 DBN 模型中的方法。所开发的方法有四个基本假设,具体如下[47-50]:(
1)光伏系统从完美运行开始,其中所有光伏组件都正常运行。
(2) 光伏组件的转换率,包括故障率和修复率是不同的,但是是恒定的。这些组件的寿命呈指数分布,因为它们主要是电子产品。
(3) 所有组件的状态在统计上是独立的。
(4) 光伏系统在维修后被认为“和新的一样好”。
间歇性和永久性故障的概念可以纳入三态马尔可夫模型,如图 1 所示。5[25,26]. 该模型规定NF状态可以转换为PF和IF状态,故障率l1和l2, 分别。间歇性故障会导致组件进入 PF 和 NF 状态。因此,IF 状态可以变为 PF 状态,故障率为l3并达到修复率的 NF 状态米1(自动恢复),如图 5a 所示。如果一旦发生永久性故障就修复了故障组件,则应将修复弧添加到状态转换图中。在这种情况下,PF 状态可以变为 NF 状态,修复率为米2(手动修复),如图所示。5 b. 当不考虑修复动作时,可以计算光伏系统的可靠性。当考虑修复措施时,可以使用建议的 DBN 模型计算光伏系统的可用性。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
