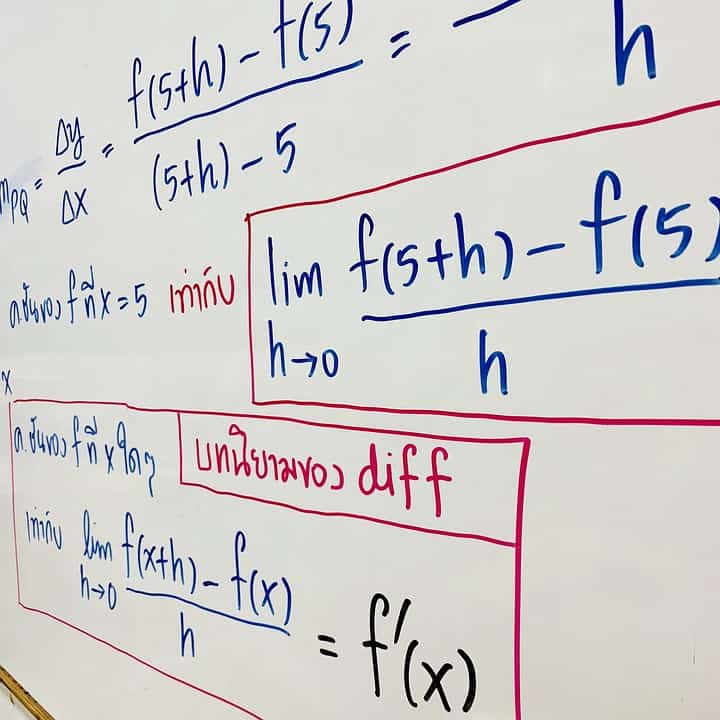如果你也在 怎样代写微积分Calculus 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。微积分Calculus 基本上就是非常高级的代数和几何。从某种意义上说,它甚至不是一门新学科——它采用代数和几何的普通规则,并对它们进行调整,以便它们可以用于更复杂的问题。(当然,问题在于,从另一种意义上说,这是一门新的、更困难的学科。)
微积分Calculus数学之所以有效,是因为曲线在局部是直的;换句话说,它们在微观层面上是直的。地球是圆的,但对我们来说,它看起来是平的,因为与地球的大小相比,我们在微观层面上。微积分之所以有用,是因为当你放大曲线,曲线变直时,你可以用正则代数和几何来处理它们。这种放大过程是通过极限数学来实现的。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写微积分Calculus方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写微积分Calculus代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写微积分Calculus相关的作业也就用不着说。
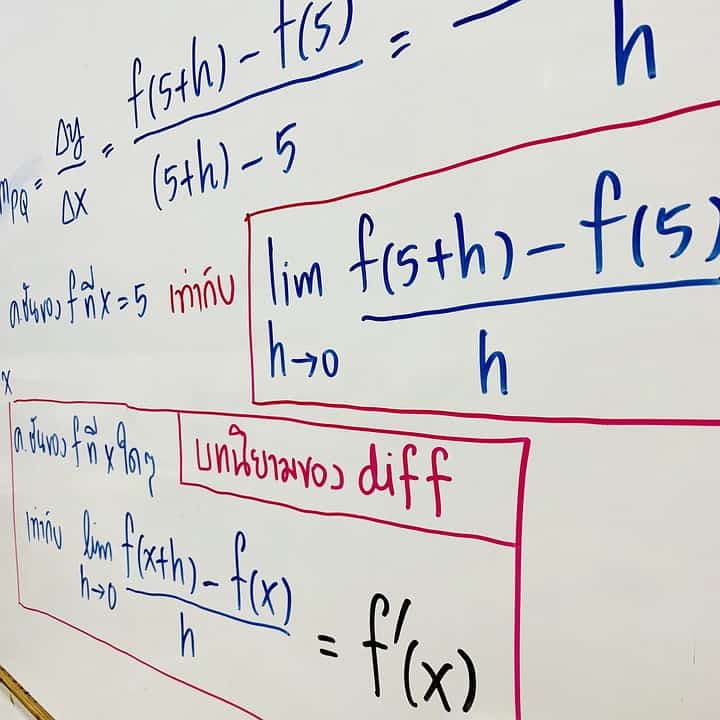
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Tricky Trig Integrals
In this section, you integrate powers of the six trigonometric functions, like $\int \sin ^3(x) d x$ and $\int \sec ^4(x) d x$, and products or quotients of trig functions, like $\int \sin ^2(x) \cos ^3(x) d x$ and $\int \frac{\csc ^2(x)}{\cot (x)} d x$. This is a bit tedious – time for some caffeine. To use the following techniques, you must have an integrand that contains just one of the six trig functions like $\int \csc ^3(x) d x$ or a certain pairing of trig functions, like $\int \sin ^2(x) \cos (x) d x$. If the integrand has two trig functions, the two must be one of these three pairs: sine with cosine, secant with tangent, or cosecant with cotangent. For an integrand containing something other than one of these pairs, you can convert the problem into one of these pairs by using trig identities like $\sin (x)=1 / \csc (x)$ and $\tan (x)=\sin (x) / \cos (x)$. For instance,
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \int \sin ^2(x) \sec (x) \tan (x) d x \
= & \int \sin ^2(x) \frac{1}{\cos (x)} \cdot \frac{\sin (x)}{\cos (x)} d x \
= & \int \frac{\sin ^3(x)}{\cos ^2(x)} d x
\end{aligned}
$$
After any needed conversions, you get one of three cases:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \int \sin ^m(x) \cos ^n(x) d x \
& \int \sec ^m(x) \tan ^n(x) d x \
& \int \csc ^m(x) \cot ^n(x) d x
\end{aligned}
$$
where either $m$ or $n$ is a positive integer.
