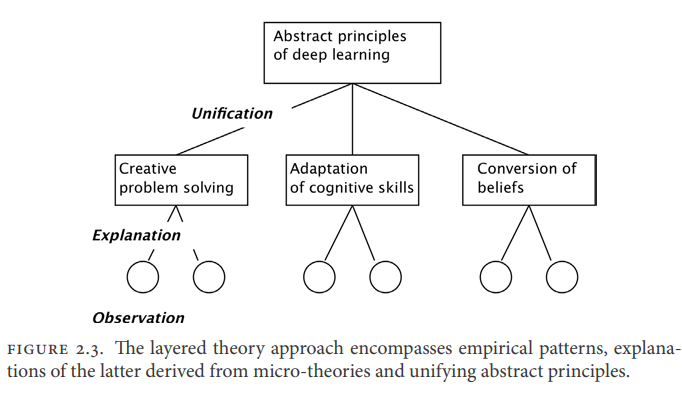
计算机代写|深度学习代写deep learning代考|T81-558
如果你也在 怎样代写深度学习Deep Learning 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。深度学习Deep Learning(是机器学习的一种,也是人工智能的一种方法。通过用简单的世界来构建复杂的世界表示,深度学习技术在计算机视觉、语音识别、自然语言处理、临床应用和其他领域取得了最先进的成果——有望(也有可能)改变社会。
深度学习Deep Learning架构,如深度神经网络、深度信念网络、深度强化学习、递归神经网络、卷积神经网络和变形金刚,已被应用于包括计算机视觉、语音识别、自然语言处理、机器翻译、生物信息学、药物设计、医学图像分析、气候科学、材料检测和棋盘游戏程序等领域,它们产生的结果与人类专家的表现相当,在某些情况下甚至超过了人类专家。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写深度学习deep learning方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写深度学习deep learning代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写深度学习deep learning相关的作业也就用不着说。
计算机代写|深度学习代写deep learning代考|Knowledge Retrieval
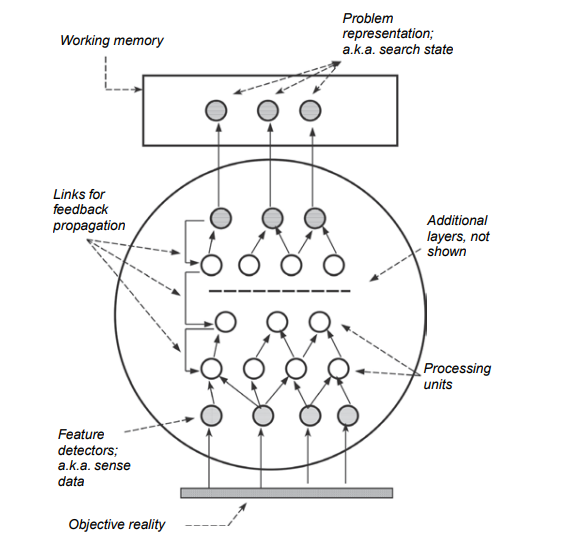
A person’s knowledge store is vast. ${ }^{26}$ At any one moment, only a small number of all the knowledge elements in long-term memory are active. When a person is faced with a problem, particularly an unfamiliar one, every piece of his prior knowledge is potentially relevant. To be applied to the situation at hand, a knowledge element has to be retrieved through spread of activation. ${ }^{27}$ To visualize this process, it is useful to conceptualize long-term memory as a network in which knowledge elements are nodes and the relations between them are links. Each node is associated with a level of activation that fluctuates over time. At each moment in time, a small subset of the nodes have activation levels above a threshold. Those elements are immediately available for processing; they form the current content of working memory. Activation is passed along the links from elements that are currently above threshold to other, related but not yet active nodes. If a knowledge element receives enough activation to rise above threshold, it “comes to mind” as we say. “Retrieval” is a label for the event that occurs when the activation of a knowledge element rises above threshold. As activation spreads from a source node $N$, it is passed along its outbound links. A certain amount of activation is lost in each step of the spreading process, so the amount that is spread from a given source node $N$ decreases gradually with increased distance from $N$. There are several variants of this theory that differ in the quantitative details of the spreading process, but those details need not concern us here.
Memory retrieval is selective. A person can keep only a small amount of information in an active state at any one time – working memory has a limited capacity – but the knowledge store is vast, so the retrieval process necessarily makes choices, however implicit and unconscious, about what to retrieve. Retrieving an element $X$ constrains which other elements can also be retrieved at the same time. In a problem situation, activation initially spreads from the problem representation and the goal. The initial encounter with the problem thus determines the knowledge elements that are initially marshaled to solve it, and those elements in turn become sources from which activation spreads. Retrieval is a cyclic, iterative search through memory for those knowledge elements that are most likely to be relevant for the problem at hand.
计算机代写|深度学习代写deep learning代考|Anticipation
When we perceive an object, we register certain actions that we can perform vis-à-vis that object and certain functions that the object can perform for us. Seeing a chair, the thought of sitting down is not far away; seeing a soccer ball on a lawn, the thought of kicking it not only comes to mind but is hard to resist. Children need no instruction to figure out that pebbles on a beach can be thrown into the sea. In general, the mere perception of an object is sufficient to activate certain actions and dispositions vis-à-vis that object. The opportunities for action associated with an object are called the affordances of that object. ${ }^{30}$ We can think about overt actions without performing them, so we must possess mental representations of them.
