数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography代考|COMP537
如果你也在 怎样密码学与系统安全Cryptography and System Security 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。密码学Cryptography也不是一门新科学,尽管有些人会说,它直到最近才被正式视为一门新科学。几个世纪以来,它一直被用来保护敏感信息,尤其是在冲突时期。
密码学与系统安全Cryptography and System Security是一门与日常生活相关的学科,它经历了巨大的变化。密码学曾经通过其历史用途在公众的想象中表现出来,主要是为了保护军事通信,以及通过娱乐谜题。然而,很大程度上由于计算机网络的发展,特别是因特网,我们大多数人现在每天都在使用密码学。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写密码学Cryptography方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写密码学Cryptography代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写密码学Cryptography相关的作业也就用不着说。
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography代考|Problems with passwords
The attractive properties of passwords are they are simple and familiar. These are the reasons they are ubiquitously used as identity information. However, they have several flaws which severely limit the security of any application employing them:
Length. Since passwords are designed to be memorised by humans, there is a natural limit to their length. This means the password space (all possible passwords) is limited in size, thus restricting the amount of work required for an exhaustive search of all passwords.
Complexity. The full password space is rarely used in applications because humans find randomly generated passwords hard to remember. As a result, we often work from highly restricted password spaces, which greatly reduces the security. This makes dictionary attacks possible, where an attacker simply exhaustively tries all the ‘likely’ passwords and hopes to eventually find the correct one (see Section 1.6.5). Clever mnemonic techniques can slightly increase the size of a usable password space. Where users are requested to adopt complex passwords, a usabilitysecurity trade-off is soon reached, since it is more likely a complex password will be transferred into ‘something the claimant has’ in the form of a written note, which in many cases defeats the purpose of using passwords in the first place. Moving from passwords to passphrases can improve this situation by significantly increasing the password space; however, many of the other problems with passwords remain.
Repeatability. For the lifetime of a password, each time it is used it is exactly the same. This means that if an attacker can obtain the password, then there is a period of time (often significant) within which the password can be used to fraudulently claim the identity of the original owner. One measure which can be taken to restrict this threat is to regularly force password change. However, this again raises a usability issue since regular password change is confusing for humans and can lead to insecure password storage practices.
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography代考|Cryptographic password protection
