如果你也在 怎样代写管理会计Management Accounting ACCT6001这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。管理会计Management Accounting为组织的内部管理部门、其雇员、经理和行政人员提供财务信息,以便为决策提供依据并提高绩效。换句话说,管理会计师是战略伙伴。在管理会计或管理会计中,管理人员在决策中使用会计信息,并协助管理和履行其控制职能。
管理会计 Management Accounting的一个简单定义是向管理人员提供财务和非财务决策信息。换句话说,管理会计帮助组织内部的董事进行决策。这也可以被称为成本会计。这是区分、检查、破译和向主管人员传授数据的方式,以帮助完成商业目标。收集的信息包括所有领域的会计,教育行政部门识别财务支出和组织决策的业务任务。会计师使用计划来衡量组织内的整体运营战略。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写管理会计Management Accounting方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写管理会计Management Accounting代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写管理会计Management Accounting相关的作业也就用不着说。
会计代写|管理会计代写Management Accounting代考|Differences in Economic Development
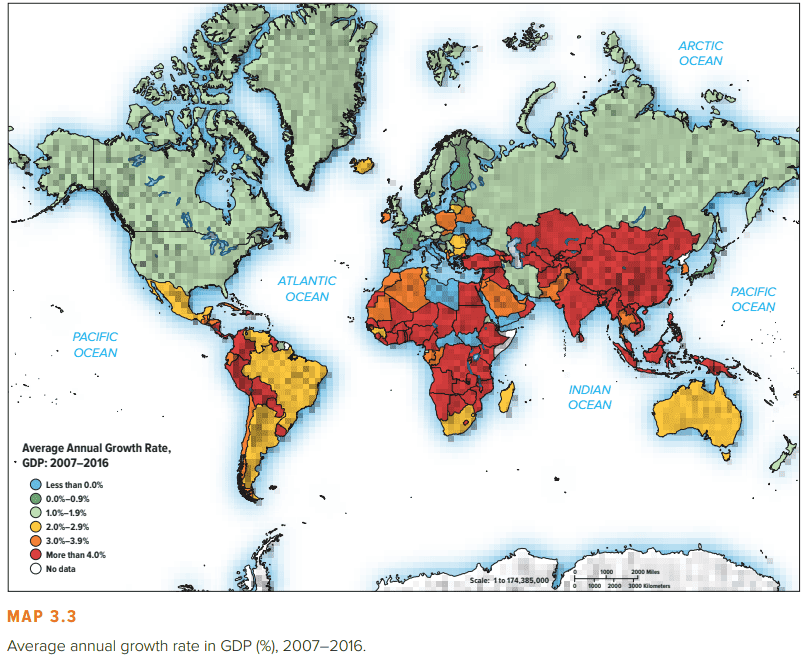
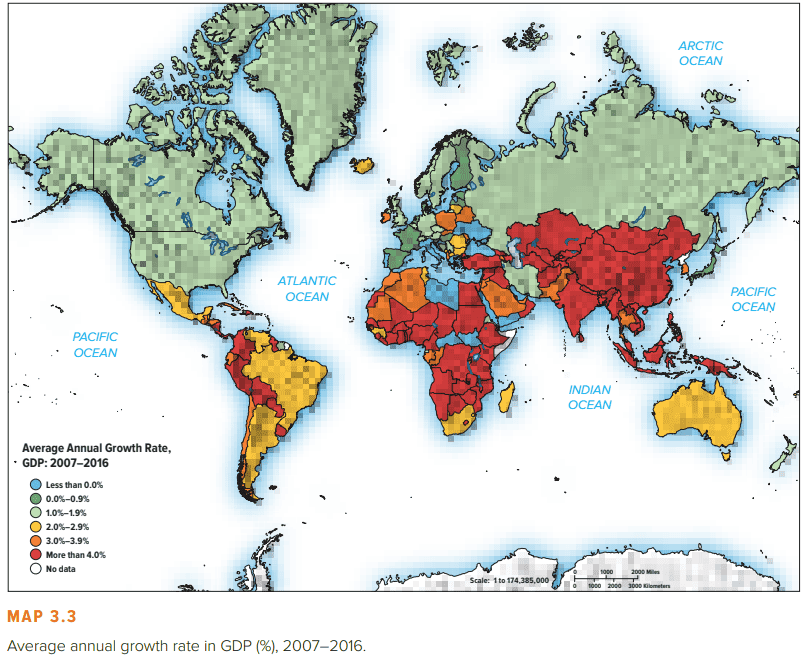
Different countries have dramatically different levels of economic development. One common measure of economic development is a country’s gross national income (GNI) per head of population. GNI is regarded as a yardstick for the economic activity of a country; it measures the total annual income received by residents of a nation. Map 3.1 summarizes the GNI per capita of the world’s nations in 2016. As can be seen, countries such as Japan, Sweden, Switzerland, the United States, and Australia are among the richest on this measure, whereas the large developing countries of China and India are significantly poorer. Japan, for example, had a 2016 GNI per capita of $\$ 38,000$, but China achieved only $\$ 8,260$ and India just $\$ 1,680 .^1$
GNI per person figures can be misleading because they don’t consider differences in the cost of living. For example, although the 2016 GNI per capita of Switzerland at $\$ 81,240$ exceeded that of the United States by a wide margin, the higher cost of living in Switzerland meant that U.S. citizens could actually afford almost as many goods and services as the average Swiss citizen. To account for differences in the cost of living, one can adjust GNI per capita by purchasing power. Referred to as a purchasing power parity (PPP) adjustment, it allows a more direct comparison of living standards in different countries. The base for the adjustment is the cost of living in the United States. The PPP for different countries is then adjusted (up or down) depending on whether the cost of living is lower or higher than in the United States. For example, in 2016 the GNI per capita for China was $\$ 8,260$, but the PPP per capita was $\$ 15,500$, suggesting that the cost of living was lower in China and that $\$ 8,260$ in China would buy as much as $\$ 15,500$ in the United States. Table 3.1 gives the GNI per capita measured at PPP in 2016 for a selection of countries, along with their GNI per capita and their growth rate in gross domestic product (GDP) from 2007 to 2016. Map 3.2 summarizes the GNI PPP per capita in 2016 for the nations of the world.
