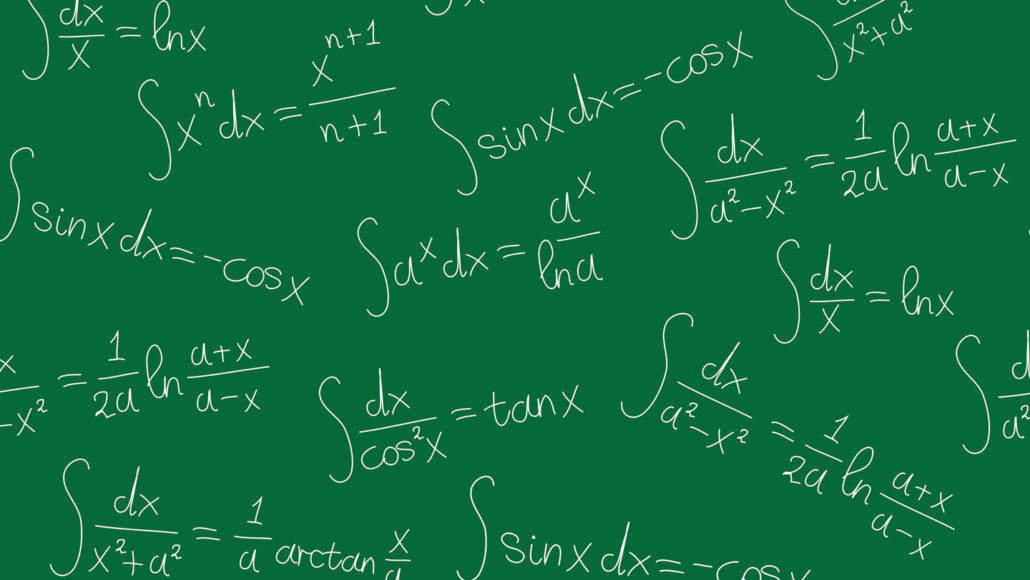微积分代写Calculus代考2023
如果你也在微积分Calculus这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时添加vx号联系我们的代写客服。我们会为你提供专业的服务。
statistics-lab™ 长期致力于留学生网课服务,涵盖各个网络学科课程:金融学Finance,经济学Economics,数学Mathematics,会计Accounting,文学Literature,艺术Arts等等。除了网课全程托管外,statistics-lab™ 也可接受单独网课任务。无论遇到了什么网课困难,都能帮你完美解决!
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写代考微积分Calculus方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质量且原创的统计Statistics和数学Math代写服务。我们的专家在代考微积分Calculus代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写微积分Calculus相关的作业也就用不着说。
微积分代写Calculus代考
微积分或微积分学是数学领域之一,是分析研究的基础部分。 微积分由两个支柱组成:微分和积分,前者捕捉局部变化,后者处理局部量的全局聚合,虽然很难确定该领域的范围,但一般包括与多元实值函数的微分和积分有关的事项(包括反函数定理和向量分析)。
微分是考虑函数在某一点的切线或切面的操作。 用其他数学术语来说,它基本上是通过线性近似来捕捉复变函数的思想。 因此,导数是一种线性映射。 然而,将多元函数的导数视为线性映射的想法直到 20 世纪才出现。 微分方程是这一思想的自然延伸。
相比之下,积分在几何上等同于求曲线或曲面与坐标轴之间区域的面积(体积)。 黎曼(Bernhard Riemann)将定积分(单变量)的值直接定义为矩形近似的极限,并证明了连续函数有积分。 根据他的定义,积分被称为黎曼积分。
导数和积分是完全不同的概念,但又密切相关,在单变量的情况下,它们与另一变量的逆运算具有相同的含义(微积分基本定理)。 导数是斜率,积分是面积。
微积分包含几个不同的主题,列举如下:
多元微积分Multivariable calculus代写代考
多变量微积分(也称为多元微积分)是一变量微积分到多变量函数微积分的扩展:涉及多个变量(多变量)的函数的微分和积分,而不仅仅是一个变量。
多元微积分可以被认为是高级微积分的基本部分。 对于高级微积分,请参阅欧几里得空间上的微积分。 三维空间中微积分的特殊情况通常称为向量微积分。
偏微分方程Partial Differential Equations代写代考
微分方程通常有很多解,常常添加边界条件来限制解集。 在常微分方程的情况下,每个解都有一系列由某些参数的值表征的解,但在偏微分方程的情况下,将参数视为取函数值更有用。 除非方程组是超定的,否则这通常是正确的。
偏微分方程作为描述与流体、引力场和电磁场等场相关的自然现象的模型出现在自然科学领域。 这些领域是在飞行模拟、计算机图形学或天气预报等处理中发挥重要作用的工具。 广义相对论和量子力学的基本方程也是偏微分方程。 它也是经济学尤其是金融工程中的一个重要概念。
其他相关科目课程代写:
- 常微分方程Ordinary Differential Equations
- 微分几何学Differential Geometry
微积分Calculus近代史
在欧洲,博纳文图拉-卡瓦列里在他的论文中讨论了将面积和体积确定为极精细区域的面积和体积之和的方法,从而奠定了微分学和积分学的基础。
他在微积分表述方面的工作促使卡瓦列里的微积分与大约同时在欧洲出现的有限差分法相结合。 约翰-沃利斯、艾萨克-巴罗和詹姆斯-格里高利进行了这一整合,巴罗和格里高利在 1675 年左右证明了微积分基本定理的第二定理。
艾萨克-牛顿以独特的符号引入了乘积微分定律、链式法则、高阶微分符号、泰勒级数和解析函数等概念,并用它们解决了数学物理中的问题。 在出版时,牛顿用等效的几何科目取代了微分,以适应当时的数学术语并避免受到指责。 牛顿在《自然哲学的数学原理》中用微分和积分的方法讨论了各种问题,包括天体的轨道、旋转流体表面的形状、地球的偏心率和重物在摆线上滑动的运动。 除此之外,牛顿还发展了函数的级数展开,显然他了解泰勒级数的原理。
戈特弗里德-莱布尼兹最初被怀疑剽窃牛顿未发表的论文,但现在被公认为是微积分发展的原始贡献者之一。
正是戈特弗里德-莱布尼茨将这些思想系统化,并将微积分确立为一门严谨的学科。 当时,他被指责剽窃牛顿,但今天,他已被公认为建立和发展微分学和积分学的最初贡献者之一。 莱布尼茨明确定义了微量的操作规则,使二阶和高阶导数的计算成为可能,并定义了莱布尼茨法则和链式法则。 与牛顿不同,莱布尼茨非常注重形式主义,他花了很多天来苦苦思索用什么符号来表示每个概念。
