如果你也在 怎样代写中级财务会计Intermediate Financial Accounting这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
财务会计是通过财务报表记录、总结和报告公司业务交易的过程。这些报表是:利润表、资产负债表、现金流量表和留存收益表。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写中级财务会计Intermediate Financial Accounting方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写中级财务会计Intermediate Financial Accounting代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写中级财务会计Intermediate Financial Accounting相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的中级财务会计Intermediate Financial Accounting及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
会计代写|中级财务会计代写Intermediate Financial Accounting代考|The Historical Cost Principle
The historical cost principle states that assets should be recorded at their actual cost, measured on the date of purchase as the amount of cash paid plus noncash types of compensation given in exchange. For example, suppose The Walt Disney Company wants to purchase a building for a new Disney Store. The building’s current owner is asking $\$ 6,000,000$ for the building. Disney’s managers believe the building is worth $\$ 5,850,000$ and offer that amount. Two real estate professionals appraise the building at $\$ 6,100,000$. The buyer and seller then compromise and agree on a price of $\$ 5,900,000$. The historical cost principle requires Disney to initially record the building at its actual cost of $\$ 5,900,000$-not at $\$ 5,850,000, \$ 6,000,000$, or $\$ 6,100,000$, even though those amounts were what some people believed the building was worth. The $\$ 5,900,000$ cost is both the relevant amount of the building’s worth and the amount that faithfully represents a reliable figure for the price the company paid for it.
Based on the historical cost principle and the continuity assumption, The Walt Disney Company should continue to use historical cost to value the asset for as long as the business owns it. Why? Because cost is a verifiable measure that is relatively free from bias. Suppose that after the company has owned the building for six years, it can be sold for $\$ 6,500,000$ because real estate prices have gone up. Should Disney increase the value of the building on the company’s books to $\$ 6,500,000$ at this point? No. According to the historical cost principle, the building remains on The Walt Disney Company’s books at its historical cost of $\$ 5,900,000$, less accumulated depreciation. According to the continuity assumption, Disney intends to stay in business and use the building-not sell it—so its historical cost is the most relevant and the most faithful representation of its value. It is also the most easily verifiable amount. Should the company decide to sell the building later at a price above or below its value, it will record the cash received, remove the value of the building from the books, and record a gain or a loss for the difference at that time.
Although the historical cost principle is used widely in the United States to value assets, accounting is moving in the direction of reporting more assets and liabilities at their fair values. Fair value is the amount that the business could sell the asset for, or the amount that the business could pay to settle the liability. The FASB has issued guidance for companies to report many assets and liabilities at fair values. ‘ Moreover, in recent years, the FASB has agreed to “harmonize” U.S. GAAP with IFRS. IFRS generally allow more types of assets to be periodically adjusted to their fair values than U.S. GAAP. We will discuss the trend toward globalization of accounting standards in the following Global View feature, and we will illustrate it in later chapters throughout the book.
会计代写|中级财务会计代写Intermediate Financial Accounting代考|The Stable-Monetary-Unit Assumption
In the United States, we record transactions in dollars because that is our medium of exchange. British accountants record transactions in pounds sterling, Japanese in yen, and some continental Europeans in euros.
Unlike a liter or a mile, the value of a dollar changes over time. A rise in the general price level is called inflation. Inflation results in a dollar purchasing less food, less toothpaste, and less of other goods and services. When prices are stable-there is little inflation-a dollar’s purchasing power is also stable.
Under the stable-monetary-unit assumption, accountants assume that the dollar’s purchasing power is stable over time. We ignore inflation, and this allows us to add and subtract dollar amounts as though the dollar’s purchasing power hasn’t changed. This is important because businesses that report their financial information publicly usually report comparative financial information (that is, the current year along with one or more prior years). If we could not assume a stable monetary unit, assets and liabilities denominated in prior years’ dollars would have to be adjusted to current-year price levels. In developed countries like the United States, inflation levels have been at very low levels for several decades and are expected to remain so for the foreseeable future. As a result, adjusting accounting information for inflation to make the information comparable over time isn’t considered necessary.
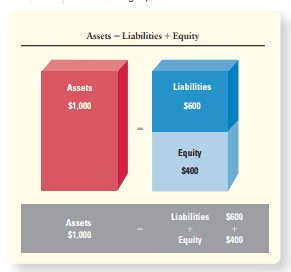
The financial statements are based on the accounting equation. This equation presents the resources of a company and the claims to those resources.
- Assets are economic resources that are expected to produce a benefit in the future. The Walt Disney Company’s cash, receivables, inventory, attractions, buildings, and equipment are examples of assets.
Claims on assets come from two sources: - Liabilities are “outsider claims.” They are debts owed to people and organizations outside of the business (creditors). For example, a creditor who has loaned money to The Walt Disney Company has a claim-a legal right-to a part of the company’s assets until the company repays the debt.
