金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial derivatives代考|ECON6042
如果你也在 怎样代写金融衍生品Financial derivatives这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
金融衍生品是与特定的金融工具或指标或商品相联系的金融工具,通过它,特定的金融风险可以在金融市场上以其本身的名义进行交易。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写金融衍生品Financial derivatives方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写金融衍生品Financial derivatives代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写金融衍生品Financial derivatives相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的金融衍生品Financial derivatives及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial derivatives代考|OTC Derivatives Documentation
The financial institutions offering derivative products and services control and monitor their counterparty risk with the trading counterparty. Some products such as a deposit or a structured note imply one-way counterparty risk where the end investor takes the counterparty risk of the financial institution but the financial institution has no risk from the end investor. However, in some other products such as forward and swap, both parties are taking counterparty risk. The growth of OTC derivatives business prompted the standardization for the contract terms as well as the counterparty credit risk management which are widely used by the institutions and corporates actively involved in financial market.
ISDA (International Swaps and Derivatives Association) Master Agreement, initially developed in the 1980 s to cover the IRS and currency swaps, has been progressively updated to include the derivatives such as forward, swap and option linked to equities, commodities and funds. It sets out standard terms applied to all trades between the two parties.
In general, two parties set up their trading relationship for OTC derivatives by negotiating the applicability and eventual adjustment of the standard terms. The document containing the agreed terms is the ISDA Master Agreement signed by both parties.
CSA (Credit Support Annex) is the document for credit support (i.e. collateral) for derivative transactions. It defines the acceptable collaterals with the “haircuts”. In particular, it defines the “Threshold” which is the consolidated MtM level of all the trades to trigger the margin call. The “Independent Amount (IA)” is the initial margin (collateral) required by one party (usually the dealer) to the other party (usually the end user) for mitigating the counterparty risk linked to an OTC transaction. It is returned only after the termination of the transaction. Its level depends on the volatility of the mark-to-market value of the trade as well as the credit worthiness of the counterparty. During the life of the trade, “variation margin” will be exchanged according to its mark-to-market.
The institutions and corporates actively transacting derivatives usually establish an ISDA/CSA Master Agreement with their counterparties. Normally, the credit agreement between two financial institutions is a two-way CSA in which both parties may post margins for their OTC trades. Between a financial institution and a corporate (especially the small ones), the credit agreement may be a one-way CSA, meaning that only the corporate posts margins to the financial institution. Under a master agreement (ISDA/CSA or any bespoke master agreement), the specific terms and conditions of each OTC derivative trade will take a short form called term sheet or transaction supplement. The individual investors, small corporates and other nonactive entities involved in financial market normally trade with financial institutions with a hespoke agreement or a long form confirmation which contains all terms and conditions for each trade.
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial derivatives代考|Securities Borrowing & Lending and Repo
A repurchase agreement is a contract for the sale of a security (e.g. stock or bond) with a commitment by the seller to buy the same security back from the buyer at a specified price at a future date. During the tenor of the trade, the seller (also called the lender) of the security surrenders the legal ownership of the security. There are two activities based on the repurchase agreement: Securities Lending and Repo.
Securities Borrowing \& Lending $(S B L)$ transaction allows the lender to lend securities to the borrower on either “Open” (i.e. anytime callable) or “Term” (a fixed tenor) basis. Upon the trade termination, the securities will be returned to the lender. The borrower posts collateral with daily adjustment and pays fees to the lender. The fee rate depends on the borrow supply/demand for the underlying security. The eligible collateral can be cash or other securities negotiated by the parties. The cash collateral level is usually $\sim 105 \%$ of the latest closing price of the security. The International Securities Lending Association has developed a standard agreement called Global Master Securities Lending Agreement (GMSLA) which is followed by most of the institutions. The motivation for the borrower includes short position recovering, hedging of derivatives, corporate action arbitrage, etc.
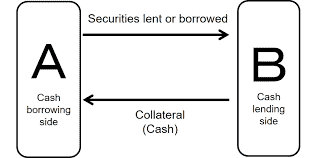
In a sale and repurchase agreement (Repo), one counterparty (the repo seller) is borrowing money and providing collateral (mostly fixed-income assets) for the loan. See Fig. 1.1 for reference. The seller gains access to funds at lower funding costs than are typically available elsewhere as the loan is collateralized. The collateral eligibility and haircuts are negotiable between the repo counterparties. The standard agreement for Repo is Global Master Repurchase Agreement (GMRA), published by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA). A Reverse Repo is the opposite transaction seen by the other counterparty of the Repo trade. Some central banks use Repo/Reverse Repo operations to regulate the money supply in the financial system.
