会计代写|国际商贸代写International Business代考|IBUS3600
如果你也在 怎样代写国际商贸International Business 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。国际商贸International Business是指具有国际性质的私人商业交易。当当事人的营业地点在不同的民族国家时,就存在国际因素;当这些交易涉及商品、服务、技术或资本在不同国家之间的流动时;或者当一个州的各方之间的交易对另一个州有直接影响时。
国际商贸International Business可以根据在国际市场的渗透程度进行分类,至少在一般情况下是这样。第一级渗透是简单的进出口交易,例如,涉及来自美国的卖方和来自德国的买方的货物销售。如果这是成功的,公司发现对其产品有足够的需求,卖方可以在德国建立一个代理商或其产品的分销商,他们将试图增加卖方对目标市场的渗透。在这一步之后,美国卖方可能决定从事合同制造,这是第三个渗透层次。这可能涉及授权德国实体在德国生产其产品,并在德国和其他欧洲国家销售和分销。在这种许可交易中,一个重要的问题是技术转让,因为卖方需要允许德国制造商在一定程度上获得卖方的知识产权。或者,在许可协议期满后,美国卖方可以决定在德国建立自己的业务实体,由其作为唯一或部分所有者。美国卖方可以选择通过建立德国子公司从零开始建立自己的业务,或者收购一家现有的德国商业实体。在任何一种情况下,这都是所谓的“外国直接投资”。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写国际商贸International Business方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写国际商贸International Business代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写国际商贸International Business相关的作业也就用不着说。

会计代写|国际商贸代写International Business代考|The World Trade Organization
The WTO acts as an umbrella organization that encompasses the GATT along with two new sister bodies, one on services and the other on intellectual property. The WTO’s General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) has taken the lead to extending free trade agreements to services. The WTO’s Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) is an attempt to narrow the gaps in the way intellectual property rights are protected around the world and to bring them under common international rules. WTO has taken over responsibility for arbitrating trade disputes and monitoring the trade policies of member countries. While the WTO operates on the basis of consensus as the GATT did, in the area of dispute settlement, member countries are no longer able to block adoption of arbitration reports. Arbitration panel reports on trade disputes between member countries are automatically adopted by the WTO unless there is a consensus to reject them. Countries that have been found by the arbitration panel to violate GATT rules may appeal to a permanent appellate body, but its verdict is binding. If offenders fail to comply with the recommendations of the arbitration panel, trading partners have the right to compensation or, in the last resort, to impose (commensurate) trade sanctions. Every stage of the procedure is subject to strict time limits. Thus, the WTO has something that the GATT never had-teeth. ${ }^{23}$
WTO: EXPERIENCE TO DATE
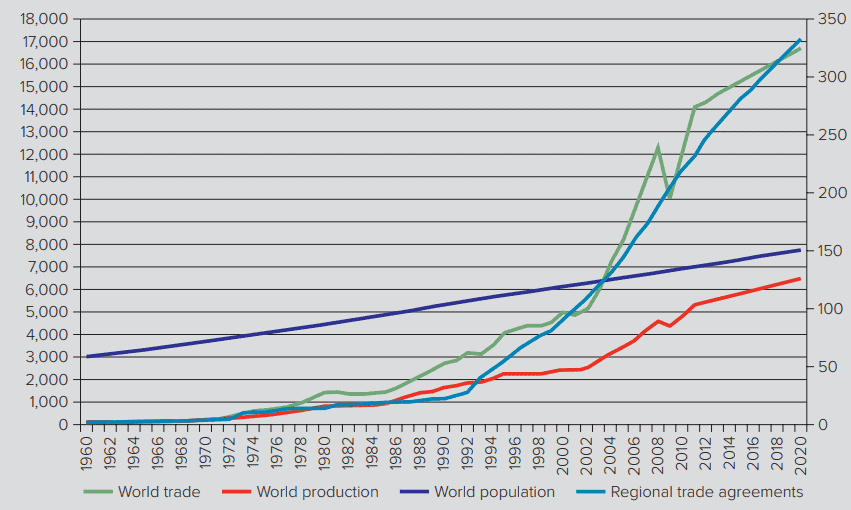
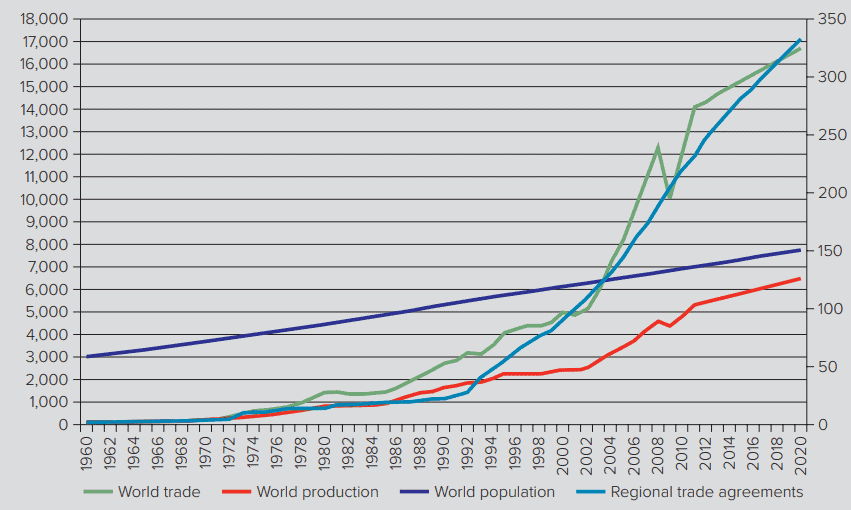
By 2016, the WTO had 164 members, including China, which joined at the end of 2001, and Russia, which joined in 2012. WTO members collectively account for 98 percent of world trade. Since its formation, the WTO has remained at the forefront of efforts to promote global free trade. Its creators expressed the belief that the enforcement mechanisms granted to the WTO would make it more effective at policing global trade rules than the GATT had been. The great hope was that the WTO might emerge as an effective advocate and facilitator of future trade deals, particularly in areas such as services. The experience so far has been mixed. After a strong early start, since the late 1990 s the WTO has been unable to get agreements to further reduce barriers to international trade and trade and investment. There has been very slow progress with the current round of trade talks (the Doha Round). There was also a shift back toward some limited protectionism following the global financial crisis of 2008-2009. More recently, the 2016 vote by the British to leave the European Union (Brexit) and the election of Donald Trump to the presidency in the United States have suggested that the world may be shifting back toward greater protectionism. These developments have raised a number of questions about the future direction of the WTO.
会计代写|国际商贸代写International Business代考|Expanded Trade Agreements
