会计代写|初级管理会计代写Principles of Management Accounting代考|ACCT7104
如果你也在 怎样代写初级管理会计Principles of Management Accounting这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
管理会计是识别、衡量、分析、解释和向管理人员传达财务信息以实现组织目标的实践。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写初级管理会计Principles of Management Accounting方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写初级管理会计Principles of Management Accounting代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写初级管理会计Principles of Management Accounting相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的初级管理会计Principles of Management Accounting及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
会计代写|初级管理会计代写Principles of Management Accounting代考|management accounting’s most important challenge
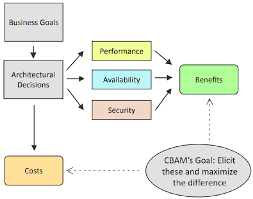
Over time, the emphasis placed on the themes in Exhibit $1.4$ will change and new themes will emerge. This is because any change requires reaction and more action. In many sectors of the economy, the use of new technologies in the recent past has made possible the shift from selling mass-market, generic products and services to operating in more profitable niches with specialpurpose products sold in very small volumes. Such changes mean that management accountants have to ensure that they remain useful to the organisations they serve and that they alter their management practices where required (Bhimani 2020). The global economic crisis, which began in 2008, altered the role of finance specialists in the eyes of governmental regulators and financial markets. Calls for more accountability and transparency were made and enterprises had to respond positively to these demands. Today, demands are expressed that enterprises should move towards models of functioning that are more sustainable and which show evidence of higher standards of corporate responsibility. Compliance requirements naturally need to be balanced with the need for high organisational performance and maintaining global competitiveness and so organisations have to balance the various demands placed on them. Changes in markets, societal structures and norms and in the general business environment in which firms operate have always been of concern to practicing management accountants. Ongoing global and business environment changes will continue to impact management accounting practices.
In fact, the pace of change is ultra-rapid and goes unabated today. A principal concern to all accountancy organisations globally right now is that professional relevance is upheld. Consider for instance, the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC), which has established a Professional Accountants in Business Committee (PAIB) with responsibility to provide guidance on management accounting issues to IFAC member bodies (which represent more than one million professional accountants worldwide working in commerce, industry, the public sector, education and the not-for-profit sector (see www.ifac.org)). In a PAIB report entitled ‘Developing a future ready profession’ (May 2017), the Chair, Charles Tilley, noted that ‘If the accountancy profession and professional accountants in business do not embrace change, other current or emerging professions will take our coveted place at the heart of business… The character traits, attributes, and skills that accountants in business will need to be equipped with for the future represent a significant departure from the accountant stereotype.’ The most significant challenge facing accountants today is to address the impast of digitalisation. For many snterprises, digitalisation is the process by which they become digital businesses, where the use of digital technologies changes the business model and provides new revenue and value-producing possibilities. Digitalisation is about enterprises not just having to become digitised but being digital. As noted, broad technological change has always concerned management accounting, because: ‘Technology is the principal driver that enables the finance function to be a more effective business partner working with the business by helping provide security, control, and quality decisions focused on value creation and preservation’ (Tilley 2017).
会计代写|初级管理会计代写Principles of Management Accounting代考|Ethical guidelines
Professional accounting organisations representing management accountants exist in many countries. For example, CIMA in the UK provides a programme leading to membership of the institute. Membership signals that the holder has passed the admission criteria and demonstrated the competence of technical knowledge required by the CIMA to become a chartered management accountant. To become a CIMA member, students complete examinations on operational, management and strategic aspects of the field and must show professional competence in management accounting (see www.cimaglobal.com for more information).
Management accounting topics are also covered by several other professional bodies. The syllabus for the examinations of the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) includes a variety of examinations, practical work experience and knowledge of ethics requirements (see www.accaglobal.com). Other accounting bodies include the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales (ICAEW) (see www.icaew.co.uk) and the Institute for Chartered Accountants of Scotland (ICAS) (see www.icas.org.uk). These institutes have requirements that cover proficiency in general management topics as well as professional accounting and ethics topics.
