如果你也在 怎样代写matlab这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
MATLAB是一个编程和数值计算平台,被数百万工程师和科学家用来分析数据、开发算法和创建模型。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写matlab方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写matlab代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写matlab相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的matlab及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
数学代写|matlab代写|Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning which is itself a subset of artificial intelligence and statistics. Artificial intelligence research began shortly after World War II [35]. Early work was based on the knowledge of the structure of the brain, propositional logic, and Turing’s theory of computation. Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts created a mathematical formulation for neural networks based on threshold logic. This allowed neural network research to split into two approaches: one centered on biological processes in the brain and the other on the application of neural networks to artificial intelligence. It was demonstrated that any function could be implemented through a set of such neurons and that a neural net could learn to recognize patterns. In 1948, Norbert Wiener’s book Cybernetics was published which described concepts in control, communications, and statistical signal processing. The next major step in neural networks was Donald Hebb’s book in 1949, The Organization of Behavior, connecting connectivity with learning in the brain. His book became a source of learning and adaptive systems. Marvin Minsky and Dean Edmonds built the first neural computer at Harvard in 1950.
The first computer programs, and the vast majority now, have knowledge built into the code by the programmer. The programmer may make use of vast databases. For example, a model of an aircraft may use multidimensional tables of aerodynamic coefficients. The resulting software, therefore, knows a lot about aircraft, and running simulations of the models may present surprises to the programmer and the users since they may not fully understand the simulation, or may have entered erroneous inputs. Nonetheless, the programmatic relationships between data and algorithms are predetermined by the code.
In machine learning, the relationships between the data are formed by the learning system. Data is input along with the results related to the data. This is the system training. The machine learning system relates the data to the results and comes up with rules that become part of the system. When new data is introduced, it can come up with new results that were not part of the training set.
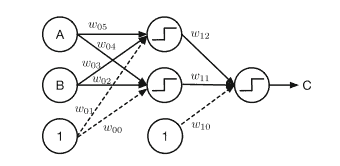
Deep learning refers to neural networks with more than one layer of neurons. The name “deep learning” implies something more profound, and in the popular literature, it is taken to imply that the learning system is a “deep thinker.” Figure $1.1$ shows a single-layer and multi-layer network. It turns out that multi-layer networks can learn things that single-layer networks cannot. The elements of a network are nodes, where weighted signals are combined and biases added. In a single layer, the inputs are multiplied by weights and then added together at the end, after passing through a threshold function. In a multi-layer or “deep learning” network, the inputs are combined in the second layer before being output. There are more weights and the added connections allow the network to learn and solve more complex problems.
数学代写|matlab代写|History of Deep Learning
Minsky wrote the book Perceptrons with Seymour Papert in 1969 , which was an early analysis of artificial neural networks. The book contributed to the movement toward symbolic processing in AI. The book noted that single-layer neurons could not implement some logical functions such as exclusive or (XOR) and implied that multi-layer networks would have the same issue. It was later found that three-layer networks could implement such functions. We give the XOR solution in this book.
Multi-layer neural networks were discovered in the 1960 s but not studied until the 1980 s. In the 1970 s, self-organizing maps using competitive learning were introduced [15]. A resurgence in neural networks happened in the 1980s. Knowledge-based, or “expert,” systems were also introduced in the 1980s. From Jackson [18]
An expert system is a computer program that represents and reasons with knowledge of some specialized subject to solve problems or give advice.
-Peter Jackson, Introduction to Expert Systems
Backpropagation for neural networks, a learning method using gradient descent, was reinvented in the 1980 s leading to renewed progress in this field. Studies began with both human neural networks (i.e., the human brain) and the creation of algorithms for effective computational neural networks. This eventually led to deep learning networks in machine learning applications.
Advances were made in the 1980 s as AI researchers began to apply rigorous mathematical and statistical analysis to develop algorithms. Hidden Markov Models were applied to speech. A Hidden Markov Model is a model with unobserved (i.e., hidden) states. Combined with massive databases, they have resulted in vastly more robust speech recognition. Machine translation has also improved. Data mining, the first form of machine learning as it is known today, was developed.