As can be seen, there are striking differences in the standards of living among countries. Table 3.1 suggests the average Indian citizen can afford to consume only about 11 percent of the goods and services consumed by the average U.S. citizen on a PPP basis. Given this, we might conclude that despite having a population of 1.2 billion, India is unlikely to be a very lucrative market for the consumer products produced by many Western international businesses. However, this would be incorrect because India has a fairly wealthy middle class of close to 250 million people, despite its large number of poor citizens. In absolute terms, the Indian economy now rivals that of Russia.
会计代写|管理会计代写Management Accounting代考|BROADER CONCEPTIONS OF DEVELOPMENT: AMARTYA SEN
The Nobel Prize-winning economist Amartya Sen has argued that development should be assessed less by material output measures such as GNI per capita and more by the capabilities and opportunities that people enjoy. ${ }^3$ According to Sen, development should be seen as a process of expanding the real freedoms that people experience. Hence, development requires the removal of major impediments to freedom: poverty as well as tyranny, poor economic opportunities as well as systematic social deprivation, and neglect of public facilities as well as the intolerance of repressive states. In Sen’s view, development is not just an economic process but a political one too, and to succeed requires the “democratization” of political communities to give citizens a voice in the important decisions made for the community. This perspective leads Sen to emphasize basic health care, especially for children, and basic education, especially for women. Not only are these factors desirable for their instrumental value in helping achieve higher income levels, but they are also beneficial in their own right. People cannot develop their capabilities if they are chronically ill or woefully ignorant.
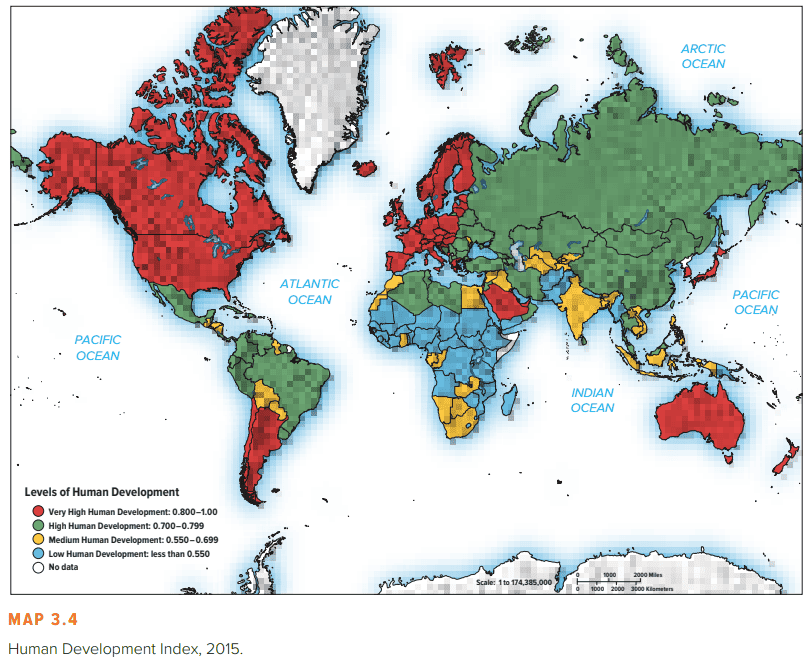
Sen’s influential thesis has been picked up by the United Nations, which has developed the Human Development Index (HDI) to measure the quality of human life in different nations. The HDI is based on three measures: life expectancy at birth (a function of health care); educational attainment (measured by a combination of the adult literacy rate and enrollment in primary, secondary, and tertiary education); and whether average incomes, based on PPP estimates, are sufficient to meet the basic needs of life in a country (adequate food, shelter, and health care). As such, the HDI comes much closer to Sen’s conception of how development should be measured than narrow economic measures such as GNI per capita-although Sen’s thesis suggests that political freedoms should also be included in the index, and they are not. The HDI is scaled from 0 to 1 . Countries scoring less than 0.5 are classified as having low human development (the quality of life is poor), those scoring from 0.5 to 0.8 are classified as having medium human development, and those that score above 0.8 are classified as having high human development. Map 3.4 summarizes the HDI scores for 2015 .
