如果你也在 怎样代写计算复杂度理论Computational complexity theory这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
计算复杂度理论的重点是根据资源使用情况对计算问题进行分类,并将这些类别相互联系起来。计算问题是一项由计算机解决的任务。一个计算问题是可以通过机械地应用数学步骤来解决的,比如一个算法。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写计算复杂度理论Computational complexity theory方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写计算复杂度理论Computational complexity theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写计算复杂度理论Computational complexity theory相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的计算复杂度理论Computational complexity theory及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
数学代写|计算复杂度理论代写Computational complexity theory代考|General Background
Evolutionary Game Theory (hereinafter EGT) represents the attempt to study the dynamics of a population, combining the principles of Game Theory with those of the Darwinian theory of evolution. At the first glance, these two fields have very few things in common. In very few words, Game Theory can be referred as an approach/framework aimed at finding the optimal strategy in a “competition,” as well as the way for finding a kind of equilibrium among the competitors. Instead, the Darwinian Theory deals with the evolution of life, considering both its competitive aspect and the idea of “transmission and optimization of information.” However, as later discussed, a closer look to these theories shows different points of connection. It is worth to remind that the early developments of the Game Theory, resulting from the works of John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern, were mainly focused on the modeling of the human behavior, with a clear reference to economic contexts. Later on, this area of Mathematics was strongly influenced by the Nobel laureate John Nash who introduced, among his relevant contributions to science, the so-called Nash equilibrium. The latter can be viewed as a particular state of a game, involving a number of “rational” agents that have to take an action without prior communications. On the other hand, the Darwinian theory of evolution, that constitutes one of the most important breakthroughs in Biology and more in general in science, after more than a century still constitutes a living theory, although yet debated in particular outside academia. His father, Charles Darwin, proposed it after a challenging journey around the world, which gave the opportunity to perform direct observations on a wild and unexplored Nature. So, after this experience, the young scientist envisioned a general theory for explaining natural evolution of life. As result, this fascinating combination of Game Theory and Darwinian Theory constitutes a powerful framework for modeling several scenarios, spanning from social systems to biological phenomena, and representing specific mechanisms (e.g., reproduction, imitation), interaction patterns, and behaviors. Therefore, a number of “complex phenomena” can be characterized by EGT models. Then, in full agreement with the conclusions reported in the famous Anderson’s work “More is different,” this modern and interdisciplinary area can be actually classified as one of the components of the field of complexity. For instance, emergent behaviors that can be referred as a kind of phase transition can be observed studying an agent population whose local interactions are simple, e.g., based on a game like the Prisoner’s Dilemma. Notably, from a state of disorder one can observe an evolution toward an ordered equilibrium, and the latter can be even opposite to the expected one (i.e., the Nash equilibrium). The last observation deserves particular attention, since one may experience some confusion. Notably, while the mathematical framework of Game Theory has very solid roots and deep basis, direct observations on the real world suggest that the Nash equilibrium is not always respected. For example, cooperation is a common phenomenon and takes different forms also in Nature, like mutualism. Here, one of the goals of EGT is to find out the motivations, and the mechanisms, that can lead to the phenomena we observe and that cannot be predicted using only the Game Theory. At the same time, also the Darwinian Theory takes profit by its combination with Game Theory. For instance, the altruistic behaviors detected among animals cannot be explained referring only to the Darwin’s Theory. So, in this case as well as in others, the contribution of the Game Theory allows to cover this important lack. A fundamental key point of EGT is given by the adaptive behavior introduced in the dynamics of a population. Notably, this behavior is driven by a “rational mindset,” obtained by implementing agents that take actions for optimizing their own gain. The latter, usually defined as “payoff”, in EGT is equivalent to the concept of “fitness.” This correspondence (i.e., payoff-fitness) is quite important since it represents one of the most relevant connections between the Game Theory and the Darwinian Theory, where the best individual is not the strongest but the fittest one or, in general, that who better adapts herself/himself to new environments. Thus, the equivalence payoff-fitness has a deep meaning that allows to use the “rationality” of Game Theory and the “evolutionary mechanisms” of the Darwinian Theory. In particular, as discussed later with more detail, “rationality” and “evolutionary mechanisms” are implemented in the process defined “strategy revision phase.” The latter allows agents to revise their strategy, e.g., imitating their neighbors, and to support the replication of successful strategies. Accordingly, this process is fundamental for the actual evolution of a population and allows to introduce different mechanisms that can influence the way the system moves toward an equilibrium. Finally, even if EGT models can be based on different kinds of games, in this book we refer to the twostrategy games, i.e., games characterized by only two strategies. Even if this choice can be perceived as too limiting for modeling real scenarios, in our view it offers two main advantages. First, it allows to introduce in a very easy way the field of EGT; second, it facilitates the connection with models well-known in Statistical Physics. We can now go on with the next sections of this chapter, reporting some important concepts useful for proceeding through the presentation of more interesting models (i.e., Chap. 3).