In the early 1990s, Vladimir Vapnik and coworkers invented a computationally powerful class of supervised learning networks known as support-vector machines (SVM). These networks could solve problems of pattern recognition, regression, and other machine learning problems.
matlab代写
数学代写|matlab代写|Deep Learning
深度学习是机器学习的一个子集,机器学习本身是人工智能和统计学的一个子集。第二次世界大战后不久就开始了人工智能研究 [35]。早期的工作是基于大脑结构、命题逻辑和图灵的计算理论的知识。Warren McCulloch 和 Walter Pitts 基于阈值逻辑为神经网络创建了一个数学公式。这使得神经网络研究分为两种方法:一种以大脑中的生物过程为中心,另一种以神经网络在人工智能中的应用为中心。事实证明,任何功能都可以通过一组这样的神经元来实现,并且神经网络可以学习识别模式。1948年,诺伯特·维纳 (Norbert Wiener) 的著作《控制论》(Cybernetics) 出版,描述了控制、通信和统计信号处理方面的概念。神经网络的下一个重要步骤是唐纳德·赫布 (Donald Hebb) 于 1949 年出版的《行为组织》(The Organization of Behavior) 一书,该书将连通性和大脑学习联系起来。他的书成为学习和自适应系统的源泉。Marvin Minsky 和 Dean Edmonds 于 1950 年在哈佛建造了第一台神经计算机。
第一批计算机程序,以及现在的绝大多数计算机程序,都由程序员将知识内置到代码中。程序员可以使用庞大的数据库。例如,飞机模型可能使用空气动力学系数的多维表。因此,由此产生的软件对飞机了解很多,并且对模型进行模拟可能会给程序员和用户带来惊喜,因为他们可能不完全理解模拟,或者可能输入了错误的输入。尽管如此,数据和算法之间的编程关系是由代码预先确定的。
在机器学习中,数据之间的关系是由学习系统形成的。数据连同与数据相关的结果一起输入。这就是系统培训。机器学习系统将数据与结果相关联,并提出成为系统一部分的规则。当引入新数据时,它可以得出不属于训练集的新结果。
深度学习是指具有不止一层神经元的神经网络。“深度学习”这个名字意味着更深刻的东西,在通俗文学中,它被用来暗示学习系统是一个“深度思考者”。数字1.1显示单层和多层网络。事实证明,多层网络可以学习单层网络无法学习的东西。网络的元素是节点,加权信号在其中组合并添加了偏差。在单层中,输入乘以权重,然后在通过阈值函数后在最后相加。在多层或“深度学习”网络中,输入在输出之前在第二层中组合。有更多的权重和增加的连接允许网络学习和解决更复杂的问题。
数学代写|matlab代写|History of Deep Learning
Minsky 于 1969 年与 Seymour Papert 合着了《感知器》一书,这是对人工神经网络的早期分析。这本书推动了 AI 中符号处理的发展。该书指出,单层神经元无法实现一些逻辑功能,例如异或(XOR),并暗示多层网络也会有同样的问题。后来发现三层网络可以实现这样的功能。我们在本书中给出了 XOR 的解决方案。
多层神经网络在 1960 年代被发现,但直到 80 年代才被研究。在 1970 年代,引入了使用竞争性学习的自组织映射 [15]。神经网络的复兴发生在 1980 年代。1980 年代还引入了基于知识的或“专家”系统。来自 Jackson [18]
专家系统是一种计算机程序,它代表和推理某些专业主题的知识以解决问题或提供建议。
-Peter Jackson,专家系统简介
神经网络的反向传播是一种使用梯度下降的学习方法,在 1980 年代被重新发明,导致该领域取得新的进展。研究始于人类神经网络(即人脑)和有效计算神经网络算法的创建。这最终导致了机器学习应用中的深度学习网络。
随着 AI 研究人员开始应用严格的数学和统计分析来开发算法,在 1980 年代取得了进展。隐马尔可夫模型应用于语音。隐马尔可夫模型是具有未观察到(即隐藏)状态的模型。与海量数据库相结合,它们产生了更加强大的语音识别。机器翻译也有所改进。数据挖掘是当今已知的第一种机器学习形式,它已经开发出来。
在 1990 年代初期,Vladimir Vapnik 及其同事发明了一种计算能力强大的监督学习网络,称为支持向量机 (SVM)。这些网络可以解决模式识别、回归和其他机器学习问题。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
