计算机代写|Java代写|Java’s Lineage: C and C++
如果你也在 怎样代写Java这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
Java是一种广泛使用的计算机编程语言,拥有跨平台、面向对象、泛型编程的特性,广泛应用于企业级Web应用开发和移动应用开发。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写Java方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写Java代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写Java相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的Java及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
计算机代写|Java代写|Java’s Lineage: C and C++
The history of computer languages is not one of isolated events. Rather, it is a continuum in which each new language is influenced in one way or another by what has come before. In this regard, Java is no exception. Before moving on, it is useful to understand where Java fits into the family tree of computer languages.
The two languages that form Java’s closest ancestors are $\mathrm{C}$ and $\mathrm{C}++$. As you may know, $\mathrm{C}$ and $\mathrm{C}++$ are among the most important computer languages ever invented and are still in widespread use today. From C, Java inherits its syntax. Java’s object model is adapted from $\mathrm{C}++$. Java’s relationship to $\mathrm{C}$ and $\mathrm{C}++$ is important for a number of reasons. First, at the time of Java’s creation, many programmers were familiar with the $\mathrm{C} / \mathrm{C}++$ syntax. Because Java uses a similar syntax, it was relatively easy for a $\mathrm{C} / \mathrm{C}++$ programmer to learn Java. This made it possible for Java to be readily utilized by the pool of existing programmers, thus facilitating Java’s acceptance by the programming community.
Second, Java’s designers did not “reinvent the wheel.” Instead, they further refined an already highly successful programming paradigm. The modern age of programming began with $\mathrm{C}$. It moved to $\mathrm{C}++$ and then to Java. By inheriting and building on that rich heritage, Java provides a powerful, logically consistent programming environment that takes the best of the past and adds new features related to the online environment and advances in the art of programming. Perhaps most important, because of their similarities, C, C++, and Java define a common, conceptual framework for the professional programmer. Programmers do not face major rifts when switching from one language to another.
Java has another attribute in common with $\mathrm{C}$ and $\mathrm{C}++$ : it was designed, tested, and refined by real working programmers. It is a language grounded in the needs and experiences of the people who devised it. There is no better way to produce a top-flight professional programming language.
One last point: although $\mathrm{C}++$ and Java are related, especially in their support for objectoriented programming, Java is not simply the “Internet version of C++.” Java has significant practical and philosophical differences from $\mathrm{C}++$. Furthermore, Java is not an enhanced version of $\mathrm{C}++$. For example, it is neither upwardly nor downwardly compatible with $\mathrm{C}++$. Moreover, Java was not designed to replace $\mathrm{C}++$. Java was designed to solve a certain set of problems. $\mathrm{C}++$ was designed to solve a different set of problems. They will coexist for many years to come.
计算机代写|Java代写|How Java Impacted the Internet
The Internet helped catapult Java to the forefront of programming, and Java, in turn, had a profound effect on the Internet. First, the creation of Java simplified Internet programming in general, acting as a catalyst that drew legions of programmers to the Web. Second, Java innovated a new type of networked program called the applet that changed the way the online world thought about content. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, Java addressed some of the thorniest issues associated with the Internet: portability and security.
From the start, Java simplified web-based programming in a number of ways. Arguably the most important is found in its ability to create portable, cross-platform programs. Of nearly equal importance is Java’s support for networking. Its library of ready-to-use functionality enabled programmers to easily write programs that accessed or made use of the Internet. It also provided mechanisms that enabled programs to be readily delivered over the Internet. Although the details are beyond the scope of this book, it is sufficient to know that Java’s support for networking was a key factor in its rapid rise.
计算机代写|Java代写|Java Applets
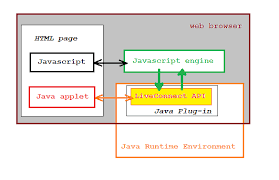
At the time of Java’s creation, one of its most exciting features was the applet. An applet is a special kind of Java program that is designed to be transmitted over the Internet and automatically executed inside a Java-compatible web browser. If the user clicks a link that contains an applet, the applet will download and run in the browser automatically. Applets were intended to be small programs, typically used to display data provided by the server, handle user input, or provide simple functions, such as a loan calculator. The key feature of applets is that they execute locally, rather than on the server. In essence, the applet allowed some functionality to be moved from the server to the client.
The creation of the applet was important because, at the time, it expanded the universe of objects that could move about freely in cyberspace. In general, there are two very broad categories of objects that are transmitted between the server and the client: passive information and dynamic active programs. For example, when you read your e-mail, you are viewing passive data. Even when you download a program, the program’s code is still only passive data until you execute it. By contrast, the applet is a dynamic, self-executing program. Such a program is an active agent on the client computer, yet it is delivered by the server.