数学代写|计算复杂度理论代写Computational complexity theory代考|Nash Equilibrium
Developed by John Forbes Nash Jr., the Nash equilibrium constitutes a milestone in Game Theory. For the sake of simplicity, let us consider two agents playing a generic game that are not allowed to communicate before to take an action (i.e., a move). Here, the Nash equilibrium represents the particular situation where neither of them has something to gain from being the only one to change strategy. The lack of opportunities in doing prior agreements, i.e., preliminary communications, has deep consequences. First of all, if both agents want to increase their gain, some form of “blind coordination” is required, which in turn entails that reaching the maximum gain might need to take a very risky strategy. In the next section, introducing real games like the Prisoner’s Dilemma, the “risky” side of some strategies will become more clear. Beyond its general description, the Nash equilibrium has obviously a formal mathematical definition. Let us consider a game described by a set $S$ of strategy profiles and a payoff function $f$, i.e., $(S, f)$. This game might involve $n$ players, so that each one adopts a strategy. Here, a strategy profile $S$ is defined as $S=S_{1} \times S_{2} \times \ldots \times S_{n}$, and the payoff function computes that gain for a specific $x \in S$ as $f(x)=\left(f_{1}(x), f_{2}(x), \ldots, f_{n}(x)\right)$. Then, a set of strategies $x^{} \in S$ is a Nash equilibrium if $\forall_{i}, x_{i} \in S_{i}: f_{i}\left(x_{i}^{}, x_{-i}^{}\right) \geq f_{i}\left(x_{i}, x_{-i}^{}\right)$. Summarizing, reaching the Nash equilibrium can be viewed as a tradeoff, which ensures the potentiality of a good payoff while reducing possible risks. For this reason, if we consider a population whose agents interact according to a dilemma game, the expected equilibrium should correspond to the Nash equilibrium, i.e., all agents take the most convenient strategy, following a selfish behavior. However, in doing so, our population, as a whole, risks to be unable to produce a common wellness. The latter, in this context, has a very general meaning, as for instance might refer to people paying taxes for receiving public services or to people who vaccinate themselves for avoiding viral spreading, and so on. Now, beyond the need to identify strategies for the common wellness, a challenging point in EGT is the understanding of the mechanisms that lead toward non-expected equilibria, in particular because, often, the real world shows the emergence of equilibria different from the Nash equilibrium.
