数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|MTH251
如果你也在 怎样代写微积分Calculus 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。微积分Calculus 基本上就是非常高级的代数和几何。从某种意义上说,它甚至不是一门新学科——它采用代数和几何的普通规则,并对它们进行调整,以便它们可以用于更复杂的问题。(当然,问题在于,从另一种意义上说,这是一门新的、更困难的学科。)
微积分Calculus数学之所以有效,是因为曲线在局部是直的;换句话说,它们在微观层面上是直的。地球是圆的,但对我们来说,它看起来是平的,因为与地球的大小相比,我们在微观层面上。微积分之所以有用,是因为当你放大曲线,曲线变直时,你可以用正则代数和几何来处理它们。这种放大过程是通过极限数学来实现的。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写微积分Calculus方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写微积分Calculus代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写微积分Calculus相关的作业也就用不着说。
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
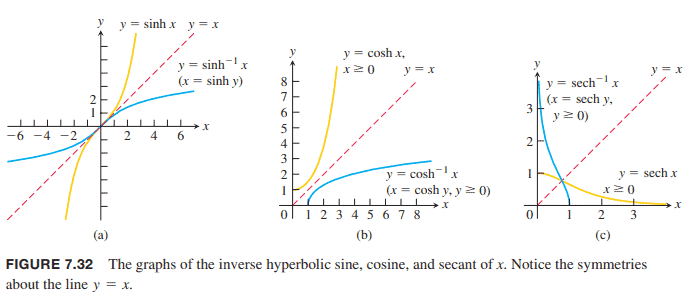
The inverses of the six basic hyperbolic functions are very useful in integration . Since $d(\sinh x) / d x=\cosh x>0$, the hyperbolic sine is an increasing function of $x$. We denote its inverse by
$$
y=\sinh ^{-1} x .
$$
For every value of $x$ in the interval $-\infty<x<\infty$, the value of $y=\sinh ^{-1} x$ is the number whose hyperbolic sine is $x$. The graphs of $y=\sinh x$ and $y=\sinh ^{-1} x$ are shown in Figure 7.32a.
The function $y=\cosh x$ is not one-to-one because its graph in Table 7.5 does not pass the horizontal line test. The restricted function $y=\cosh x, x \geq 0$, however, is oneto-one and therefore has an inverse, denoted by
$$
y=\cosh ^{-1} x .
$$
For every value of $x \geq 1, y=\cosh ^{-1} x$ is the number in the interval $0 \leq y<\infty$ whose hyperbolic cosine is $x$. The graphs of $y=\cosh x, x \geq 0$, and $y=\cosh ^{-1} x$ are shown in Figure 7.32b.
Like $y=\cosh x$, the function $y=\operatorname{sech} x=1 / \cosh x$ fails to be one-to-one, but its restriction to nonnegative values of $x$ does have an inverse, denoted by
$$
y=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x .
$$
For every value of $x$ in the interval $(0,1], y=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x$ is the nonnegative number whose hyperbolic secant is $x$. The graphs of $y=\operatorname{sech} x, x \geq 0$, and $y=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x$ are shown in Figure 7.32c.
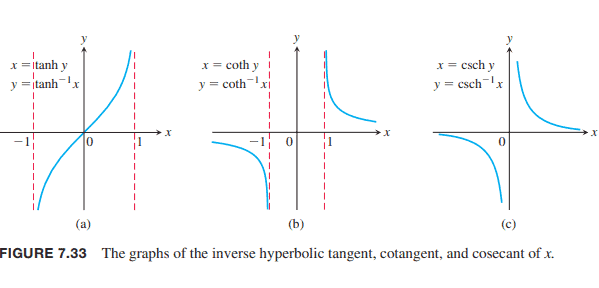
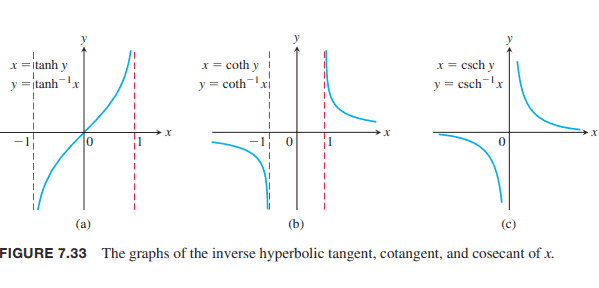
The hyperbolic tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are one-to-one on their domains and therefore have inverses, denoted by
$$
y=\tanh ^{-1} x, \quad y=\operatorname{coth}^{-1} x, \quad y=\operatorname{csch}^{-1} x .
