如果你也在 怎样代写密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
密码学创造了具有隐藏意义的信息;密码分析是破解这些加密信息以恢复其意义的科学。许多人用密码学一词来代替密码学;然而,重要的是要记住,密码学包括了密码学和密码分析。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考|Towards Block Ciphers
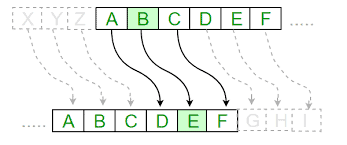
One counter to frequency analysis is to permute pairs of letters, that is, our permutation acts on the set $S$ of pairs of letters, not the alphabet.
Exercise 1.15. For a substitution cipher based on permutations on pairs, write down carefully what the three sets $\mathfrak{R}, \mathfrak{P}, \mathfrak{C}$ are, and implement the two algorithms $\mathcal{E}$ and $\mathcal{D}$. Show that $(\mathfrak{R}, \mathfrak{P}, \mathfrak{C}, \mathcal{E}, \mathcal{D})$ is a symmetric cryptosystem.
Unfortunately, the frequencies of pairs are uneven, which means that frequency analysis still works, although it is less effective. A permutation on triples of letters would be better, but still not perfect.
Even better would be $L$-tuples. The number $L$ is called the block length. Unfortunately, representing a random permutation over a large set is impractical. Merely writing down a permutation requires at least $\log _2\left(|S|^{L} !\right) \approx$ $|S|^L\left(\ln |S|^L-1\right) / \ln 2$ binary digits.
One idea would be to use not a random permutation, but instead use a random member of some smaller family of permutations.
Example 1.5. The Hill cipher is an example of such a family of permutations, the permutations given by invertible matrices. We give our alphabet $R$ a ring structure, say $\mathbb{Z}_{26}$. We denote an $L$-tuple of letters as $\mathrm{m} \in R^L$. An invertible $L \times L$ matrix $\mathbf{K}$ acts on $L$-tuples through matrix multiplication, denoted by $\mathrm{Km}$.
The plaintext $m$ is a sequence of $L$-tuples of letters $\mathrm{m}_1 \mathrm{~m}_2 \ldots \mathrm{m}_l$. The key is an invertible $L \times L$ matrix $\mathbf{K}$. We encrypt the message using the formula
$$
\mathrm{c}_i=\mathbf{K}_i, \quad 1 \leq i \leq l .
$$
The ciphertext $c$ is the sequence of $L$-tuples $c_1 c_2 \ldots c_l$.
To decrypt a ciphertext $c=\mathrm{c}_1 \ldots \mathrm{c}_l$, we compute the $i$ th plaintext tuple using the formula
$$
\mathbf{m}_i=\mathbf{K}^{-1} \mathbf{c}_i, \quad 1 \leq i \leq l .
$$
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考|Practical Mathematical Cryptography
Choosing a good round function is difficult, especially when the goal is to find a round function that can be computed very quickly and that does not require many rounds. Again, this problem is out of scope for this book.
Padding Schemes The plaintext set for the cryptosystem from Exercise $1.24$ is the set of finite sequences of elements from $S$, where each set element is typically an $L$-tuple of letters from the alphabet. In other words, the plaintext set is the set of letter sequences whose length is divisible by $L$.
But when $L$ is large, it is unreasonable to expect message lengths to be a multiple of $L$. We usually need to encrypt arbitrary sequences of letters. Since we need to decrypt correctly, we cannot just append some fixed letter until the sequence length is a multiple of $L$.
We extend a cryptosystem to accept sequences of any length by applying a suitable injective function before encryption.
Definition 1.3. Let $\mathfrak{P}$ and $\mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ be sets. A padding scheme for $\mathfrak{P}$ and $\mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ consists of two functions $\iota: \mathfrak{F} \rightarrow \mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ and $\lambda: \mathfrak{P}^{\prime} \rightarrow \mathfrak{P} \cup{\perp}$ satisfying
$$
\lambda(\iota(m))=m \text { for all } m \in \mathfrak{P} \text {. }
$$
Exercise 1.25. Suppose you have a cryptosystem $\left(\mathfrak{k}, \mathfrak{P}^{\prime}, \mathfrak{C}, \mathcal{E}^{\prime}, \mathcal{D}^{\prime}\right)$ and a padding scheme $(\iota, \lambda)$ for $\mathfrak{F}$ and $\mathfrak{F}^{\prime}$. Based on the padding scheme and the cryptosystem, construct a new cryptosystem $(\mathfrak{K}, \mathfrak{P}, \mathfrak{C}, \mathcal{E}, \mathcal{D})$. Show that it is indeed a cryptosystem.
Typically, the alphabet is ${0,1}$ and the set is $S={0,1}^L$, bit strings of length $L$. The plaintext set $\mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ will then be bit strings of length divisible by $L$.