As explained earlier, the Uruguay Round of GATT negotiations extended global trading rules to cover trade in services. The WTO was given the role of brokering future agreements to open up global trade in services. The WTO was also encouraged to extend its reach to encompass regulations governing foreign direct investment, something the GATT had never done. Two of the first industries targeted for reform were the global telecommunication and financial services industries.
In February 1997, the WTO brokered a deal to get countries to agree to open their telecommunication markets to competition, allowing foreign operators to purchase ownership stakes in domestic telecommunication providers and establishing a set of common rules for fair competition. Most of the world’s biggest markets-including the United States, European Union, and Japan-were fully liberalized by January 1, 1998, when the pact went into effect. All forms of basic telecommunication service are covered, including voice telephone, data, and satellite and radio communications. Many telecommunication companies responded positively to the deal, pointing out that it would give them a much greater ability to offer their business customers one-stop shopping-a global, seamless service for all their corporate needs and a single bill.
This was followed in December 1997 with an agreement to liberalize cross-border trade in financial services. The deal covered more than 95 percent of the world’s financial services market. Under the agreement, which took effect at the beginning of March 1999, 102 countries pledged to open (to varying degrees) their banking, securities, and insurance sectors to foreign competition. In common with the telecommunication deal, the accord covers not just cross-border trade but also foreign direct investment. Seventy countries agreed to dramatically lower or eradicate barriers to foreign direct investment in their financial services sector. The United States and the European Union (with minor exceptions) are fully open to inward investment by foreign banks, insurance, and securities companies. As part of the deal, many Asian countries made important concessions that allow significant foreign participation in their financial services sectors for the first time.
THE FUTURE OF THE WTO: UNRESOLVED ISSUES AND THE DOHA ROUND
Since the successes of the 1990s, the World Trade Organization has struggled to make progress on the international trade front. Confronted by a slower growing world economy after 2001, many national governments have been reluctant to agree to a fresh round of policies designed to reduce trade barriers. Political opposition to the WTO has been growing in many nations. As the public face of globalization, some politicians and nongovernmental organizations blame the WTO for a variety of ills, including high unemployment, environmental degradation, poor working conditions in developing nations, falling real wage rates among the lower paid in developed nations, and rising income inequality. The rapid rise of China as a dominant trading nation has also played a role here. Reflecting sentiments like those toward Japan 25 years ago, many perceive China as failing to play by the international trading rules, even as it embraces the WTO.
Against this difficult political backdrop, much remains to be done on the international trade front. Four issues at the forefront of the agenda of the WTO are antidumping policies, the high level of protectionism in agriculture, the lack of strong protection for intellectual property rights in many nations, and continued high tariff rates on nonagricultural goods and services in many nations. We shall look at each in turn before discussing the latest round of talks between WTO members aimed at reducing trade barriers, the Doha Round, which began in 2001 and now seem to be stalled.