- Equity (also called capital, owners’ equity, or stockholders’ equity for a corporation) represents the “insider claims” of a business. Equity means ownership, so The Walt Disney Company’s equity is the stockholders’ interest in the assets of the corporation. Throughout most of this book we will be discussing corporations, so the term stockholders’ equity is most likely to be used.
财务会计代考
会计代写|中级财务会计代写中间财务会计代考|历史成本原则
. The . The
历史成本原则指出,资产应按其实际成本入账,在购买之日以支付的现金加上作为交换的非现金类型的报酬来计量。例如,假设华特迪士尼公司想为新的迪士尼商店购买一栋大楼。该建筑的现任所有者要求$\$ 6,000,000$出售该建筑。迪士尼的经理认为这座建筑价值$\$ 5,850,000$,并给出了这个价格。两位房地产专业人士在$\$ 6,100,000$上对这栋建筑进行了评估。买方和卖方随后妥协,商定价格为$\$ 5,900,000$。历史成本原则要求迪士尼最初以这座建筑的实际成本$\$ 5,900,000$记录,而不是$\$ 5,850,000, \$ 6,000,000$或$\$ 6,100,000$,尽管这些数字是一些人认为这座建筑的价值。$\$ 5,900,000$成本既是该建筑价值的相关金额,也是该公司为其支付的可靠数字的忠实代表
根据历史成本原则和连续性假设,只要公司拥有资产,迪士尼公司就应该继续使用历史成本对资产进行估值。为什么?因为成本是一个可验证的度量,相对来说没有偏见。假设该公司拥有该建筑6年后,可以以$\$ 6,500,000$的价格出售,因为房地产价格上涨了。迪士尼是否应该将该建筑在公司账面上的价值提高到$\$ 6,500,000$ ?不。根据历史成本原则,该建筑在华特迪士尼公司的账面上仍以其历史成本$\$ 5,900,000$计算,扣除累计折旧。根据连续性假设,迪士尼打算继续经营并使用这座建筑,而不是出售它,因此它的历史成本是其价值的最相关和最忠实的代表。这也是最容易核实的数额。如果公司决定以后以高于或低于其价值的价格出售该建筑,它将记录收到的现金,从账簿上删除该建筑的价值,并记录当时的差额的收益或亏损
虽然历史成本原则在美国被广泛用于资产估值,但会计正朝着以公允价值报告更多资产和负债的方向发展。公允价值是企业出售资产的价格,或企业为清偿债务而支付的金额。FASB已经发布了指导方针,要求公司以公允价值报告许多资产和负债。此外,近年来,FASB已同意“协调”美国公认会计准则与国际财务报告准则。与美国公认会计准则相比,国际财务报告准则通常允许更多类型的资产定期调整其公允价值。我们将在接下来的全球视角专题中讨论会计准则全球化的趋势,并将在本书后面的章节中对此进行说明
会计代写|中级财务会计代写中级财务会计代考|稳定货币单位假设
在美国,我们用美元记录交易,因为美元是我们的交换媒介。英国会计用英镑记账,日本会计用日元记账,有些欧洲大陆会计用欧元记账
与一升或一英里不同,一美元的价值会随着时间而变化。一般物价水平的上升称为通货膨胀。通货膨胀导致一美元购买的食品、牙膏以及其他商品和服务减少。当价格稳定时——几乎没有通货膨胀——一美元的购买力也是稳定的
在货币单位稳定假设下,会计人员假设美元的购买力随时间推移是稳定的。我们忽略了通货膨胀,这使得我们可以加减美元金额,就好像美元的购买力没有改变一样。这一点很重要,因为公开报告其财务信息的企业通常报告比较财务信息(也就是说,当前年度与一个或多个前一年)。如果我们不能假设一个稳定的货币单位,以前几年美元计价的资产和负债就必须调整到今年的价格水平。在像美国这样的发达国家,通货膨胀水平几十年来一直处于非常低的水平,预计在可预见的未来将继续保持这种水平。因此,根据通货膨胀调整会计信息以使信息随时间的变化具有可比性被认为是没有必要的
财务报表是以会计等式为基础的。这个等式表示公司的资源和对这些资源的要求
资产是预期在未来产生效益的经济资源。华特迪士尼公司的现金、应收款、存货、景点、建筑物和设备都是资产的例子。资产索赔有两个来源:负债是“外人索赔”。它们是欠企业以外的人或组织的债务(债权人)。例如,借钱给华特迪士尼公司的债权人拥有债权——在公司偿还债务之前对公司部分资产的合法权利。权益(公司也称为资本、所有者权益或股东权益)代表企业的“内部主张”。股权意味着所有权,所以华特迪士尼公司的股权是股东对公司资产的权益。在本书的大部分篇幅中,我们将讨论公司,因此最有可能使用的术语是股东权益
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