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Sines and cosines
Case 1: The power of sine is odd and positive
If the power of sine is odd and positive, lop off one sine factor and put it to the right of the rest of the expression, convert the remaining sine factors to cosines with the Pythagorean identity, and then integrate with the substitution method where $u=\cos (x)$.
The Pythagorean identity tells you that, for any angle $x, \sin ^2(x)+$ $\cos ^2(x)=1$. And thus $\sin ^2(x)=1-\cos ^2(x)$ and $\cos ^2(x)=1-$ $\sin ^2(x)$.
Now integrate $\int \sin ^3(x) \cos ^4(x) d x$.
- Lop off one sine factor and move it to the right.
$$
\int \sin ^3(x) \cos ^4(x) d x=\int \sin ^2(x) \cos ^4(x) \sin (x) d x
$$ - Convert the remaining sines to cosines using the Pythagorean identity and simplify.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \int \sin ^2(x) \cos ^4(x) \sin (x) d x \
= & \int\left(1-\cos ^2(x)\right) \cos ^4(x) \sin (x) d x \
= & \int\left(\cos ^4(x)-\cos ^6(x)\right) \sin (x) d x
\end{aligned}
$$ - Integrate with substitution, where $u=\cos (x)$.
$$
\begin{gathered}
u=\cos (x) \
\frac{d u}{d x}=-\sin (x) \
d u=-\sin (x) d x
\end{gathered}
$$
微积分代考
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Tricky Trig Integrals
在本节中,将对六个三角函数(如$\int \sin ^3(x) d x$和$\int \sec ^4(x) d x$)的幂和三角函数(如$\int \sin ^2(x) \cos ^3(x) d x$和$\int \frac{\csc ^2(x)}{\cot (x)} d x$)的积或商进行积分。这有点乏味——是时候喝点咖啡因了。要使用下面的技巧,必须有一个只包含六个三角函数中的一个的被积函数,如$\int \csc ^3(x) d x$或某些三角函数对,如$\int \sin ^2(x) \cos (x) d x$。如果被积函数有两个三角函数,这两个三角函数必须是以下三对中的一个:正弦与余弦,正割与正切,或余割与余切。对于包含这些对之外的东西的被积函数,您可以通过使用像$\sin (x)=1 / \csc (x)$和$\tan (x)=\sin (x) / \cos (x)$这样的三角恒等式将问题转换为这些对中的一个。例如,
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \int \sin ^2(x) \sec (x) \tan (x) d x \
= & \int \sin ^2(x) \frac{1}{\cos (x)} \cdot \frac{\sin (x)}{\cos (x)} d x \
= & \int \frac{\sin ^3(x)}{\cos ^2(x)} d x
\end{aligned}
$$
在任何必要的转换之后,您将得到以下三种情况之一:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \int \sin ^m(x) \cos ^n(x) d x \
& \int \sec ^m(x) \tan ^n(x) d x \
& \int \csc ^m(x) \cot ^n(x) d x
\end{aligned}
$$
其中$m$或$n$为正整数。
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Sines and cosines
情形1:sin的幂是奇数且正的
如果sin的幂是奇数且正的,则去掉一个sin因子并将其放在表达式的其余部分的右侧,用勾股定理将剩余的sin因子转换为余弦,然后用代换法积分$u=\cos (x)$。
勾股定理告诉你,对于任意角度$x, \sin ^2(x)+$$\cos ^2(x)=1$。因此是$\sin ^2(x)=1-\cos ^2(x)$和$\cos ^2(x)=1-$$\sin ^2(x)$。
现在积分$\int \sin ^3(x) \cos ^4(x) d x$。
去掉一个正弦因子,向右移动。
$$
\int \sin ^3(x) \cos ^4(x) d x=\int \sin ^2(x) \cos ^4(x) \sin (x) d x
$$
用勾股定理把剩下的正弦转换成余弦化简。
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \int \sin ^2(x) \cos ^4(x) \sin (x) d x \
= & \int\left(1-\cos ^2(x)\right) \cos ^4(x) \sin (x) d x \
= & \int\left(\cos ^4(x)-\cos ^6(x)\right) \sin (x) d x
\end{aligned}
$$
用代换法积分,其中$u=\cos (x)$。
$$
\begin{gathered}
u=\cos (x) \
\frac{d u}{d x}=-\sin (x) \
d u=-\sin (x) d x
\end{gathered}
$$
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。