电气工程代写|通讯系统作业代写communication system代考|ELN234
如果你也在 怎样代写通讯系统communication system这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
通信系统是一个描述两点之间信息交流的系统。信息的传输和接收过程被称为通信。通信的主要要素是信息的发送者、通信的渠道或媒介以及信息的接收者。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写通讯系统communication system方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写通讯系统communication system方面经验极为丰富,各种代写通讯系统communication system相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的通讯系统communication system及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
电气工程代写|通讯系统作业代写communication system代考|Over-rotation during electro-optical sampling
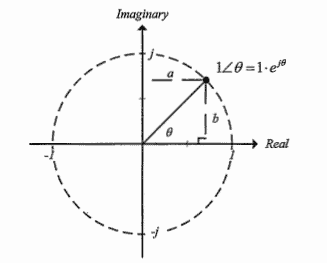
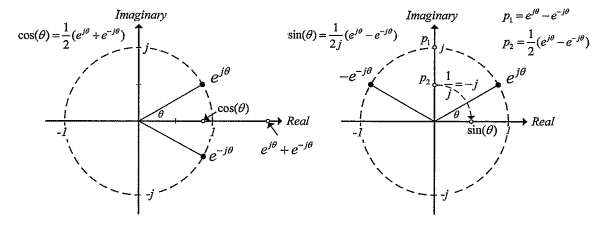
It is noted in Formula (7) that the modulation is bounded by $-1$ and 1 for phase differences of $-\pi / 2$ and $\pi / 2$, respectively. If the phase difference exceeds $\pi / 2$, the modulation decreases instead of increases since it has a sinusoidal behavior. This problem related to electro-optical detection is called over-rotation. Since a large phase difference is usually caused by a high electric field, EOS can only be used for detecting weak THz fields if over-rotation is to be avoided.
There are of course ways to work around the over-rotation problem and detect high THz fields. According to Formula (6), a smaller phase difference can be obtained by using a thinner detection crystal or having a lower electro-optical coefficient. In the first case, it should be known that a THz pulse incident on a crystal always generates reflections, which can also be detected. The thinner the crystal, the closer the reflection is temporally to the main pulse, and therefore, the more it is necessary to reduce the time window of the measurement in order to avoid measuring the reflection. However, a short time window also means a low frequency resolution, which is generally undesirable. In addition, a thinner crystal also means a shorter interaction length of the waves in the crystal, which results in a decrease in the Signalto-Noise Ratio (SNR). In the second case, it is actually possible to use a crystal with a lower electro-optical coefficient than $\mathrm{ZnTe}$, for example, gallium phosphide (GaP), and with which it is much more difficult to obtain over-rotation. On the other hand, the measured signal-to-noise ratio is then lower.
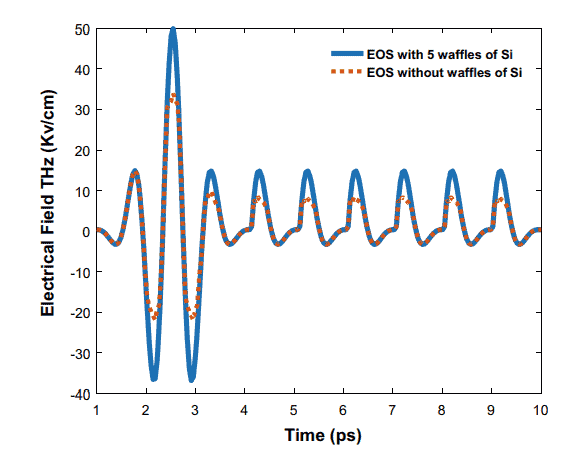
The most common solution to over-rotation is the addition of silicon waffles in the mounting just before the detection crystal (see Fig. 3). Part of the THz pulse (30\%) is reflected on each silicon waffle. The goal is to add enough silicon waffles so that the THz field reaching the crystal is both under the over-rotation limit and in the linear regime $(\sin (\Delta \varphi)=\Delta \varphi)$. However, adding several silicon waffles may cause some deformations in the detected THz field. In addition, a high THz field can induce nonlinear effects in silicon and the reflection on each waffle is then lower than $30 \%$. Also, multiple $\mathrm{THz}$ reflections on the silicon waffles are always at the tail of the main pulse in a measurement, which limits the time acquisition length and therefore the frequency resolution.
