如果你也在 怎样代写数据可视化data visualization这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
数据可视化是信息和数据的图形化表示,通过使用像图表、图形和地图这样的视觉元素,数据可视化工具提供了一种方便的方式来查看和理解数据的趋势、异常值和模式。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写数据可视化data visualization方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写数据可视化data visualization方面经验极为丰富,各种代写数据可视化data visualization相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的数据可视化data visualization及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|数据可视化作业代写data visualization代考|Selecting an Appropriate Chart
How do you choose an appropriate chart? If the goal of your chart is to explain, then the answer to this question depends on the message you wish to convey to your audience. If you are exploring data, the best chart type depends on the question you are asking and hope
to answer from the data. Also, the type of data you have may influence your chart selection. A few of the more common goals for charts are to show the following:
- Composition-Composition is what makes up the whole of an entity under consideration. An example is the bar chart in Figure 2.2.
- Ranking-Ranking is the relative order of items. Figure $2.2$ is also an example of ranking, because we have sorted the categories by bar length, which is proportional to the amounts allocated.
- Correlation/Relationship-Correlation is how two variables are related to one another. An example of this is the relationship between average low temperature and average annual snowfall for various cities in the United States.
- Distribution-Distribution is how items are dispersed. An example of this is the number of calls received by a call center in a day, measured on an hourly basis.
The type of data you have should also influence your chart selection. For example, a bar or column chart is often an appropriate chart when we are summarizing data about categories. Students’ letter grades in a college course are categories. For summarizing the number of students earning each letter grade, a bar or column chart would be appropriate.
The relationship between two quantitative variables often makes a scatter chart an appropriate choice. Bar charts, scatter charts, and line charts with the horizontal axis being time, are often the best choice for time series data. If your data have a spatial component, a geographic map might be a good choice.
Creating great data visualizations is a skill that is best learned by doing. Therefore, before getting into more detail on the various types of charts and in what circumstances they are most appropriate, we provide detailed instructions on how to create and edit charts in Excel.
统计代写|数据可视化作业代写data visualization代考|Scatter Charts and Bubble Charts
When exploring data, we are often interested in the relationship between two quantitative variables. For example, we might be interested in the square footage of a house and the cost of the house, or the age of a car and its annual maintenance cost. A scatter chart is a graphical presentation of the relationship between two quantitative variables. One variable is shown on the horizontal axis and the other is shown on the vertical axis, and a symbol is used to plot ordered pairs of the quantitative variable values. A scatter chart is appropriate for better understanding the relationship between two quantitative variables. As we shall also see, a bubble chart is an appropriate chart when trying to show relationships with more than two quantitative variables.
The file Snow contains the average low temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and the average annual snowfall in inches for 51 major cities in the United States. A portion of the data are shown in Figure 2.6. These averages are based on thirty years of data. Suppose we are interested in the relationship between these two variables. Intuition tells us that the higher the average low temperature the lower the average snowfall, but what is the nature of this relationship?
The data are plotted in Figure 2.7. This scatter chart is created using the following steps.
Step 1. Select cells Cl:D52
Stẹp 2. Click the Insert tabb oñ the Ribbon
Step 3. Click the Insert Scatter (X,Y) or Bubble Chart button $\because \times$ in the Charts group
When the list chart subtypes appears, click the Scatter button $\angle \%$ Then edit the chart as outlined in Section 2-2.
Each point on the chart in Figure $2.7$ represents a pair of numbers. In this case, we have a pair of measurements for each of 51 cities. The measurements are average low temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and average annual amount of snowfall in inches. We can see from the chart that average annual amount of snowfall intuitively levels off at zero for warmweather cities.
Scatter charts are among the most useful charts for exploring pairs of quantitative data. But, what if you wish to explore the relationships between more than two quantitative variables? When exploring the relationships between three quantitative variables, a bubble chart may be useful.
统计代写|数据可视化作业代写data visualization代考|Bubble Charts
A bubble chart is a scatter chart that displays a third quantitative variable using different sized dots, which we refer to as bubbles.
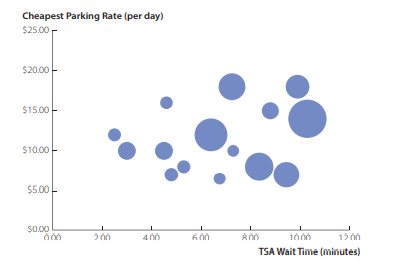
The file AirportData contains data on a sample of 15 airports. These data are shown in Figure 2.8. For each airport, we have the following quantitative variables: average wait time in the non-priority Transportation Security Authority (TSA) queue measured in minutes, the cheapest on-site daily rate for parking at the airport measured in dollars, and the number of enplanements in a year (the number of passengers who board including transfers) measured in millions of passengers.
Step 3. Click the Insert Scatter (X,Y) or Bubble Chart button When the list of chart subtypes appears, click the Bubble button 88 Then edit the chart as outlined in Section 2-2.
We plot the TSA wait time along the horizontal axis and the parking rate along the vertical axis, and vary the size of each bubble to represent the number of enplanements. We see that airports with fewer passengers tend to have lower wait times than those with more passengers. There seems to be less of a relationship between parking rate and number of passengers. Airports with lower wait times do tend to have lower parking rates.
In a bubble chart, you might wish to change which variables correspond to the $x$ (horizontal) values, the $y$ (vertical) values, and the bubble sizes. Once the chart has been created in Excel, the following steps can be used to change these assignments.