In Europe, Bonaventure Cavalieri laid the foundations of differential and integral calculus by discussing in his dissertation the method of determining the area and volume as the sum of the areas and volumes of very fine regions.
His work on the formulation of the calculus led to the combination of Cavalieri’s calculus with the finite difference method, which appeared in Europe at about the same time. This integration was carried out by John Wallis, Isaac Barrow, and James Gregory, with Barrow and Gregory proving the Second Theorem of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus around 1675.
Isaac Newton introduced the concepts of the law of product differentiation, the chain rule, higher-order differential notation, Taylor series, and analytic functions in a unique notation, and used them to solve problems in mathematical physics. At the time of publication, Newton replaced differentiation with equivalent geometric subjects to accommodate the mathematical terminology of the time and to avoid censure. In Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy, Newton used differential and integral methods to discuss a variety of problems, including the orbits of celestial bodies, the shapes of the surfaces of rotating fluids, the eccentricity of the earth, and the motion of a heavy object sliding on a pendulum. In addition to this, Newton developed the series expansion of functions, and it is clear that he understood the principles of Taylor’s series.
Gottfried Leibniz was initially suspected of plagiarizing Newton’s unpublished papers, but is now recognized as one of the original contributors to the development of calculus.
It was Gottfried Leibniz who systematized these ideas and established calculus as a rigorous discipline. At the time, he was accused of plagiarizing Newton, but today he is recognized as one of the original contributors to the establishment and development of differential and integral calculus. Leibniz explicitly defined the rules for the operation of differentials, made possible the computation of second- and higher-order derivatives, and defined Leibniz’s law and the chain rule. Unlike Newton, Leibniz was very much a formalist and spent many days agonizing over what symbols to use for each concept.