Of course, if silicon waffles are added to the assembly, this must be taken into account when calculating the THz field. By also adding the reflection losses on the detection crystal, we obtain:
$$
E_{\mathrm{THz}}=\frac{d M}{2 \pi n_0^3 L r_{41} \Gamma 0.7^N}
$$
where $\Gamma$ is the transmission coefficient through the detection crystal and $N$ is the number of waffles of Si. Each waffle transmits $70 \%$ of the THz wave.
电气工程代写|通讯系统作业代写communication system代考|THz Detection by Plasma in Air
There are two methods of plasma THz detection in air called THz-ABCD. The first is $\mathrm{THz}$ Air Breakdown Coherent Detection. The principle is very similar to $\mathrm{THz}$ generation by plasma in the air: A femtosecond laser is focused in the air, which generates a plasma whose charges are accelerated. If one sends a $\mathrm{THz}$ pulse to be detected on the plasma at the same time (or almost) as the laser pulse, there will be generation of the second harmonic of the laser beam. By detecting this second harmonic using a photomultiplier tube, the THz field can be deduced:
$$
I_{2 \omega} \propto\left|E_{2 \omega}\right|^2 \propto\left(W^{(3)} E_\omega E_\omega\right)^2 E_{\mathrm{THz}}^2
$$
where $I_{2 \omega}$ is the intensity of the second harmonic of the laser, $W^{(3)}$ is the 3rd order nonlinear coefficient of the plasma, $E_\omega$ is the laser electric field, $E_{2 \omega}$ is the electric field of the second harmonic of the laser, and $E_{\mathrm{THz}}$ is the electric field THz.
Unfortunately, since we only measure the intensity of the second harmonic, we cannot measure the electric field coherently. To achieve consistent detection, a very intense laser intensity must be used. At high pump intensity, the white light generated by the plasma contains a non-negligible second harmonic component that must be considered in the calculation [31]:
$$
I_{2 \omega} \propto\left|E_{2 \omega}\right|^2 \propto\left(W^{(3)} E_\omega E_\omega\right)^2 E_{\mathrm{THz}}^2+2\left(W^{(3)} E_\omega E_\omega\right) E_{\mathrm{THz}} E_{\mathrm{SH}}^{2 \omega}+\left(E_{\mathrm{SH}}^{2 \omega}\right)^2
$$
where $E_{\mathrm{SH}}^{2 \omega}$ is the electric field of the second harmonic from the plasma.
If the field of the second harmonic coming from the plasma is high enough, the first term of Formula (11) becomes negligible and the intensity detected by the photomultiplier tube is then proportional to the electric field $\mathrm{THz}$, making the detection method consistent. Of course, a drawback is that it is not possible to detect a $\mathrm{THz}$ field that is too large (or it is necessary to compensate with the intensity of the pump laser) since the first term of Formula (11) would then no longer be negligible. The second THz method is THz Air Bias Coherent Detection (THz-ABCD). This method requires a lower laser intensity, but an $\mathrm{AC}$ electric field must be applied close to the focal point.