Professional accounting organisations play an important role in promoting a high standard of ethics. CIMA has issued a code of ethics for its members. Exhibit $1.6$ presents a summary of CIMA’s ‘fundamental principles’.
管理会计代考
会计代写|初级管理会计代写管理会计的原则代考|管理会计的最重要的挑战
随着时间的推移,对展品$1.4$中主题的强调将会改变,新的主题将会出现。这是因为任何改变都需要反应和更多的行动。在许多经济部门,近年来新技术的使用使得从销售大众市场的通用产品和服务转变为在利润更高的利基市场经营,以非常小的销量销售特殊用途的产品。这些变化意味着管理会计师必须确保他们对所服务的组织仍然有用,并在需要时改变其管理实践(Bhimani 2020)。始于2008年的全球经济危机改变了金融专家在政府监管机构和金融市场眼中的角色。有人呼吁提高问责制和透明度,企业必须积极响应这些要求。今天,有人提出要求,要求企业应转向更可持续的运作模式,并显示出有证据表明企业责任的更高标准。合规要求自然需要与高组织绩效和保持全球竞争力的需要相平衡,因此组织必须平衡施加在它们身上的各种要求。市场、社会结构和规范的变化以及公司所处的一般商业环境的变化一直是执业管理会计师所关注的问题。持续的全球和商业环境变化将继续影响管理会计实践
事实上,这种变化的速度是超快的,而且时至今日仍有增无减。目前全球所有会计组织关注的一个主要问题是保持专业相关性。例如,国际会计师联合会(IFAC)设立了一个商业专业会计师委员会(PAIB),负责向IFAC成员机构(代表全球商业、工业、公共部门、教育和非营利部门的100多万专业会计师)提供管理会计问题的指导(见www.ifac.org)。在PAIB题为“发展一个为未来做好准备的职业”(2017年5月)的报告中,主席Charles Tilley指出,“如果会计专业和商业专业会计师不接受变化,其他当前或新兴的职业将取代我们在商业中心的渴望的位置……未来商业会计需要具备的性格特征、属性和技能代表着与会计固有形象的显著背离。”当今会计师面临的最重大挑战是解决数字化的难题。对于许多企业来说,数字化是他们成为数字企业的过程,数字技术的使用改变了商业模式,提供了新的收入和价值创造的可能性。数字化意味着企业不仅要数字化,还要数字化。如前所述,广泛的技术变革一直与管理会计有关,因为:“技术是主要的驱动因素,使财务职能部门通过帮助提供安全、控制和专注于价值创造和保存的质量决策,成为与业务合作的更有效的业务伙伴”(Tilley 2017)。
会计代写|初级管理会计代写管理会计原则代考|道德准则
.
代表管理会计师的专业会计组织在许多国家都存在。例如,英国的CIMA提供了一个可以成为该协会会员的课程。会员资格标志着持卡人已通过CIMA的准入标准,并展示了成为特许管理会计师所需的技术知识能力。要成为CIMA会员,学生必须完成该领域的运营、管理和战略方面的考试,并必须在管理会计方面显示专业能力(更多信息见www.cimaglobal.com)
管理会计主题也包括其他几个专业团体。特许注册会计师公会(ACCA)的考试大纲包括各种考试、实际工作经验和道德要求的知识(见www.accaglobal.com)。其他会计机构包括英格兰和威尔士特许会计师协会(ICAEW)(见www.icaew.co.uk)和苏格兰特许会计师协会(ICAS)(见www.icas.org.uk)。这些学院的要求包括精通一般管理主题以及专业会计和伦理主题
专业会计组织在促进高标准的道德规范方面发挥着重要作用。CIMA为其成员发布了一份道德规范。展品$1.6$展示了CIMA的“基本原则”的摘要
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。