国际商贸代考
会计代写|国际商贸代写International Business代考|The World Trade Organization
世贸组织作为一个伞形组织,包括关贸总协定以及两个新的姊妹机构,一个是服务机构,另一个是知识产权机构。世界贸易组织的服务贸易总协定(GATS)率先将自由贸易协定扩展到服务领域。世界贸易组织的《与贸易有关的知识产权协定》(TRIPS)旨在缩小世界各地知识产权保护方式的差距,并将其纳入共同的国际规则之下。世贸组织承担了仲裁贸易争端和监督成员国贸易政策的责任。虽然世贸组织和关贸总协定一样是在协商一致的基础上运作的,但在争端解决领域,成员国不再能够阻止仲裁报告的通过。仲裁小组关于成员国之间贸易争端的报告将自动被世贸组织采纳,除非各方达成共识予以拒绝。被仲裁小组认定违反关贸总协定规则的国家可以向常设上诉机构提出上诉,但其裁决具有约束力。如果违规者不遵守仲裁小组的建议,贸易伙伴有权要求赔偿,或在最后手段时实施(相称的)贸易制裁。程序的每个阶段都有严格的时间限制。因此,世贸组织拥有关贸总协定从未拥有过的东西。$ {} ^ {23} $
Wto:迄今为止的经验
截至2016年,世贸组织共有164个成员,其中包括2001年底加入的中国和2012年加入的俄罗斯。世贸组织成员占世界贸易总量的98%。自成立以来,世界贸易组织一直走在促进全球自由贸易的前列。它的创始者表示相信,授予世贸组织的执行机制将使其在维护全球贸易规则方面比关贸总协定更有效。人们寄予厚望的是,世贸组织可能成为未来贸易协议的有效倡导者和推动者,尤其是在服务等领域。到目前为止,人们的体验好坏参半。在经历了一个强劲的早期开端之后,自20世纪90年代末以来,世贸组织一直无法达成进一步减少国际贸易以及贸易和投资壁垒的协议。目前这一轮贸易谈判(多哈回合)进展非常缓慢。2008-2009年全球金融危机之后,也出现了向某种程度的保护主义倒退的趋势。最近,2016年英国投票退出欧盟(Brexit)和唐纳德·特朗普当选美国总统表明,世界可能正在转向更大的保护主义。这些发展对世贸组织的未来方向提出了一些问题。
会计代写|国际商贸代写International Business代考|Expanded Trade Agreements
如前所述,关贸总协定乌拉圭回合谈判扩大了全球贸易规则,以涵盖服务贸易。世贸组织被赋予了斡旋未来开放全球服务贸易协议的角色。世贸组织还被鼓励扩大其范围,包括管理外国直接投资的规定,这是关贸总协定从未做过的事情。首批改革的两个行业是全球电信业和金融服务业。
1997年2月,世贸组织促成了一项协议,让各国同意向竞争开放电信市场,允许外国运营商购买国内电信提供商的股权,并建立了一套公平竞争的共同规则。世界上大多数最大的市场——包括美国、欧盟和日本——在1998年1月1日该协定生效之前都实现了完全自由化。包括话音电话、数据通信、卫星通信和无线电通信在内的各种形式的基本电信服务都已覆盖。许多电信公司对这项交易做出了积极的回应,指出这将使他们更有能力为他们的商业客户提供一站式购物——一个全球性的、无缝的服务,满足他们所有的企业需求,只需一张账单。
随后在1997年12月签署了一项金融服务跨境贸易自由化协议。该协议覆盖了全球95%以上的金融服务市场。根据1999年3月初生效的协议,102个国家承诺(在不同程度上)向外国竞争开放其银行、证券和保险部门。与电信协议一样,该协议不仅涵盖跨境贸易,还涵盖外国直接投资。70个国家同意大幅降低或消除外国直接投资进入其金融服务部门的壁垒。美国和欧盟(除了少数例外)对外国银行、保险和证券公司的投资完全开放。作为协议的一部分,许多亚洲国家做出了重要让步,首次允许外资大量参与其金融服务业。
wto的未来:未解决的问题和多哈回合
自上世纪90年代取得成功以来,世界贸易组织一直在努力在国际贸易领域取得进展。2001年后,面对全球经济增长放缓的局面,许多国家的政府一直不愿同意新一轮旨在减少贸易壁垒的政策。在许多国家,反对加入世贸组织的政治呼声日益高涨。作为全球化的公众形象,一些政治家和非政府组织指责世贸组织造成了各种各样的弊病,包括高失业率、环境恶化、发展中国家恶劣的工作条件、发达国家低收入人群实际工资率下降以及收入不平等加剧。中国作为主要贸易国的迅速崛起也起到了一定作用。与25年前对日本的看法类似,许多人认为中国即使加入了世贸组织,也没有遵守国际贸易规则。
在这种困难的政治背景下,在国际贸易方面仍有许多工作要做。世贸组织议程上最重要的四个问题是:反倾销政策、高度的农业保护主义、许多国家对知识产权缺乏强有力的保护,以及许多国家对非农业产品和服务继续征收高关税。在讨论世贸组织成员国之间旨在减少贸易壁垒的最新一轮谈判——多哈回合谈判之前,我们将依次讨论这些问题。多哈回合谈判始于2001年,现在似乎陷入了僵局。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。