Step 1. Right-click any bubble and choose Select Data…
Step 2. When the Select Data Source dialog box appears, click the Edit button under Legend Entries (Series)
Step 3. Enter the location of the data you want to correspond to the horizontal values in the Series X values: box (see Figure 2.10). Do not include column headers Step 4. Repeat Step 3 for Series Y Values: box and the Series bubble size: box Click OK.
数据可视化代写
统计代写|数据可视化作业代写data visualization代考|Selecting an Appropriate Chart
如何选择合适的图表?如果图表的目标是解释,那么这个问题的答案取决于您希望传达给听众的信息。如果您正在探索数据,最佳图表类型取决于您提出的问题和希望
从数据中回答。此外,您拥有的数据类型可能会影响您的图表选择。图表的一些更常见的目标是显示以下内容:
- Composition-Composition 构成了所考虑的实体的整体。一个例子是图 2.2 中的条形图。
- Ranking-Ranking是项目的相对顺序。数字2.2也是排名的一个例子,因为我们已经按照条形长度对类别进行了排序,条形长度与分配的数量成正比。
- 相关性/关系-相关性是两个变量相互关联的方式。这方面的一个例子是美国各个城市的平均低温和年平均降雪量之间的关系。
- Distribution-Distribution 是项目的分散方式。这方面的一个例子是呼叫中心在一天内接到的电话数量,按小时计算。
您拥有的数据类型也应该影响您的图表选择。例如,当我们汇总有关类别的数据时,条形图或柱形图通常是合适的图表。大学课程中学生的字母成绩属于类别。为了总结获得每个字母等级的学生人数,条形图或柱形图将是合适的。
两个定量变量之间的关系通常使散点图成为合适的选择。横轴为时间的条形图、散点图和折线图通常是时间序列数据的最佳选择。如果您的数据具有空间组件,则地图可能是一个不错的选择。
创建出色的数据可视化是一项最好通过实践来学习的技能。因此,在详细了解各种类型的图表以及它们最适合的情况之前,我们提供了有关如何在 Excel 中创建和编辑图表的详细说明。
统计代写|数据可视化作业代写data visualization代考|Scatter Charts and Bubble Charts
在探索数据时,我们经常对两个定量变量之间的关系感兴趣。例如,我们可能对房屋的平方英尺和房屋成本感兴趣,或者对汽车的使用年限及其年度维护成本感兴趣。散点图是两个定量变量之间关系的图形表示。一个变量显示在水平轴上,另一个显示在垂直轴上,并且使用符号来绘制定量变量值的有序对。散点图适用于更好地理解两个定量变量之间的关系。正如我们还将看到的,当试图显示与两个以上定量变量的关系时,气泡图是一种合适的图表。
文件 Snow 包含美国 51 个主要城市的平均低温(以华氏度为单位)和年平均降雪量(以英寸为单位)。部分数据如图 2.6 所示。这些平均值基于三十年的数据。假设我们对这两个变量之间的关系感兴趣。直觉告诉我们,平均低温越高,平均降雪量越低,但这种关系的本质是什么?
数据绘制在图 2.7 中。此散点图是使用以下步骤创建的。
步骤 1. 选择单元格 Cl:D52
Stẹp 2. 单击功能区上的插入选项卡
步骤 3. 单击插入散点图 (X,Y) 或气泡图按钮∵×在 Charts 组中
当列表图表子类型出现时,单击 Scatter 按钮∠%然后按照第 2-2 节所述编辑图表。
图中图表上的每个点2.7代表一对数字。在这种情况下,我们对 51 个城市中的每一个都有一对测量值。测量值是以华氏度为单位的平均低温和以英寸为单位的年平均降雪量。从图表中我们可以看出,对于温暖天气的城市,年平均降雪量直观地趋于零。
散点图是探索定量数据对的最有用的图表之一。但是,如果您想探索两个以上定量变量之间的关系怎么办?在探索三个定量变量之间的关系时,气泡图可能很有用。
统计代写|数据可视化作业代写data visualization代考|Bubble Charts
气泡图是一种散点图,它使用不同大小的点显示第三个定量变量,我们将其称为气泡。
文件 AirportData 包含 15 个机场样本的数据。这些数据如图 2.8 所示。对于每个机场,我们有以下定量变量:非优先运输安全局 (TSA) 队列中的平均等待时间(以分钟为单位)、机场最便宜的现场停车日费率(以美元为单位)以及停车人数一年中的飞机数量(包括转机在内的登机乘客人数)以百万乘客计。
步骤 3. 单击插入散点图 (X,Y) 或气泡图按钮 当图表子类型列表出现时,单击气泡按钮 88 然后按照第 2-2 节所述编辑图表。
我们沿横轴绘制 TSA 等待时间,沿纵轴绘制停车率,并改变每个气泡的大小以表示飞机的数量。我们发现,乘客较少的机场的等待时间往往比乘客较多的机场要短。停车费和乘客数量之间的关系似乎不大。等待时间较短的机场确实往往有较低的停车费。
在气泡图中,您可能希望更改哪些变量对应于X(水平)值,是(垂直)值和气泡大小。在 Excel 中创建图表后,可以使用以下步骤更改这些分配。
步骤 1. 右键单击任何气泡并选择 Select Data…
Step 2. 当 Select Data Source 对话框出现时,单击 Legend Entries (Series) 下的 Edit 按钮
Step 3. 输入您想要对应的数据的位置Series X values: 框中的水平值(参见图 2.10)。不包括列标题 第 4 步。对 Y 系列值重复第 3 步:框和系列气泡大小:框单击确定。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
