如果你也在 怎样代写量子力学Quantum mechanics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。量子力学Quantum mechanics在理论物理学中,量子场论(QFT)是一个结合了经典场论、狭义相对论和量子力学的理论框架。QFT在粒子物理学中用于构建亚原子粒子的物理模型,在凝聚态物理学中用于构建准粒子的模型。
量子力学Quantum mechanics产生于跨越20世纪大部分时间的几代理论物理学家的工作。它的发展始于20世纪20年代对光和电子之间相互作用的描述,最终形成了第一个量子场理论–量子电动力学。随着微扰计算中各种无限性的出现和持续存在,一个主要的理论障碍很快出现了,这个问题直到20世纪50年代随着重正化程序的发明才得以解决。第二个主要障碍是QFT显然无法描述弱相互作用和强相互作用,以至于一些理论家呼吁放弃场论方法。20世纪70年代,规整理论的发展和标准模型的完成导致了量子场论的复兴。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写量子力学quantum mechanics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写量子力学quantum mechanics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写量子力学quantum mechanics相关的作业也就用不着说。
物理代写|量子力学代写quantum mechanics代考|Isometric Extension of a Quantum Channel
We now give a general definition for an isometric extension of a quantum channel:
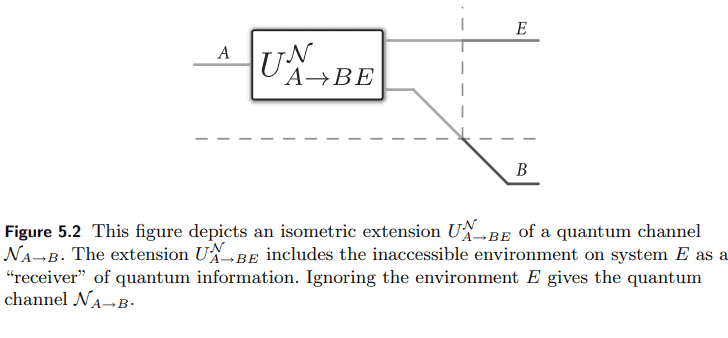
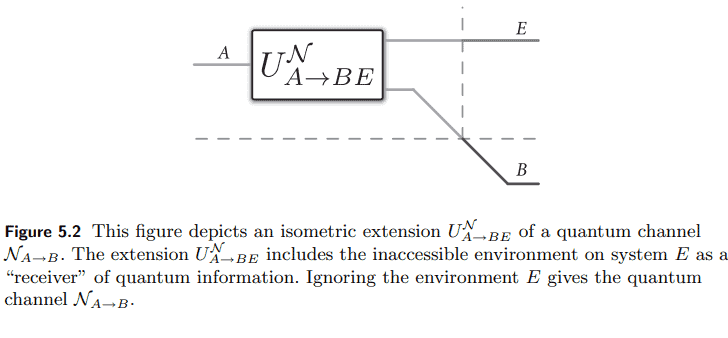
DEfinition 5.2.1 (Isometric Extension) Let $\mathcal{H}A$ and $\mathcal{H}_B$ be Hilbert spaces, and let $\mathcal{N}: \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_A\right) \rightarrow \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_B\right)$ be a quantum channel. Let $\mathcal{H}_E$ be a Hilbert space with dimension no smaller than the Choi rank of the channel $\mathcal{N}$. An isometric extension or Stinespring dilation $U: \mathcal{H}_A \rightarrow \mathcal{H}_B \otimes \mathcal{H}_E$ of the channel $\mathcal{N}$ is a linear isometry such that $$ \operatorname{Tr}_E\left{U X_A U^{\dagger}\right}=\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}\left(X_A\right),
$$
for $X_A \in \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}A\right)$. The fact that $U$ is an isometry is equivalent to the following conditions: $$ U^{\dagger} U=I_A, \quad U U^{\dagger}=\Pi{B E},
$$
where $\Pi_{B E}$ is a projection of the tensor-product Hilbert space $\mathcal{H}B \otimes \mathcal{H}_E$. NOtATION 5.2.1 We often write a channel $\mathcal{N}: \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_A\right) \rightarrow \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_B\right)$ as $\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$ in order to indicate the input and output systems explicitly. Similarly, we often write an isometric extension $U: \mathcal{H}A \rightarrow \mathcal{H}_B \otimes \mathcal{H}_E$ of $\mathcal{N}$ as $U{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$ in order to indicate its association with $\mathcal{N}$ explicitly, as well the fact that it accepts an inputsystem $A$ and has output systems $B$ and $E$. The system $E$ is often referred to as an “environment” system. Finally, there is a quantum channel $\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$ associated to an isometric extension $U{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$, which is defined by
$$
\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}\left(X_A\right)=U X_A U^{\dagger} $$ for $X_A \in \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_A\right)$. Note that $\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$ is a quantum channel with a single Kraus operator $U$ given that $U^{\dagger} U=I_A$.