数学代写|计算复杂度理论代写Computational complexity theory代考|The Prisoner’s Dilemma
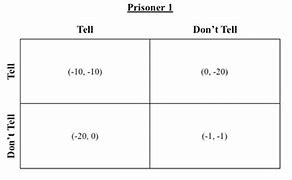
The Prisoner’s Dilemma (PD hereinafter) is one of the most famous games who shows why rational approaches might lead people to avoid cooperation. Its general dynamics can be told using different stories; however, here, we report the classical one who gave the name to this game, i.e., the story of two criminals captured by police, and undergone to a questioning. Notably, after being captured, our criminals are separated to avoid potential agreements. In addition, in order to ensure at least one guilty, they are offered a bargain: each criminal has two options, i.e., betray (i.e., to defect) or remaining silent (i.e., to cooperate). Thus, despite what that the common sense might suggest, in this case being a cooperator indicates to collaborate with the “partner,” not with the police. So, if the two criminals cooperate, they are sentenced to 1 year in prison, while if both betray the conviction is 2 years in prison. Instead, in the third case, i.e., one betrays and the other remains silent, the cooperator is sentenced to 5 years in prison, whereas the defector is set free. Recalling that they cannot communicate before to take an action (i.e., remaining silent or betray), it appears quite clear the motivation that leads our criminals to defect. The Nash equilibrium of this game is “defection,” entailing criminals will spend 2 years in prison. At the same time, if both cooperate they can save 1 year, so that the highest “common” benefit can be achieved only by a coordinate action of cooperation, although very risky. Anyway, beyond this story or similar ones, the PD can be characterized by the following payoff matrix:
$$
\begin{array}{cc}
C & D \
C & \left(\begin{array}{cc}
1 & S \
T & 0
\end{array}\right)
\end{array}
$$
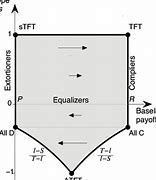
with $T$ representing the Temptation, i.e., the payoff an agent gains defecting when the other cooperates, and $S$ representing the Sucker’s payoff, i.e., the gain achieved by a cooperator when its opponent defects. In principle, the general structure of the payoff matrix (3.1) can be adapted also for describing other games (e.g., the HawkDove game). Notably, on varying the range of $T$ and $S$, one can refer to