$$
These functions are graphed in Figure 7.33.
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Useful Identities
We use the identities in Table 7.9 to calculate the values of $\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x, \operatorname{csch}^{-1} x$, and $\operatorname{coth}^{-1} x$ on calculators that give only $\cosh ^{-1} x, \sinh ^{-1} x$, and $\tanh ^{-1} x$. These identities are direct consequences of the definitions. For example, if $0<x \leq 1$, then
$$
\operatorname{sech}\left(\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)\right)=\frac{1}{\cosh \left(\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)\right)}=\frac{1}{\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)}=x .
$$
We also know that $\operatorname{sech}\left(\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x\right)=x$, so because the hyperbolic secant is one-to-one on $(0,1]$, we have
$$
\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x
$$
微积分代考
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
六个基本双曲函数的逆在积分中非常有用。由于$d(\sinh x) / d x=\cosh x>0$,双曲正弦函数是$x$的递增函数。我们用
$$
y=\sinh ^{-1} x .
$$
对于区间$-\infty<x<\infty$中每个$x$的值,$y=\sinh ^{-1} x$的值是双曲正弦值为$x$的数。$y=\sinh x$和$y=\sinh ^{-1} x$的曲线图如图7.32a所示。
函数$y=\cosh x$不是一对一的,因为它在表7.5中的图形没有通过水平线检验。然而,受限函数$y=\cosh x, x \geq 0$是一对一的,因此有一个逆,表示为
$$
y=\cosh ^{-1} x .
$$
对于$x \geq 1, y=\cosh ^{-1} x$的每个值,表示在$0 \leq y<\infty$区间内的双曲余弦值为$x$的数。$y=\cosh x, x \geq 0$和$y=\cosh ^{-1} x$的曲线图如图7.32b所示。
像$y=\cosh x$一样,函数$y=\operatorname{sech} x=1 / \cosh x$不是一对一的,但是它对$x$的非负值的限制确实有一个逆,表示为
$$
y=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x .
$$
对于区间内$x$的每一个值$(0,1], y=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x$都是其双曲正割为$x$的非负数。$y=\operatorname{sech} x, x \geq 0$和$y=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x$的图形如图7.32c所示。
双曲正切,余切和余割在它们的定义域上是一对一的,因此有逆,表示为
$$
y=\tanh ^{-1} x, \quad y=\operatorname{coth}^{-1} x, \quad y=\operatorname{csch}^{-1} x .
$$
这些函数如图7.33所示。
数学代写|微积分代写Calculus代写|Useful Identities
我们使用表7.9中的恒等式在只给出$\cosh ^{-1} x, \sinh ^{-1} x$和$\tanh ^{-1} x$的计算器上计算$\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x, \operatorname{csch}^{-1} x$和$\operatorname{coth}^{-1} x$的值。这些恒等式是定义的直接结果。例如,如果$0<x \leq 1$,则
$$
\operatorname{sech}\left(\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)\right)=\frac{1}{\cosh \left(\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)\right)}=\frac{1}{\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)}=x .
$$
我们还知道$\operatorname{sech}\left(\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x\right)=x$,因为双曲正割在$(0,1]$上是一对一的,我们有
$$
\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)=\operatorname{sech}^{-1} x
$$
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。