数学代写|图论作业代写Graph Theory代考|MA57500
如果你也在 怎样代写图论Graph Theory 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。图论Graph Theory有趣的部分原因在于,图可以用来对某些问题中的情况进行建模。这些问题可以在图表的帮助下进行研究(并可能得到解决)。因此,图形模型在本书中经常出现。然而,图论是数学的一个领域,因此涉及数学思想的研究-概念和它们之间的联系。我们选择包含的主题和结果是因为我们认为它们有趣、重要和/或代表主题。
图论Graph Theory通过熟悉许多过去和现在对图论的发展负责的人,可以增强对图论的欣赏。因此,我们收录了一些关于“图论人士”的有趣评论。因为我们相信这些人是图论故事的一部分,所以我们在文中讨论了他们,而不仅仅是作为脚注。我们常常没有认识到数学是一门有生命的学科。图论是人类创造的,是一门仍在不断发展的学科。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写图论Graph Theory方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写图论Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写图论Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着说。
数学代写|图论作业代写Graph Theory代考|Hamiltonian Graphs
An Eulerian circuit visits each edge exactly once, but may visit some vertices more than once. In this section, we consider a round trip through a given graph $G$ such that every vertex is visited exactly once. The original question was posed by a well-known Irish mathematician, Sir William Rowan Hamilton.
Let $G$ be a graph. A path in $G$ that includes every vertex of $G$ is called a Hamiltonian path of $G$. A cycle in $G$ that includes every vertex in $G$ is called a Hamiltonian cycle of $G$. If $G$ contains a Hamiltonian cycle, then $G$ is called a Hamiltonian Graph.
Every Hamiltonian cycle of a Hamiltonian graph of $n$ vertices has exactly $n$ vertices and $n$ edges. If the graph is not a cycle, some edges of $G$ are not included in a Hamiltonian Cycle.
Not all graphs are Hamiltonian. For example, the graph in Fig. 3.6(a) is Hamiltonian, since $a, b, c, d, a$ is a Hamiltonian cycle. On the other hand, the graph in Fig. 3.6(b) is not Hamiltonian, since there is no Hamiltonian cycle in this graph. Note that the path $a, b, c, d, e$ is a Hamiltonian path in the graph in Fig. 3.6(b). Thus a natural question is: What is the necessary and sufficient condition for a graph to be Hamiltonian? Clearly a Hamiltonian graph must be connected and cannot be acyclic, but these are not sufficient. The graph in Fig. 3.6(b) is connected and not acyclic but it is not Hamiltonian. The following lemma gives a necessary condition which is not also sufficient.
数学代写|图论作业代写Graph Theory代考|Connectivity
The connectivity $\kappa(G)$ of a connected graph $G$ is the minimum number of vertices whose removal results in a disconnected graph or a single vertex graph $K_1$. A graph $G$ is $k$-connected if $\kappa(G) \geq k$. A separating set or a vertex cut of a connected graph $G$ is a set $S \subset V(G)$ such that $G-S$ has more than one component. If a vertex cut contains exactly one vertex, then we call the vertex cut a cut vertex. If a vertex cut in a 2-connected graph contains exactly two vertices, then we call the two vertices a separation-pair.
The edge connectivity $\kappa^{\prime}(G)$ of a connected graph $G$ is the minimum number of edges whose removal results in a disconnected graph. A graph is $k$-edge-connected if $\kappa^{\prime}(G) \geq k$. A disconnecting set of edges in a connected graph is a set $F \subseteq E(G)$ such that $G-F$ has more than one component. If a disconnecting set contains exactly one edge, it is called a bridge.
For two disjoint subsets $S$ and $T$ of $V(G)$, we denote [ $S, T]$ the set of edges which have one endpoint in $S$ and the other in $T$. An edge cut is an edge set of the form $[S, \bar{S}]$, where $S$ is a nonempty proper subset of $V(G)$ and $\bar{S}$ denotes $V(G)-S$.