Goals likewise suggest to us actions that accomplish them. The need to fasten two things to each other prompts us to think about gluing, nailing, taping and tying. The need to reach something on a high shelf makes us look for a box that is sturdy enough to stand on, a chair, footstool, ladder or some other means of increasing our height. Failing to find one, we might look for a broom handle or some other way to increase our reach. In short, both the current state of affairs and the goal can serve as memory probes that retrieve actions more precisely, to retrieve mental representations of actions.
In their 1972 treatise on analytical thinking, Human Problem Solving, Herbert A. Simon and Allen Newell emphasized that thinking is anticipatory. ${ }^{31}$ The representation of a familiar action contains knowledge that enables a person to execute it but also to anticipate its effects. To think about a problem is to imagine the outcomes of the possible actions before they are carried out: If I do this or that, the result, the new state of affairs, will be such-and-such. This mental look-ahead process allows us to evaluate the promise and usefulness of actions ahead of time. For example, in playing a board game like chess, a player will imagine making a move, anticipate how the relations on the board would change if he were to make that move, and use that anticipated outcome to evaluate the move before deciding what to do. Another commonplace example is to think through the effects of moving the sofa in one’s living room to the other side of the room before taking the trouble of moving it physically (if we put the sofa there, there is no place for the end table). Look-ahead is quicker, requires less effort, allows us to explore mutually exclusive options (buy house $X$ vs. buy house $Y$ ) and saves us, when consequences are costly, from having to pay the price of our poor judgment. To think analytically is, in part, to carry out actions in the mind before we carry them out in the flesh.
深度学习代写
计算机代写|深度学习代写deep learning代考|Knowledge Retrieval
一个人的知识储备是巨大的。${}^{26}$在任何时刻,长时记忆中只有一小部分的知识元素是活跃的。当一个人面对一个问题,特别是一个不熟悉的问题时,他之前的每一个知识都可能是相关的。要将知识元素应用于手头的情况,必须通过激活的扩展来检索知识元素。${}^{27}$为了可视化这个过程,将长期记忆概念化为一个网络是有用的,在这个网络中,知识元素是节点,它们之间的关系是链接。每个节点都与一个随时间波动的激活水平相关联。在每个时刻,都有一小部分节点的激活水平高于阈值。这些元素可以立即进行处理;它们构成了工作记忆的当前内容。激活沿着链接从当前高于阈值的元素传递到其他相关但尚未活动的节点。如果一个知识元素得到了足够的激活,超过了阈值,它就像我们说的那样“浮现在脑海中”。“检索”是当知识元素的激活超过阈值时发生的事件的标签。当激活从源节点$N$传播时,它将沿着其出站链接传递。在扩散过程的每一步中都会损失一定的激活量,因此从给定源节点$N$传播的激活量随着距离$N$的增加而逐渐减少。这个理论有几种变体,它们在传播过程的定量细节上有所不同,但这些细节我们在这里不需要关心。
记忆检索是选择性的。一个人在任何时候都只能在活动状态下保留少量的信息——工作记忆的容量有限——但知识存储是巨大的,因此检索过程必然会做出选择,无论多么隐式和无意识地选择要检索的内容。检索元素$X$限制了可以同时检索的其他元素。在问题情境中,激活最初是从问题表示和目标传播的。因此,最初遇到的问题决定了最初为解决问题而编组的知识元素,而这些元素反过来又成为激活传播的来源。检索是在内存中循环、迭代地搜索那些最有可能与当前问题相关的知识元素。
计算机代写|深度学习代写deep learning代考|Anticipation
当我们感知一个物体时,我们会记录我们可以对-à-vis这个物体执行的某些动作以及这个物体可以为我们执行的某些功能。看到一把椅子,想坐下来的念头就在不远处;看到草坪上的足球,踢它的想法不仅出现在脑海中,而且难以抗拒。孩子们不需要任何指导就能明白沙滩上的鹅卵石可以扔进海里。一般来说,仅仅对一个物体的感知就足以激活对-à-vis该物体的某些行为和倾向。与一个对象相关的行动机会称为该对象的能力。${}^{30}$我们可以思考公开的行为而不去执行它们,所以我们必须拥有它们的心理表征。
同样,目标也向我们提出了实现目标的行动。需要把两件东西绑在一起,这促使我们考虑用胶水、钉子、胶带和打结。为了够到高架子上的东西,我们会寻找一个足够坚固的盒子,椅子,脚凳,梯子或其他增加我们高度的方法。如果找不到,我们可能会寻找扫帚柄或其他方法来扩大我们的范围。简而言之,当前状态和目标都可以作为记忆探针,更精确地检索行为,检索行为的心理表征。
在他们1972年关于分析思维的论文《人类问题解决》中,赫伯特·a·西蒙和艾伦·纽维尔强调,思维是预期的。${}^{31}$熟悉动作的表示包含使人能够执行该动作并预测其效果的知识。思考一个问题就是在可能的行动实施之前想象它们的结果:如果我做这个或那个,结果,即新的事态,将是这样那样的。这种心理上的前瞻性过程使我们能够提前评估行动的前景和有用性。例如,在玩象棋之类的棋盘游戏时,玩家会想象要走一步棋,预测如果他要走这一步棋,棋盘上的关系会发生什么变化,并在决定怎么做之前使用预期结果来评估这一步棋。另一个常见的例子是,在麻烦地把客厅里的沙发搬到房间的另一边之前,仔细考虑一下把沙发搬到房间的另一边会产生什么影响(如果我们把沙发放在那里,就没有地方放茶几了)。前瞻性更快,需要更少的努力,允许我们探索相互排斥的选择(买房子X美元或买房子Y美元),并在后果昂贵时拯救我们,使我们不必为我们的错误判断付出代价。在某种程度上,分析性思考就是在我们肉体行动之前先在头脑中行动。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。