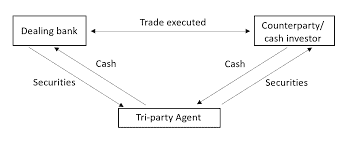
If the collateral is held at a third party, usually a custodian bank or an international central securities depository, the transaction is call a Tri-Party Repo or Tri-Party Securities Lending. The third party will provide services such as the valuation and adjustment of the collateral. The risk in a Tri-Party Repo transaction is the correlation of the default probability of the counterparty and the value of the collateral in custody.
Although most Repo activities take place on the OTC market, there exists Stock Exchange Repo (e.g. Shanghai Stock Exchange Repo) whereby the exchange determines the collateral pool and haircuts, standardizes the contract features such as size and tenor, and facilitates clearing and pledge of collateral.
金融衍生品代写
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial derivatives代考|OTC Derivatives Documentation
提供衍生产品和服务的金融机构与交易对手一起控制和监控其交易对手风险。存款或结构性票据等一些产品意味着单向交易对手风险,即最终投资者承担金融机构的交易对手风险,但金融机构没有来自最终投资者的风险。然而,在远期和掉期等其他一些产品中,双方都承担交易对手风险。场外衍生品业务的发展促进了合同条款和交易对手信用风险管理的标准化,并被积极参与金融市场的机构和企业广泛采用。
ISDA(国际掉期和衍生品协会)主协议最初于 1980 年代制定,涵盖 IRS 和货币掉期,现已逐步更新以包括与股票、商品和基金挂钩的远期、掉期和期权等衍生品。它规定了适用于双方之间所有交易的标准条款。
一般而言,交易双方通过协商标准条款的适用性和最终调整来建立场外衍生品交易关系。包含约定条款的文件是双方签署的 ISDA 主协议。
CSA(Credit Support Annex)是为衍生品交易提供信用支持(即抵押品)的文件。它用“折扣”定义了可接受的抵押品。特别是,它定义了“阈值”,即触发追加保证金的所有交易的综合 MtM 水平。“独立金额 (IA)”是一方(通常是交易商)向另一方(通常是最终用户)要求的初始保证金(抵押品),以减轻与场外交易相关的交易对手风险。它仅在交易终止后返回。其水平取决于交易按市值计价的波动性以及交易对手的信用度。在交易期间,“变动保证金”将根据其市值进行兑换。
积极从事衍生品交易的机构和企业通常会与其交易对手建立 ISDA/CSA 主协议。通常,两家金融机构之间的信贷协议是双向 CSA,双方可以在其中为其场外交易提供保证金。在金融机构和公司(尤其是小公司)之间,信贷协议可能是单向 CSA,这意味着只有公司向金融机构提供保证金。根据主协议(ISDA/CSA 或任何定制的主协议),每个场外衍生品交易的具体条款和条件将采用称为条款清单或交易补充的简短形式。个人投资者,
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial derivatives代考|Securities Borrowing & Lending and Repo
回购协议是一种出售证券(例如股票或债券)的合同,卖方承诺在未来某个日期以指定价格从买方手中购回相同的证券。在交易期限内,证券的卖方(也称为贷方)交出证券的合法所有权。基于回购协议的活动有两种:证券借贷和回购。
证券借贷(小号乙大号)交易允许贷方在“公开”(即随时可赎回)或“期限”(固定期限)的基础上将证券借给借款人。交易终止后,证券将退还给贷方。借款人提供每日调整的抵押品,并向贷方支付费用。费率取决于基础证券的借贷供应/需求。合格抵押品可以是现金或双方协商确定的其他有价证券。现金抵押品水平通常是∼105%证券的最新收盘价。国际证券借贷协会制定了一个名为全球主证券借贷协议(GMSLA)的标准协议,大多数机构都遵循该协议。借款人的动机包括恢复空头头寸、衍生品对冲、公司行为套利等。
在销售和回购协议 (Repo) 中,一个交易对手(回购卖方)正在借款并为贷款提供抵押品(主要是固定收益资产)。参考图 1.1。由于贷款是有抵押的,因此卖方可以以低于通常在其他地方获得的融资成本获得资金。回购交易对手之间可以协商抵押品资格和折扣。回购的标准协议是国际资本市场协会(ICMA)发布的全球主回购协议(GMRA)。反向回购是回购交易的另一方看到的相反交易。一些中央银行使用回购/反向回购操作来调节金融体系中的货币供应。
如果抵押品由第三方持有,通常是托管银行或国际中央证券托管机构,则该交易称为三方回购或三方证券借贷。第三方将提供抵押物的估值、调整等服务。三方回购交易中的风险是交易对手违约概率与托管抵押品价值的相关性。
虽然大多数回购活动发生在场外交易市场,但存在证券交易所回购(例如上海证券交易所回购),交易所确定抵押品池和折扣率,标准化合约特征,例如规模和期限,并促进抵押品的清算和质押.
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。