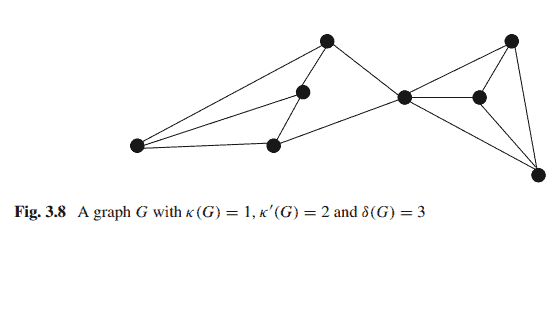
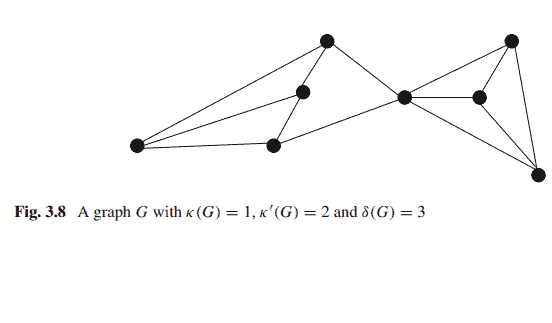
We now explore the relationship among the connectivity $\kappa(G)$, the edge connectivity $\kappa^{\prime}(G)$, and the minimum degree $\delta(G)$ of a connected simple graph $G$. In a cycle of three or more vertices $\kappa(G)=\kappa^{\prime}(G)=\delta(G)=2$. For complete graphs of $n \geq 1$ vertices $\kappa(G)=\kappa^{\prime}(G)=\delta(G)=n-1$. For the graph $G$ in Fig.3.8, $\kappa(G)=1$,$\kappa^{\prime}(G)=2$ and $\delta(G)=3$. Whitney in 1932 showed that the following relationship holds [3].
图论代考
数学代写|图论作业代写Graph Theory代考|Hamiltonian Graphs
欧拉电路只访问每条边一次,但可能访问一些顶点不止一次。在本节中,我们考虑通过给定图$G$的往返行程,这样每个顶点都只访问一次。最初的问题是由著名的爱尔兰数学家威廉·罗文·汉密尔顿爵士提出的。
假设$G$是一个图表。在$G$中包含$G$的每个顶点的路径称为$G$的哈密顿路径。$G$中包含$G$中所有顶点的循环称为$G$的哈密顿循环。如果$G$包含哈密顿循环,则$G$称为哈密顿图。
一个含有$n$个顶点的哈密顿图的每个哈密顿循环都有$n$个顶点和$n$条边。如果图不是一个环,$G$的一些边不包含在哈密顿环中。
不是所有的图都是哈密顿图。例如,图3.6(a)中的图是哈密顿循环,因为$a, b, c, d, a$是哈密顿循环。另一方面,图3.6(b)中的图不是哈密顿图,因为图中没有哈密顿循环。注意,路径$a, b, c, d, e$是图3.6(b)图中的哈密顿路径。因此一个自然的问题是:一个图是哈密顿图的充要条件是什么?显然,哈密顿图必须是连通的,不能是无环的,但这是不够的。图3.6(b)中的图是连通的,不是无环的,但不是哈密顿的。下面的引理给出了一个必要条件,但不是充分条件。
数学代写|图论作业代写Graph Theory代考|Connectivity
连通图的连通性$\kappa(G)$$G$是指去除连通图或单顶点图的最小顶点数$K_1$。如果$\kappa(G) \geq k$,图形$G$是$k$连接的。连通图$G$的分离集或顶点切割是一个集$S \subset V(G)$,使得$G-S$有多个组件。如果一个顶点切面只包含一个顶点,那么我们称这个顶点切面为切面顶点。如果一个2连通图中的顶点切割恰好包含两个顶点,那么我们称这两个顶点为分离对。
连通图的边连通性$\kappa^{\prime}(G)$$G$是指去除连通图的最小边数。图是$k$ -边连通的,如果$\kappa^{\prime}(G) \geq k$。连通图中的断开边集是一个集$F \subseteq E(G)$,使得$G-F$有多个组件。如果一个断开集只包含一条边,它被称为桥。
对于$V(G)$的两个不相交的子集$S$和$T$,我们将[$S, T]$]表示为一个端点在$S$而另一个端点在$T$的边集。切边是形式为$[S, \bar{S}]$的边集,其中$S$是$V(G)$的非空固有子集,$\bar{S}$表示$V(G)-S$。
我们现在探索连通度$\kappa(G)$、边连通度$\kappa^{\prime}(G)$和连通简单图$G$的最小度$\delta(G)$之间的关系。在三个或更多顶点的循环中$\kappa(G)=\kappa^{\prime}(G)=\delta(G)=2$。对于$n \geq 1$顶点的完整图$\kappa(G)=\kappa^{\prime}(G)=\delta(G)=n-1$。对于图3.8中的$G$,分别为$\kappa(G)=1$、$\kappa^{\prime}(G)=2$和$\delta(G)=3$。Whitney(1932)表明以下关系成立[3]。

统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。