One padding scheme is the following: We first add one 1-bit, then we add 0-bits until the total length is divisible by $L$. If the block size $L$ is 8 , the bit string 10101 will become 10101100 . If the block size $L$ is 5 , the bit string 01010 becomes 0101010000 .
密码学代写
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考|Towards Block Ciphers
频率分析的一个反例是排列成对的字母,也就是说,我们的排列作用于集合 $S$ 成对的字母,而不是字母表。
练习 1.15。对于基于对排列的替代密码,请仔细写下这三个集合 $\Re, \mathfrak{P}, \mathfrak{C}$ 是,并实现这两种算法 $\mathcal{E}$ 和 $\mathcal{D}$. 显示 $(\Re, \mathfrak{P}, \mathfrak{C}, \mathcal{E}, \mathcal{D})$ 是对称密码体制。
不幸的是,对的频率是不均匀的,这意味着频率分析仍然有效,尽管它不太有效。字母三元组的排列会更好,但 仍不完美。
更好的是 $L$-元组。号码 $L$ 称为块长度。不幸的是,表示一个大集合的随机排列是不切实际的。仅仅写下一个排列 至少需要 $\log 2\left(|S|^{L} !\right) \approx|S|^L\left(\ln |S|^L-1\right) / \ln 2$ 二进制数字。 一个想法是不使用随机排列,而是使用一些较小排列族的随机成员。 例 1.5。希尔密码就是这种排列族的一个例子,由可逆矩阵给出的排列。我们给我们的字母表 $R$ 环形结构,比如 说 $\mathbb{Z}{26}$. 我们表示一个 $L$-字母元组为 $\mathrm{m} \in R^L$. 一个可翻转的 $L \times L$ 矩阵 $\mathbf{K}$ 作用于 $L$-通过矩阵乘法的元组,表示 为 $\mathrm{Km}$.
明文 $m$ 是一个序列 $L$-字母元组 $\mathrm{m}_1 \mathrm{~m}_2 \ldots \mathrm{m}_l$. 钥题是可逆的 $L \times L$ 矩阵 $\mathbf{K}$. 我们使用公式加密消息
$$
\mathrm{c}_i=\mathbf{K}_i, \quad 1 \leq i \leq l .
$$
解密密文 $c=c_1 \ldots c_l$ ,我们计算 $i$ 使用公式的第 th 个明文元组
$$
\mathbf{m}_i=\mathbf{K}^{-1} \mathbf{c}_i, \quad 1 \leq i \leq l
$$
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考|Practical Mathematical Cryptography
选择一个好的轮函数很困难,尤其是当目标是找到一个可以非常快速地计算并且不需要很多轮的轮函数时。同 样,这个问题超出了本书的范围。
填充方案练习中密码系统的明文集 $1.24$ 是元素的有限序列的集合 $S$ ,其中每个集合元素通常是一个 $L$-字母表中 字母的元组。换句话说,明文集是字母序列的集合,其长度可以被整除 $L$.
但当 $L$ 很大,期望消息长度是以下的倍数是不合理的 $L$. 我们通常需要加密任意字母序列。因为我们需要正确解 密,所以我们不能只附加一些固定的字母,直到序列长度是以下的倍数 $L$.
我们通过在加密前应用合适的单射函数来扩展密码系统以接受任何长度的序列。
定义 1.3。让 $\mathfrak{P}$ 和 $\mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ 被套。一个填充方案 $\mathfrak{P}$ 和 $\mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ 由两个函数组成 $\iota: \mathfrak{F} \rightarrow \mathfrak{P}^{\prime}$ 和 $\lambda: \mathfrak{P}^{\prime} \rightarrow \mathfrak{P} \cup \perp$ 令人满意的 $\lambda(\iota(m))=m$ for all $m \in \mathfrak{P}$.
练习 1.25。假设你有一个密码系统 $\left(\mathfrak{k}, \mathfrak{P}^{\prime}, \mathfrak{C}, \mathcal{E}^{\prime}, \mathcal{D}^{\prime}\right)$ 和填充方案 $(\iota, \lambda)$ 为了 $\mathfrak{F}$ 和 $\mathfrak{F}^{\prime}$. 基于填充方案和密码体制, 构造一个新的密码体制 $(\mathfrak{K}, \mathfrak{P}, \mathfrak{C}, \mathcal{E}, \mathcal{D})$. 证明它确实是一个密码系统。
通常,字母表是 0,1 集合是 $S=0,1^L$ ,位串长度 $L$. 明文集郋 然后将是长度可被整除的位串 $L$.
一种填充方案如下: 我们首先添加一个 1 位,然后我们添加 0 位,直到总长度可以被 $L$. 如果块大小 $L$ 为 8 ,位 串 10101 将变为 10101100 。如果块大小 $L$ 是 5,位串 01010 变成 0101010000 。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