different scenarios. In our case, i.e., in the PD, the values of $T$ and $S$ are $1 \leq T \leq 2$ and $-1 \leq S \leq 0$. Accordingly, we can draw the $T-S$ plane and analyze the outcomes of the game from point to point, among the possible combinations $(T, S)$. For instance, low values of $T$ entail defectors receive a small payoff when they meet cooperators, while high value of $S$ entail cooperators have small losses when meet defectors.
计算复杂度理论代考
数学代写|计算复杂度理论代写Computational complexity theory代考|General Background
进化博弈论(以下简称 EGT)代表了研究种群动态的尝试,将博弈论的原理与达尔文进化论的原理相结合。乍一看,这两个领域几乎没有共同点。简而言之,博弈论可以被称为一种旨在在“竞争”中找到最优策略的方法/框架,以及在竞争者之间找到一种平衡的方法。相反,达尔文理论处理生命的进化,同时考虑其竞争方面和“信息传输和优化”的理念。然而,正如稍后所讨论的,仔细研究这些理论会发现不同的联系点。值得提醒的是,博弈论的早期发展,源于约翰·冯·诺伊曼和奥斯卡·摩根斯坦的作品,主要集中在人类行为的建模上,并明确参考了经济背景。后来,这一数学领域受到诺贝尔奖获得者约翰·纳什的强烈影响,他在对科学的相关贡献中引入了所谓的纳什均衡。后者可以被视为游戏的特定状态,涉及许多“理性”代理,他们必须在没有事先沟通的情况下采取行动。另一方面,达尔文的进化论构成了生物学和更普遍的科学领域最重要的突破之一,在一个多世纪之后仍然构成了一个活的理论,尽管在学术界之外尤其受到争论。他的父亲查尔斯·达尔文 在一次充满挑战的环游世界之后提出它,这使我们有机会对野生和未开发的自然进行直接观察。因此,在这次经历之后,这位年轻的科学家设想了一个解释生命自然进化的一般理论。因此,博弈论和达尔文理论的这种迷人结合构成了一个强大的框架,用于对从社会系统到生物现象的多种场景进行建模,并代表特定的机制(例如,复制、模仿)、交互模式和行为。因此,许多“复杂现象”可以用 EGT 模型来表征。然后,与著名的安德森著作《更多不同,” 这个现代的跨学科领域实际上可以归类为复杂领域的组成部分之一。例如,可以观察到可以被称为一种相变的紧急行为,研究一个代理群体,其局部交互很简单,例如,基于像囚徒困境这样的游戏。值得注意的是,从无序状态可以观察到向有序平衡的演变,而后者甚至可能与预期的相反(即纳什平衡)。最后一个观察值得特别注意,因为人们可能会遇到一些困惑。值得注意的是,虽然博弈论的数学框架有着非常坚实的根基和深厚的基础,但对现实世界的直接观察表明,纳什均衡并不总是得到尊重。例如,合作是一种普遍现象,在自然界中也有不同的形式,如互惠主义。在这里,EGT 的目标之一是找出可能导致我们观察到的现象的动机和机制,而这些现象仅使用博弈论是无法预测的。同时,达尔文理论也通过与博弈论相结合而获利。例如,在动物中发现的利他行为不能仅用达尔文理论来解释。因此,在这种情况下以及在其他情况下,博弈论的贡献可以弥补这一重要缺陷。EGT 的一个基本关键点是由种群动态中引入的适应性行为给出的。值得注意的是,这种行为是由“理性思维方式”驱动的,这种思维方式是通过执行代理来优化自己的收益而获得的。后者,通常定义为“收益”,在 EGT 中相当于“适应度”的概念。这种对应关系(即收益-适应度)非常重要,因为它代表了博弈论和达尔文理论之间最相关的联系之一,其中最好的个体不是最强的而是最适合的,或者一般来说,谁更好使自己/他自己适应新的环境。因此,等价收益拟合具有很深的含义,它允许使用博弈论的“理性”和达尔文理论的“进化机制”。特别是,正如稍后更详细讨论的那样,“理性”和“进化机制”在定义的“战略修订阶段”过程中实施。后者允许代理人修改他们的策略,例如,模仿他们的邻居,并支持成功战略的复制。因此,这一过程对于种群的实际进化至关重要,并允许引入不同的机制来影响系统走向平衡的方式。最后,即使 EGT 模型可以基于不同类型的博弈,在本书中我们指的是双策略博弈,即仅以两种策略为特征的博弈。即使这种选择对于模拟真实场景而言过于局限,但在我们看来,它提供了两个主要优势。首先,它允许以非常简单的方式介绍 EGT 领域;其次,它促进了与统计物理学中众所周知的模型的联系。我们现在可以继续本章的下一部分,
数学代写|计算复杂度理论代写Computational complexity theory代考|Nash Equilibrium
