如果你也在 怎样代写电磁学Electromagnetism 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。电磁学Electromagnetism是物理学的一个分支,涉及到对电磁力的研究,这是一种发生在带电粒子之间的物理作用。电磁力是由电场和磁场组成的电磁场所承载的,它是诸如光这样的电磁辐射的原因。它与强相互作用、弱相互作用和引力一起,是自然界的四种基本相互作用(通常称为力)之一。在高能量下,弱力和电磁力被统一为单一的电弱力。
电磁学Electromagnetism是以电磁力来定义的,有时也称为洛伦兹力,它包括电和磁,是同一现象的不同表现形式。电磁力在决定日常生活中遇到的大多数物体的内部属性方面起着重要作用。原子核和其轨道电子之间的电磁吸引力将原子固定在一起。电磁力负责原子之间形成分子的化学键,以及分子间的力量。电磁力支配着所有的化学过程,这些过程是由相邻原子的电子之间的相互作用产生的。电磁学在现代技术中应用非常广泛,电磁理论是电力工程和电子学包括数字技术的基础。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写电磁学electromagnetism方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写电磁学electromagnetism代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写电磁学electromagnetism相关的作业也就用不着说。
物理代写|电磁学代写electromagnetism代考|Eddy Currents in Cores with Regular Polygonal Cross-Sections
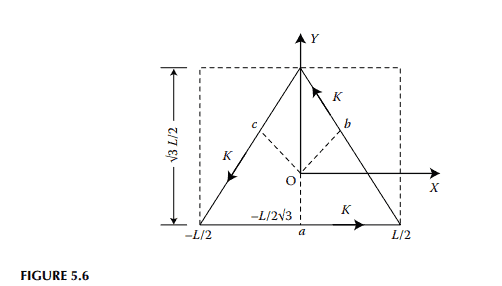
Distributions of magnetic fields in solid cores with rectangular and circular cross-sections due to alternating current excitation have been analytically determined. ${ }^{2,3}$ For cores with uncommon cross-sections, field distributions are usually evaluated using numerical methods., ${ }^{4,8}$ Analytical solutions are available $e^{5-7}$ for field distributions in cores with cross-sections in the shape of isosceles right-angled triangles. A quasi-analytical method for the determination of the approximate distribution of magnetic field intensity in cores with regular polygonal cross-sections is presented in this section as an alternative to the existing numerical methods. Although only three types of core sections, namely, cores with triangular, hexagonal and octagonal cross-sections, as shown in Figures 5.6 through 5.8 are considered, the method can be readily extended for other regular polygonal sections.
Consider a long conducting core carrying a surface current sheet with density $K$ simulating a uniformly distributed current-carrying winding wound around the core. The winding current is at power frequency. The magnetic field outside the core will be zero if the displacement currents are neglected. Inside the core, the magnetic field will be axial, that is in the $z$-direction such that just under the current sheet
$$
\left.H_z\right|_{\text {core surface }}=K
$$
where $|K|$ indicates the root mean square (rms) value of the surface current density on the conductor surface flowing in the anticlockwise direction, and $\mathrm{H}_z$ indicates the magnetic field in the axial direction, both in phasor form.
The eddy current equation for the magnetic field is
$$
\nabla^2 H_z=\eta^2 H_z
$$
where
$$
\eta^2=j \omega_0 \cdot \mu \sigma
$$
$\omega_0=$ frequency of the sinusoidally time-varying field
$\mu=$ permeability of the core
$\sigma=$ conductivity of the core
This is a two-dimensional problem as fields vary along $x$ – and $y$-directions only. Thus,
$$
\frac{\partial H_z}{\partial x^2}+\frac{\partial H_z}{\partial y^2}=\eta^2 H_z
$$
The solutions of this equation for solid cores with triangular, hexagonal and octagonal cross-sections are discussed in the following three subsections.
物理代写|电磁学代写electromagnetism代考|Cores with Triangular Cross-Sections
Consider a long solid-conducting core with a triangular cross-section shown in Figure 5.6. Let the length of each side of the triangle be $L$. A rectangle constructed using the base of this equilateral triangle is shown by dotted lines. Let the torch function be defined by the finite Fourier series:
$$
\left.H_z^{\prime}\right|{y=L / \sqrt{3}}=\sum{m-\text { odd }}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x\right)
$$
where $T_m$ indicates a set of Fourier coefficients.