通讯系统代考
电气工程代写|通讯系统作业代写communication system代考|Over-rotation during electro-optical sampling
在公式 (7) 中注意到,调制的边界为 $-1$ 和 1 的相位差 $-\pi / 2$ 和 $\pi / 2$ ,分别。如果相位差超过 $\pi / 2$ ,调制减少而不 是增加,因为它具有正弦行为。这个与电光检则有关的问题称为过旋转。由于大的相位差通常是由高电场引起的, 为了避免过旋转, $E O S$ 只能用于检测弱太赫兹场。
当然,有一些方法可以解决过度旋转问题并检测高 THz 场。根据公式(6),可以通过使用更薄的检测晶体或具有更 低的电光系数来获得更小的相位差。在第一种情况下,应该知道入射到晶体上的太赫兹脉冲总是会产生反射,这也 是可以检测到的。晶体越薄,反射在时间上越接近主脉冲,因此越需要减小测量的时间窗口以避免测量反射。然 而,短时间窗口也意味着低频率分辨率,这通常是不希望的。此外,更薄的晶体还意味着晶体中波的相互作用长度 更短,这会导致信橾比 (SNR) 降低。 $\mathrm{ZnTe}$ ,例如,磷化镓 (GaP),用它来获得过度旋转要困难得多。另一方面, 测得的信噪比则较低。
最常见的过度旋转解决方案是在检测晶体之前的安装中添加硅华夫饼 (见图 3)。太赫兹脉冲的一部分 (30\%) 反映 在每个硅华夫饼上。目标是添加足够的硅华夫饼,以使到达晶体的太赫兹场既低于过旋转限制又处于线性状态 $(\sin (\Delta \varphi)=\Delta \varphi)$. 然而,添加几个硅华夫饼可能会导致检测到的太赫兹场发生一些变形。此外,高太赫兹场可 以在硅中引起非线性效应,每个华夫饼上的反射低于 $30 \%$. 还有,多 $\mathrm{THz}$ 在测量中,硅华夫饼上的反射始终位于主 脉冲的尾部,这限制了时间采集长度,从而限制了频率分辨率。
当然,如果将硅华夫饼添加到组件中,则在计算太赫兹场时必须考虑到这一点。通过增加检测晶体上的反射损耗, 我们得到:
$$
E_{\mathrm{THz}}=\frac{d M}{2 \pi n_0^3 L r_{41} \Gamma 0.7^N}
$$
在哪里 $\Gamma$ 是通过检测晶体的透射系数和 $N$ 是 Si 的华夫饼数量。每个华夫饼传输 $70 \%$ 太赫兹波。
电气工程代写|通讯系统作业代写communication system代考|THz Detection by Plasma in Air
空气中的等离子太赫兹检测方法有两种,称为太赫兹-ABCD。第一个是 $T H z$ 空气击穿相干检测。原理非常相似 $\mathrm{THz}$ 通过空气中的等离子体产生:飞秒激光聚焦在空气中,产生等离子体,其电荷被加速。如果有人发送 $\mathrm{THz}$ 在 等离子体上与激光脉冲同时 (或几乎) 检测到的脉冲,将产生激光束的二次堦波。通过使用光电倍增管检测该二次 谐波,可以推断出太赫兹场:
$$
I_{2 \omega} \propto\left|E_{2 \omega}\right|^2 \propto\left(W^{(3)} E_\omega E_\omega\right)^2 E_{\mathrm{THz}}^2
$$
在哪里 $I_{2 \omega}$ 是激光的二次谐波的强度, $W^{(3)}$ 是等离子体的三阶非线性系数, $E_\omega$ 是激光电场, $E_{2 \omega}$ 是激光的二次谐 波的电场,并且 $E_{\mathrm{THz}}$ 是电场太赫兹。
不幸的是,由于我们只测量二次谐波的强度,我们无法连贯地测量电场。为了实现一致的检测,必须使用非常强的 激光强度。在高氷浦强度下,等离子体产生的白光包含不可忽略的二次谐波分量,在计算中必须考虑 [31]:
$$
I_{2 \omega} \propto\left|E_{2 \omega}\right|^2 \propto\left(W^{(3)} E_\omega E_\omega\right)^2 E_{\mathrm{THz}}^2+2\left(W^{(3)} E_\omega E_\omega\right) E_{\mathrm{THz}} E_{\mathrm{SH}}^{2 \omega}+\left(E_{\mathrm{SH}}^{2 \omega}\right)^2
$$
在哪里 $E_{\mathrm{SH}}^{2 \omega}$ 是来自等离子体的二次谐波的电场。
如果来自等离子体的二次谐波的场足够高,则公式 (11) 的第一项可以忽略不计,光电倍增管检测到的强度与电场 成正比 $\mathrm{THz}$ ,使检测方法一致。当然,缺点是无法检测到 $\mathrm{THz}$ 由于公式 (11) 的第一项将不再可忽略,因此太大的 场 (或必须用百浦激光器的强度进行补偿) 。第二种太赫兹方法是太赫兹空气偏置相干检测 (THz-ABCD) 。这种 方法需要较低的激光强度,但 $\mathrm{AC}$ 电场必须靠近焦点施加。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。