Consider a large organisation wishing to authenticate many users onto its internal system using passwords. One obvious way of implementing this is to use a system which compares offered passwords with those stored on a centralised password database. This presents the password database as a highly attractive target for attackers, since this database potentially contains a complete list of account names and passwords. Even if this database is managed carefully, the administrators of the system potentially have access to this list, which may not be desirable.
One area where cryptography can be used to help to implement an identification system based on passwords is in securing the password database. This is because, in order to authenticate a user, the system does not actually need to know a user’s password. Rather, the device simply needs to know whether a supplied password is the correct one. The point is that while a user does need to enter the correct password, the system does not need to store a copy of this password in order to verify it is correct.
In Section 6.2.2, we described an application of hash functions which implemented password database protection. The idea is to store hashes of the passwords, rather than the actual passwords in the password database. This allows them to be checked, while preventing anyone who gains access to the password database from recovering the passwords themselves. We observed that any function regarded as being one-way (which includes hash functions) could in theory be used to provide this service.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO UNIX PASSWORD PROTECTION
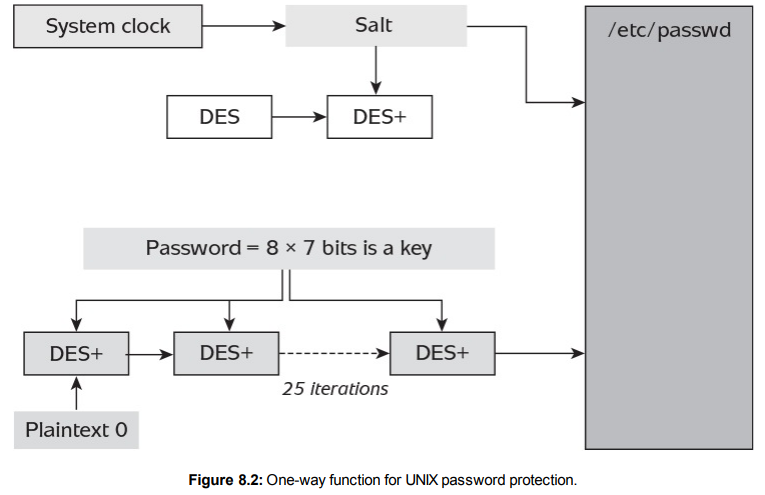
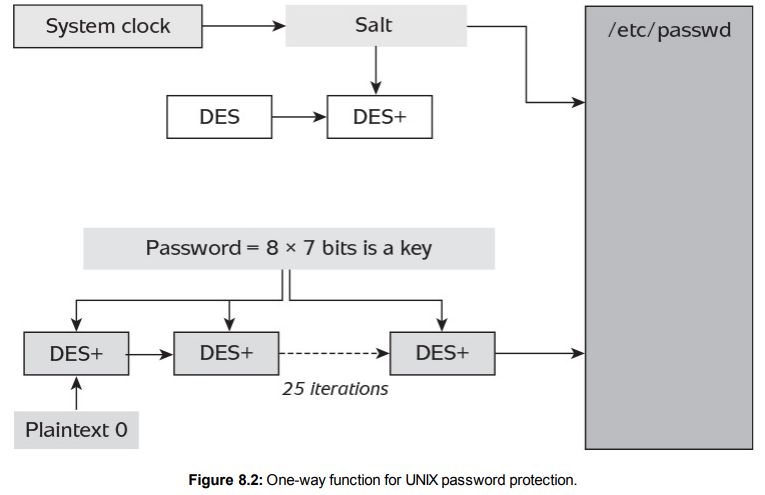
One example of a cryptographic primitive being used to create a one-way function is illustrated in Figure 8.2. This function was used in many early UNIX operating systems for password database protection.
密码学代写
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography代考|Problems with passwords
密码吸引人的特点是简单和熟悉。这就是它们被普遍用作身份信息的原因。然而,它们有几个缺陷,严重限制了使用它们的任何应用程序的安全性:
长度。由于密码是为人类记忆而设计的,所以它们的长度是有自然限制的。这意味着密码空间(所有可能的密码)的大小是有限的,从而限制了对所有密码进行详尽搜索所需的工作量。
的复杂性。在应用程序中很少使用完整的密码空间,因为人们发现随机生成的密码很难记住。因此,我们经常使用高度受限的密码空间,这大大降低了安全性。这使得字典攻击成为可能,攻击者简单地尝试所有“可能”的密码,并希望最终找到正确的密码(参见第1.6.5节)。聪明的助记技术可以稍微增加可用密码空间的大小。当用户被要求使用复杂的密码时,很快就会达到可用性和安全性之间的权衡,因为复杂的密码更有可能以书面形式被转移到“索赔人拥有的东西”中,这在很多情况下违背了使用密码的初衷。从密码到密码短语可以通过显著增加密码空间来改善这种情况;然而,密码的许多其他问题仍然存在。
可重复性。在密码的生命周期内,每次使用它都是完全相同的。这意味着,如果攻击者可以获得密码,那么就会有一段时间(通常很长),在这段时间内,密码可以被用来欺诈性地声称原始所有者的身份。限制这种威胁的一种措施是定期强制更改密码。然而,这再次引发了可用性问题,因为定期更改密码会让人们感到困惑,并可能导致不安全的密码存储实践。
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography代考|Cryptographic password protection
考虑一个大型组织希望使用密码对其内部系统的许多用户进行身份验证。实现这一点的一个明显方法是使用一个系统,将提供的密码与存储在集中密码数据库中的密码进行比较。这使得密码数据库成为攻击者极具吸引力的目标,因为该数据库可能包含帐户名称和密码的完整列表。即使这个数据库得到了仔细的管理,系统的管理员也有可能访问这个列表,这可能是不可取的。
密码学可以用来帮助实现基于密码的识别系统的一个领域是保护密码数据库。这是因为,为了对用户进行身份验证,系统实际上并不需要知道用户的密码。相反,设备只需要知道提供的密码是否正确。关键是,虽然用户确实需要输入正确的密码,但系统不需要存储该密码的副本来验证它是否正确。
在6.2.2节中,我们描述了一个实现密码数据库保护的哈希函数的应用。其思想是在密码数据库中存储密码的哈希值,而不是实际的密码。这样可以检查密码,同时防止任何获得密码数据库访问权限的人自己恢复密码。我们观察到,任何被认为是单向的函数(包括散列函数)理论上都可以用来提供此服务。
传统的Unix密码保护方法
图8.2展示了使用加密原语创建单向函数的一个示例。这个函数在许多早期的UNIX操作系统中用于密码数据库保护。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。