In the early days of Java, applets were a crucial part of Java programming. They illustrated the power and benefits of Java, added an exciting dimension to web pages, and enabled programmers to explore the full extent of what was possible with Java. Although it is likely that there are still applets in use today, over time they became less important, and for reasons that will be explained shortly, JDK 9 began their phase-out process. Finally, applet support was removed by JDK $11 .$
Java代考
计算机代写|Java代写|Java’s Lineage: C and C++
计算机语言的历史并不是孤立事件之一。相反,它是一个连续统一体,其中每一种新语言都以一种或另一种方式受到以前的影响。在这方面,Java 也不例外。在继续之前,了解 Java 在计算机语言家族树中的位置很有用。
形成 Java 最接近祖先的两种语言是C和C++. 如你所知,C和C++是有史以来最重要的计算机语言之一,至今仍在广泛使用。Java 从 C 继承了它的语法。Java的对象模型改编自C++. Java 的关系C和C++很重要,原因有很多。首先,在 Java 创建的时候,很多程序员都熟悉C/C++句法。因为 Java 使用类似的语法,所以对于C/C++程序员学习Java。这使得 Java 可以很容易地被现有的程序员群体使用,从而促进 Java 被编程社区接受。
其次,Java 的设计者并没有“重新发明轮子”。相反,他们进一步完善了已经非常成功的编程范式。现代编程时代始于C. 它搬到了C++然后到Java。通过继承和构建这些丰富的传统,Java 提供了一个强大的、逻辑一致的编程环境,它吸收了过去的精华,并添加了与在线环境和编程艺术进步相关的新特性。也许最重要的是,由于它们的相似性,C、C++ 和 Java 为专业程序员定义了一个通用的概念框架。程序员在从一种语言切换到另一种语言时不会面临重大分歧。
Java 有另一个共同的属性C和C++:它是由真正的工作程序员设计、测试和改进的。它是一种基于设计它的人的需求和经验的语言。没有更好的方法来制作一流的专业编程语言。
最后一点:虽然C++和 Java 是相关的,特别是在它们对面向对象编程的支持方面,Java 并不是简单的“C++ 的互联网版本”。Java 在实践和哲学上与C++. 此外,Java 不是C++. 例如,它既不向上也不向下兼容C++. 此外,Java 并非旨在取代C++. Java 旨在解决某些问题。C++旨在解决一系列不同的问题。它们将在未来许多年共存。
计算机代写|Java代写|How Java Impacted the Internet
互联网帮助 Java 推到了编程的前沿,而 Java 反过来又对互联网产生了深远的影响。首先,Java 的创建总体上简化了 Internet 编程,起到了将大量程序员吸引到 Web 的催化剂的作用。其次,Java 创新了一种名为 applet 的新型网络程序,它改变了在线世界对内容的看法。最后,也许也是最重要的一点,Java 解决了与 Internet 相关的一些最棘手的问题:可移植性和安全性。
从一开始,Java 就以多种方式简化了基于 Web 的编程。可以说,最重要的是它能够创建可移植的跨平台程序。Java 对网络的支持几乎同样重要。它的即用型功能库使程序员能够轻松编写访问或使用 Internet 的程序。它还提供了使程序能够通过 Internet 轻松交付的机制。尽管细节超出了本书的范围,但只要知道 Java 对网络的支持是其迅速崛起的关键因素就足够了。
计算机代写|Java代写|Java Applets
在创建 Java 时,它最令人兴奋的特性之一是小程序。小程序是一种特殊的 Java 程序,旨在通过 Internet 传输并在与 Java 兼容的 Web 浏览器中自动执行。如果用户单击包含小程序的链接,小程序将自动下载并在浏览器中运行。Applet 旨在成为小程序,通常用于显示服务器提供的数据、处理用户输入或提供简单的功能,例如贷款计算器。小程序的关键特性是它们在本地执行,而不是在服务器上执行。本质上,applet 允许将一些功能从服务器转移到客户端。
小程序的创建很重要,因为在当时,它扩展了可以在网络空间中自由移动的对象的世界。一般来说,在服务器和客户端之间传输的对象有两大类:被动信息和动态主动程序。例如,当您阅读电子邮件时,您正在查看被动数据。即使你下载了一个程序,程序的代码在你执行之前仍然只是被动数据。相比之下,applet 是一个动态的、自动执行的程序。这样的程序是客户端计算机上的一个活动代理,但它是由服务器提供的。
在 Java 的早期,applet 是 Java 编程的关键部分。他们展示了 Java 的强大功能和优势,为网页添加了令人兴奋的维度,并使程序员能够探索 Java 的全部可能性。尽管今天很可能仍有小程序在使用,但随着时间的推移,它们变得不那么重要了,出于稍后将解释的原因,JDK 9 开始了它们的淘汰过程。最后,JDK 移除了对小程序的支持11.
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。