统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微积分Calculus的重难点
什么是极限和无穷小Limits and infinitesimals?
微积分通常是通过处理非常小的量而发展起来的。从历史上看,第一种方法就是无穷小。这些对象可以像实数一样处理,但在某种意义上是 “无限小 “的。例如,一个无穷小数可能大于 0,但小于序列 1,1 / 2,1 / 3, \ldots$中的任何数,因此小于任何正实数。从这个角度看,微积分就是处理无穷小数的一系列技术。符号 $d x$ 和 $d y$ 被认为是无穷小数,导数 $d y / d x$ 是它们的比值。${ }^{[37]}$
什么是差分微积分Differential calculus?
数学中的微积分(微分;微积分)是微分和积分微积分的一个分支,其研究重点是量的变化。 微积分与积分微积分是一个历史领域,将微积分分为两个分支。
微积分的主要研究方向是函数微分(微分商、微分系数)和相关概念,如无穷小及其应用。 函数在所选输入值中的微分商描述了函数在输入值附近的变化率。 求微分商的过程也称为微分。 从几何学角度看,图形上某一点的微分系数是函数图形切线在该点的斜率(如果存在并定义在该点上)。 对于单变量实值函数,函数在某一点的导数通常定义了函数在该点的最佳线性近似值。
什么是莱布尼兹符号Leibniz’s notation?
在微积分中,莱布尼兹符号是为了纪念17世纪德国哲学家和数学家戈特弗里德-威廉-莱布尼兹(Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz)而命名的,它使用符号$d x$和$d y$分别表示$x$和$y_1$的无限小(或无穷小)增量,正如$\Delta x$和$\Delta y$分别表示$x$和$y$的有限增量一样。
将 $y$ 视为变量 $x$ 的函数,即 $y=f(x)$。如果是这种情况,那么 $y$ 相对于 $x$ 的导数,也就是后来的极限
$$
\lim {Delta x \rightarrow 0} \frac{Delta y}{Delta x}=\lim {Delta x \rightarrow 0} \frac{f(x+\Delta x)-f(x)}{Delta x}、
$$
根据莱布尼茨的说法,是$y$的无穷小增量与$x$的无穷小增量之商,或
$$
\frac{d y}{d x}=f^{prime}(x)、
$$
其中右边是约瑟夫-路易-拉格朗日关于 $f$ 在 $x$ 处导数的符号。无穷小的增量称为微分。与此相关的是将无穷小增量相加的积分(例如,将长度、面积和体积作为微小部分的总和来计算),莱布尼茨也为此提供了一个涉及相同微分的密切相关的符号,这种符号的效率在欧洲大陆数学的发展中被证明是决定性的。
微积分Calculus的相关课后作业范例
这是一篇关于微积分Calculus的作业
Let $P=(0,1,0), Q=(2,1,3), R=(1,-1,2)$. Compute $\overrightarrow{P Q} \times \overrightarrow{P R}$ and find the equation of the plane through $P, Q$, and $R$, in the form $a x+b y+c z=d$.
$\overrightarrow{P Q}=\langle 2,0,3\rangle ; \overrightarrow{P R}=\langle 1,-2,2\rangle ; \overrightarrow{P Q} \times \overrightarrow{P R}=\left|\begin{array}{ccc}\hat{\imath} & \hat{\jmath} & k \ 2 & 0 & 3 \ 1 & -2 & 2\end{array}\right|=6 \hat{\imath}-\hat{\jmath}-4 \hat{\boldsymbol{k}}$
Equation of the plane: $6 x-y-4 z=d$. Plane passing through $P: 6 \cdot 0-1-4 \cdot 0=d$.
Equation of the plane: $6 x-y-4 z=-1$.
最后的总结:
通过对微积分Calculus各方面的介绍,想必您对这门课有了初步的认识。如果你仍然不确定或对这方面感到困难,你仍然可以依靠我们的代写和辅导服务。我们拥有各个领域、具有丰富经验的专家。他们将保证你的 essay、assignment或者作业都完全符合要求、100%原创、无抄袭、并一定能获得高分。需要如何学术帮助的话,随时联系我们的客服。