如果你也在 怎样代写概率与统计Probability and Statistics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
概率涉及预测未来事件的可能性,而统计涉及对过去事件频率的分析。概率论主要是数学的一个理论分支,它研究数学定义的后果。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写概率与统计Probability and Statistics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写概率与统计Probability and Statistics方面经验极为丰富,各种代写概率与统计Probability and Statistics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的概率与统计Probability and Statistics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|概率与统计作业代写Probability and Statistics代考|Getting Started with R
$R$ is a programming language: you can write code and have $R$ execute that code. $R$ is very well suited for analyzing data, and has many statistical operations build-in, but in the end it can be used to built all kinds of things. However, in this book we will mainly use it for analyzing data.
There are many different ways in which you can use R. One way is to use what is called the R console, which is shown in Fig. 1.1. The console comes with any default installation of $\mathrm{R}$ that you can find at https://www.r-project.org. You can use this console to type in $\mathrm{R}$ commands, and execute them line by line. The figure shows the execution of the line print ( “hello world” ) which prints the string “hello world” to the screen. Everything you do within a session (thus, without closing the console) will be remembered; if you close the console you will lose the work you have not saved explicitly.
The console is, however, not the easiest way of working with $\mathrm{R}$. There are two often used alternative ways of using R:
- Using a code editor: You can use any text/code editor, such as TextMate or Sublime text to write and store the R (analysis) code that you end up writing. Good code editors will allow you to run the code directly from the editor by sending it to the $\mathrm{R}$ console. If you have already programmed in some other language using a code editor that supports $\mathrm{R}$ this might be your best option.
- Using a graphical user interface: You can also use a point and click solution such as RStudio. For downloads see https://www.rstudio.com. RStudio is preferred by many of our students, and hence we explain installing and using RStudio in more detail in the additional materials at the end of this Chapter.
RStudio is very popular these days, but this book is not tied to using RStudio. Find something you are comfortable with and get used to it. In the end, it’s all a matter of preference.
统计代写|概率与统计作业代写Probability and Statistics代考|Scalars, Vectors, Matrices, Data.frames, Objects
The data. Erame is just one of the many objects that $\mathrm{R}$ supports. ${ }^7$ We can easily create other types of objects. For example, if we run:
$>$ id $<-10$ we create the object called $i \mathrm{a}$, which is a variable containing the value 10 . The object id lives outside or next to our dataset. Thus object id should not be confused with the column id in our dataset. Just as with our dataset (the face_data object), we can easily inspect our new object by just typing its name: $>$ id
[1] 10
To see the column id we should have used the R code
face_data\$id
indicating that the column id lives in the data frame face_data.
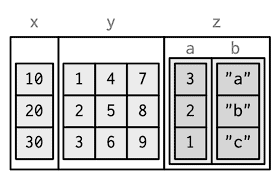
To gain some more understanding regarding $\mathrm{R}$ objects and their structure, we will dig a bit deeper into the face data object. The face data object is of type data. frame, which itself can be thought of as an extension of another type of object called a matrix. ${ }^8$ A matrix is a collection of numbers ordered by rows and columns. To illustrate, the code below creates a matrix called $M$ consisting of three rows and three columns using the matrix() function. We populate this matrix using the values $1,2, \ldots, 9$ which we generate with the $c(1: 9)$ command. ${ }^9$
The data. frame object is similar to the matrix object, but it can contain different types of data (both numbers and strings), and it can contain column names: we often call these variable names.
We can access different elements of a matrix in multiple ways. This is called indexing. Here are some examples:
Both a row or a column of numbers is called a vector, and a single numerical entry of a vector is called a scalar. Hence, the object id that we defined above was a scalar (a single number) while the command $c(1: 9)$ generates a vector. Note that “under the hood” $\mathrm{R}$ always works using vectors, which explains the [1] in front of the value of $i d$ when we printed it: $R$ is actually printing the first element of the vector $i d$.
概率与统计代考
统计代写|概率与统计作业代写概率与统计代考|从R开始
$R$是一种编程语言:您可以编写代码并让$R$执行代码。$R$非常适合用于分析数据,并且内置了许多统计操作,但最终它可以用于构建各种各样的东西。然而,在本书中,我们将主要使用它来分析数据 有许多不同的方法可以使用R,一种方法是使用所谓的R控制台,如图1.1所示。控制台附带$\mathrm{R}$的任何默认安装,您可以在https://www.r-project.org上找到它们。您可以使用这个控制台输入$\mathrm{R}$命令,并逐行执行它们。该图显示了行打印(“hello world”)的执行情况,它将字符串“hello world”打印到屏幕上。您在会话中所做的一切(因此,无需关闭控制台)将被记住;如果你关闭控制台,你将丢失你没有显式保存的工作 但是,控制台并不是使用$\mathrm{R}$的最简单的方法。通常有两种使用R的替代方法:
使用代码编辑器:您可以使用任何文本/代码编辑器,例如TextMate或Sublime文本来编写和存储您最终编写的R(分析)代码。好的代码编辑器将允许您通过将代码发送到$\mathrm{R}$控制台直接从编辑器运行代码。如果您已经使用支持$\mathrm{R}$的代码编辑器用其他语言进行编程,那么这可能是您的最佳选择。使用图形用户界面:您也可以使用点和单击解决方案,如RStudio。下载请参见https://www.rstudio.com。RStudio被我们的许多学生所偏爱,因此我们将在本章末尾的附加材料中更详细地解释安装和使用RStudio
RStudio现在非常流行,但是这本书与使用RStudio无关。找一些你觉得舒服的东西,然后习惯它。最后,这都是一个偏好的问题
统计代写|概率与统计作业代写概率与统计代考|标量,向量,矩阵,数据。帧,对象
数据。Erame只是$\mathrm{R}$支持的众多对象之一。${ }^7$我们可以轻松地创建其他类型的对象。例如,如果我们运行:
$>$ id $<-10$,我们将创建一个名为$i \mathrm{a}$的对象,它是一个包含值10的变量。对象id位于数据集的外部或旁边。因此,对象id不应该与数据集中的列id混淆。就像我们的数据集(face_data对象)一样,我们可以很容易地检查我们的新对象,只需输入它的名称:$>$ id
[1] 10
要查看列id,我们应该使用R代码
face_data$id
表示列id位于数据帧face_data中。为了对$\mathrm{R}$对象及其结构有更多的了解,我们将更深入地挖掘face数据对象。face数据对象的类型是data。框架,它本身可以被认为是另一种叫做矩阵的对象的扩展。${ }^8$矩阵是按行和列排序的数字的集合。为了说明这一点,下面的代码使用matrix()函数创建了一个名为$M$的矩阵,由三行三列组成。我们使用使用$c(1: 9)$命令生成的值$1,2, \ldots, 9$填充这个矩阵。${ }^9$
数据。Frame对象类似于matrix对象,但是它可以包含不同类型的数据(数字和字符串),并且它可以包含列名:我们通常称这些变量为变量名 我们可以用多种方式访问矩阵的不同元素。这叫做索引。下面是一些例子:
一行或一列的数字都被称为矢量,矢量的单个数字条目被称为标量。因此,我们在上面定义的对象id是一个标量(一个数字),而命令$c(1: 9)$生成一个向量。注意,“底层”$\mathrm{R}$总是使用向量工作,这解释了当我们打印$i d$值时,[1]在它前面:$R$实际上打印的是向量$i d$的第一个元素
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