管理会计代考
会计代写|管理会计代写Management Accounting代考|Differences in Economic Development
不同的国家有截然不同的经济发展水平。衡量经济发展的一个常用指标是一国人均国民总收入(GNI)。国民总收入被视为衡量一个国家经济活动的标准;它衡量的是一个国家居民的年收入总额。图3.1总结了2016年世界各国的人均国民总收入。可以看出,日本、瑞典、瑞士、美国和澳大利亚等国家在这一指标上是最富有的,而中国和印度等大型发展中国家则要穷得多。例如,日本2016年的人均国民总收入为3.8万美元,但中国仅为8260美元,印度仅为1680美元
人均国民总收入数据可能具有误导性,因为它们没有考虑到生活成本的差异。例如,尽管2016年瑞士的人均国民总收入为81240美元,远远超过美国,但瑞士较高的生活成本意味着美国公民实际上可以负担的商品和服务几乎与普通瑞士公民一样多。要考虑到生活成本的差异,可以通过购买力来调整人均国民总收入。它被称为购买力平价(PPP)调整,可以更直接地比较不同国家的生活水平。调整的基础是美国的生活成本。然后根据生活成本比美国低还是高,对不同国家的购买力平价进行调整(向上或向下)。例如,2016年中国人均国民总收入为8260美元,但人均购买力平价为15500美元,这表明中国的生活成本较低,8260美元在中国可以买到15500美元在美国。表3.1给出了2016年按购买力平价衡量的一些国家的人均国民总收入,以及2007年至2016年这些国家的人均国民总收入和国内生产总值(GDP)增长率。图3.2总结了2016年世界各国的人均国民收入购买力。
可以看出,各国的生活水平存在着显著的差异。表3.1显示,按购买力平价计算,印度普通公民只能负担得起美国普通公民消费的11%左右的商品和服务。鉴于此,我们可以得出结论,尽管拥有12亿人口,但对于许多西方国际企业生产的消费品来说,印度不太可能是一个非常有利可图的市场。然而,这是不正确的,因为印度有一个相当富裕的中产阶级,接近2.5亿人,尽管有大量的穷人。按绝对价值计算,印度经济现在可以与俄罗斯匹敌。
会计代写|管理会计代写Management Accounting代考|BROADER CONCEPTIONS OF DEVELOPMENT: AMARTYA SEN
诺贝尔奖得主、经济学家阿马蒂亚•森(Amartya Sen)认为,对发展的评估应该少用人均国民总收入(GNI)等物质产出指标,多用人们享有的能力和机会来衡量。根据森的观点,发展应该被看作是扩大人们所经历的真正自由的过程。因此,发展需要消除自由的主要障碍:贫穷和暴政,缺乏经济机会和系统的社会剥夺,忽视公共设施以及压迫国家的不容忍。在森看来,发展不仅是一个经济过程,也是一个政治过程,要取得成功,就需要政治社区的“民主化”,让公民在为社区做出的重要决策中有发言权。这一观点使森强调基本保健,特别是针对儿童,以及基础教育,特别是针对妇女。这些因素不仅因其在帮助实现更高收入水平方面的工具价值而可取,而且它们本身也是有益的。如果一个人长期患病或无知到可悲的地步,他就无法发展自己的能力。
森颇具影响力的论文被联合国采纳,联合国开发了人类发展指数(HDI)来衡量不同国家的人类生活质量。人类发展指数基于三个指标:出生时预期寿命(保健的函数);受教育程度(通过成人识字率和小学、中学和高等教育入学率的综合衡量);以及根据购买力平价估算的平均收入是否足以满足一个国家的基本生活需求(充足的食物、住所和医疗保健)。因此,人类发展指数比狭隘的经济指标(如人均国民总收入)更接近森关于如何衡量发展的概念——尽管森的论文认为政治自由也应该包括在指数中,但他们没有。HDI从0到1进行缩放。得分低于0.5的国家被归类为低人类发展国家(生活质量差),得分在0.5到0.8之间的国家被归类为中等人类发展国家,得分在0.8以上的国家被归类为高人类发展国家。图3.4总结了2015年的人类发展指数得分。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。