纳什均衡由小约翰福布斯纳什开发,是博弈论的一个里程碑。为简单起见,让我们考虑两个代理在玩一个通用游戏,在采取行动(即移动)之前不允许通信。在这里,纳什均衡代表了一种特殊情况,即他们都无法从唯一改变战略的人中获益。缺乏达成事先协议(即初步沟通)的机会会产生深远的影响。首先,如果两个智能体都想增加他们的收益,就需要某种形式的“盲目协调”,这反过来又意味着要达到最大收益可能需要采取非常冒险的策略。在下一节,介绍囚徒困境等真实游戏,一些策略的“风险”面将更加清晰。除了一般描述之外,纳什均衡显然还有一个正式的数学定义。让我们考虑一个由集合描述的游戏小号战略概况和收益函数F, IE,(小号,F). 本场比赛可能涉及n玩家,让每个人都采用一种策略。在这里,战略配置文件小号定义为小号=小号1×小号2×…×小号n,并且支付函数计算特定的增益X∈小号作为F(X)=(F1(X),F2(X),…,Fn(X)). 然后,一组策略X∈小号是纳什均衡,如果∀一世,X一世∈小号一世:F一世(X一世,X−一世)≥F一世(X一世,X−一世). 总而言之,达到纳什均衡可以被视为一种权衡,它确保了良好回报的潜力,同时降低了可能的风险。出于这个原因,如果我们考虑一个群体,其代理人根据困境博弈进行交互,预期均衡应该对应于纳什均衡,即所有代理人都采取最方便的策略,遵循自私行为。然而,在这样做的过程中,作为一个整体,我们的人口面临着无法产生共同健康的风险。在这种情况下,后者具有非常笼统的含义,例如可能指为接受公共服务而纳税的人或为避免病毒传播而为自己接种疫苗的人等等。现在,除了需要确定共同健康的策略之外,
数学代写|计算复杂度理论代写Computational complexity theory代考|The Prisoner’s Dilemma
囚徒困境(以下简称 PD)是最著名的游戏之一,它展示了为什么理性的方法可能会导致人们避免合作。它的一般动态可以用不同的故事来讲述;然而,在这里,我们报道了这个游戏的经典名称,即两个罪犯被警察抓获并接受讯问的故事。值得注意的是,在被抓获后,我们的罪犯被分开以避免潜在的协议。此外,为了确保至少有一个有罪,他们被提供了一个讨价还价:每个罪犯都有两种选择,即背叛(即背叛)或保持沉默(即合作)。因此,尽管常识可能表明,在这种情况下,作为合作者意味着与“伙伴”合作,而不是与警察合作。所以,如果两个罪犯合作,他们被判处 1 年监禁,而如果双方都背叛,则被判处 2 年监禁。相反,在第三种情况下,即一个背叛,另一个保持沉默,合作者被判处5年徒刑,而叛逃者则被释放。回顾他们在采取行动之前无法沟通(即保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的犯罪分子背叛的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:而如果双方都背叛了定罪,则判处 2 年监禁。相反,在第三种情况下,即一个背叛,另一个保持沉默,合作者被判处5年徒刑,而叛逃者则被释放。回顾他们在采取行动之前无法沟通(即保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的犯罪分子背叛的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:而如果双方都背叛了定罪,则判处 2 年监禁。相反,在第三种情况下,即一个背叛,另一个保持沉默,合作者被判处5年徒刑,而叛逃者则被释放。回顾他们在采取行动之前无法沟通(即保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的犯罪分子背叛的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:一个背叛,另一个保持沉默,合作者被判处5年监禁,而叛逃者则被释放。回顾他们在采取行动之前无法沟通(即保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的犯罪分子背叛的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:一个背叛,另一个保持沉默,合作者被判处5年监禁,而叛逃者则被释放。回顾他们在采取行动之前无法沟通(即保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的犯罪分子背叛的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的罪犯叛逃的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:保持沉默或背叛),导致我们的罪犯叛逃的动机似乎很清楚。该博弈的纳什均衡是“背叛”,犯罪分子将被判入狱 2 年。同时,如果双方合作可以节省1年的时间,那么只有通过合作的协调行动才能获得最高的“共同”收益,尽管风险很大。无论如何,除了这个故事或类似的故事之外,PD 可以通过以下收益矩阵来表征:
CD C(1小号 吨0)
和吨代表诱惑,即代理人在另一方合作时背叛获得的回报,以及小号代表 Sucker 的收益,即合作者在对手出现缺陷时所获得的收益。原则上,收益矩阵(3.1)的一般结构也可以适应描述其他游戏(例如,HawkDove 游戏)。值得注意的是,在改变范围吨和小号,可以参考不同的场景。在我们的例子中,即在 PD 中,吨和小号是1≤吨≤2和−1≤小号≤0. 据此,我们可以绘制吨−小号在可能的组合中,从点到点平面并分析游戏的结果(吨,小号). 例如,低值吨叛逃者在遇到合作者时会获得少量回报,而小号使合作者在遇到叛逃者时损失很小。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