On setting
$$
\left.H_z^{\prime}\right|{x= \pm L / 2}=\left.H_z^{\prime}\right|{y=-L /(2 \sqrt{3})}=0
$$
The solution of eddy current equation for the rectangular region can be given as
$$
H_z^{\prime}=\sum_{m-\alpha d d d}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x^{\prime}\right) \cdot \frac{\sinh \left[\alpha_m \cdot\left{y^{\prime}+L /(2 \sqrt{ } 3)\right}\right]}{\sinh \left(\alpha_m \cdot L \sqrt{3} / 2\right)}
$$
where
$$
\begin{gathered}
\alpha_m=\sqrt{\left(\frac{m \pi}{L}\right)^2+\eta^2} \
x^{\prime}=x \
y^{\prime}=y
\end{gathered}
$$
Next, we construct two more similar rectangles, each containing one or the other of the two remaining sides of the equilateral triangle. Let the field distributions in these regions be
$$
H_z^{\prime \prime}=\sum_{m-\text {-odd }}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x^{\prime \prime}\right) \cdot \frac{\sinh \left[\alpha_m \cdot\left{y^{\prime \prime}+L /(2 \sqrt{3})\right}\right]}{\sinh \left(\alpha_m \cdot L \cdot \sqrt{3} / 2\right)}
$$
$$
H_z^{\prime \prime}=\sum_{m-\text { odd }}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x^{\prime \prime}\right) \cdot \frac{\sin \left[\alpha_m \cdot\left{y^{\prime \prime}+L /(2 \sqrt{3})\right}\right]}{\sinh \left(\alpha_m \cdot L \cdot \sqrt{3} / 2\right)}
$$
where
$$
\begin{aligned}
& x^{\prime \prime}=y \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-x \cdot \frac{1}{2} \
& y^{\prime \prime}=-y \cdot \frac{1}{2}-x \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \
& x^{\prime \prime}=-y \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-x \cdot \frac{1}{2} \
& y^{\prime \prime}=-y \cdot \frac{1}{2}+x \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}
\end{aligned}
$$
电磁学代考
物理代写|电磁学代写electromagnetism代考|Eddy Currents in Cores with Regular Polygonal Cross-Sections
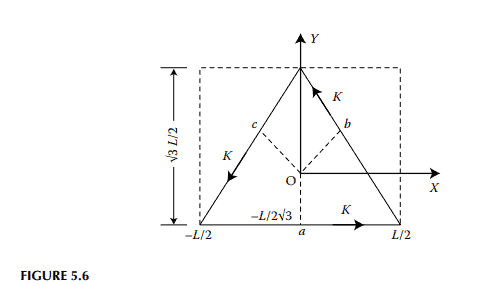
本文用解析法确定了矩形和圆形实心在交流励磁作用下的磁场分布。${ }^{2,3}$对于不常见截面的岩心,通常使用数值方法评估场分布。, ${ }^{4,8}$对于横截面为等腰直角三角形的岩心中的场分布有解析解$e^{5-7}$。本文提出了一种准解析方法来确定正多边形截面岩心磁场强度的近似分布,作为现有数值方法的一种替代方法。虽然只考虑图5.6 ~ 5.8所示的三角形、六角形和八角形截面三种类型的岩心截面,但该方法可以很容易地推广到其他正多边形截面。
考虑一个带表面电流片的长导电铁芯,其密度为$K$,模拟铁芯周围均匀分布的载流绕组。绕组电流在工频。如果忽略位移电流,磁芯外的磁场将为零。在磁芯内部,磁场将是轴向的,即在$z$ -方向,这样就在电流片下面
$$
\left.H_z\right|_{\text {core surface }}=K
$$
其中$|K|$为导体表面沿逆时针方向流动的表面电流密度的均方根值,$\mathrm{H}_z$为轴向磁场,均为相量形式。
磁场的涡流方程为
$$
\nabla^2 H_z=\eta^2 H_z
$$
在哪里
$$
\eta^2=j \omega_0 \cdot \mu \sigma
$$
$\omega_0=$正弦时变场的频率
$\mu=$岩心渗透率
$\sigma=$芯的电导率
这是一个二维问题,因为场仅沿$x$ -和$y$ -方向变化。因此,
$$
\frac{\partial H_z}{\partial x^2}+\frac{\partial H_z}{\partial y^2}=\eta^2 H_z
$$
在接下来的三个小节中讨论了具有三角形、六边形和八边形截面的实心岩心的这个方程的解。
物理代写|电磁学代写electromagnetism代考|Cores with Triangular Cross-Sections
考虑一个三角形截面的长固体导电铁芯,如图5.6所示。设三角形每条边的长度为$L$。用等边三角形的底边构成的矩形用虚线表示。设火炬函数由有限傅里叶级数定义:
$$
\left.H_z^{\prime}\right|{y=L / \sqrt{3}}=\sum{m-\text { odd }}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x\right)
$$
其中$T_m$表示一组傅里叶系数。
设置
$$
\left.H_z^{\prime}\right|{x= \pm L / 2}=\left.H_z^{\prime}\right|{y=-L /(2 \sqrt{3})}=0
$$
矩形区域涡流方程的解为
$$
H_z^{\prime}=\sum_{m-\alpha d d d}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x^{\prime}\right) \cdot \frac{\sinh \left[\alpha_m \cdot\left{y^{\prime}+L /(2 \sqrt{ } 3)\right}\right]}{\sinh \left(\alpha_m \cdot L \sqrt{3} / 2\right)}
$$
在哪里
$$
\begin{gathered}
\alpha_m=\sqrt{\left(\frac{m \pi}{L}\right)^2+\eta^2} \
x^{\prime}=x \
y^{\prime}=y
\end{gathered}
$$
接下来,我们再构造两个类似的矩形,每个矩形包含等边三角形剩下的两条边中的一条或另一条。让这些区域的场分布不变
$$
H_z^{\prime \prime}=\sum_{m-\text {-odd }}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x^{\prime \prime}\right) \cdot \frac{\sinh \left[\alpha_m \cdot\left{y^{\prime \prime}+L /(2 \sqrt{3})\right}\right]}{\sinh \left(\alpha_m \cdot L \cdot \sqrt{3} / 2\right)}
$$
$$
H_z^{\prime \prime}=\sum_{m-\text { odd }}^{(2 M-1)} T_m \cdot \cos \left(\frac{m \pi}{L} \cdot x^{\prime \prime}\right) \cdot \frac{\sin \left[\alpha_m \cdot\left{y^{\prime \prime}+L /(2 \sqrt{3})\right}\right]}{\sinh \left(\alpha_m \cdot L \cdot \sqrt{3} / 2\right)}
$$
在哪里
$$
\begin{aligned}
& x^{\prime \prime}=y \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-x \cdot \frac{1}{2} \
& y^{\prime \prime}=-y \cdot \frac{1}{2}-x \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \
& x^{\prime \prime}=-y \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-x \cdot \frac{1}{2} \
& y^{\prime \prime}=-y \cdot \frac{1}{2}+x \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}
\end{aligned}
$$
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。