物理代写|量子力学代写quantum mechanics代考|Isometric Extension from Kraus Operators
It is possible to determine an isometric extension of a quantum channel directly from a set of Kraus operators. Consider a quantum channel $\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$ with the following Kraus representation: $$ \mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}\left(\rho_A\right)=\sum_j N_j \rho_A N_j^{\dagger} .
$$
An isometric extension of the channel $\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$ is the following linear map: $$ U{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}} \equiv \sum_j N_j \otimes|j\rangle_E .
$$
It is straightforward to verify that the above map is an isometry:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\left(U^{\mathcal{N}}\right)^{\dagger} U^{\mathcal{N}} & =\left(\sum_k N_k^{\dagger} \otimes\left\langle\left. k\right|E\right)\left(\sum_j N_j \otimes|j\rangle_E\right)\right. \ & =\sum{k, j} N_k^{\dagger} N_j\langle k \mid j\rangle \
& =\sum_k N_k^{\dagger} N_k \
& =I_A .
\end{aligned}
$$
The last equality follows from the completeness condition of the Kraus operators. As a consequence, we get that $U^{\mathcal{N}}\left(U^{\mathcal{N}}\right)^{\dagger}$ is a projector on the joint system $B E$, which follows by the same reasoning given in (4.259). Finally, we should verify that $U^{\mathcal{N}}$ is an extension of $\mathcal{N}$. Applying the channel $\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$ to an arbitrary density operator $\rho_A$ gives the following map: $$ \begin{aligned} \mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}\left(\rho_A\right) & \equiv U^{\mathcal{N}} \rho_A\left(U^{\mathcal{N}}\right)^{\dagger} \
& =\left(\sum_j N_j \otimes|j\rangle_E\right) \rho_A\left(\sum_k N_k^{\dagger} \otimes\left\langle\left. k\right|E\right)\right. \ & =\sum{j, k} N_j \rho_A N_k^{\dagger} \otimes|j\rangle\left\langle\left. k\right|E,\right. \end{aligned} $$ and tracing out the environment system gives back the original quantum channel $\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$ :
$$
\operatorname{Tr}E\left{\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}\left(\rho_A\right)\right}=\sum_j N_j \rho_A N_j^{\dagger}=\mathcal{N}_{A \rightarrow B}\left(\rho_A\right)
$$
量子力学代考
物理代写|量子力学代写quantum mechanics代考|Isometric Extension of a Quantum Channel
我们现在给出量子通道等距扩展的一般定义:
定义5.2.1(等距扩展)设$\mathcal{H}A$和$\mathcal{H}B$为希尔伯特空间,设$\mathcal{N}: \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_A\right) \rightarrow \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_B\right)$为量子通道。设$\mathcal{H}_E$为希尔伯特空间,其维数不小于通道$\mathcal{N}$的Choi秩。通道的等距延伸或弹簧膨胀$U: \mathcal{H}_A \rightarrow \mathcal{H}_B \otimes \mathcal{H}_E$$\mathcal{N}$是线性等距,这样$$ \operatorname{Tr}_E\left{U X_A U^{\dagger}\right}=\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}\left(X_A\right), $$ 浏览$X_A \in \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}A\right)$。$U$是等距的事实等价于以下条件:$$ U^{\dagger} U=I_A, \quad U U^{\dagger}=\Pi{B E}, $$ 其中$\Pi{B E}$是张量积希尔伯特空间$\mathcal{H}B \otimes \mathcal{H}_E$的投影。5.2.1为了明确地指出输入和输出系统,我们经常将通道$\mathcal{N}: \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_A\right) \rightarrow \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_B\right)$写成$\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$。类似地,我们经常将$\mathcal{N}$的等长扩展$U: \mathcal{H}A \rightarrow \mathcal{H}_B \otimes \mathcal{H}_E$写成$U{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$,以便显式地表明它与$\mathcal{N}$的关联,以及它接受输入系统$A$并具有输出系统$B$和$E$的事实。系统$E$通常被称为“环境”系统。最后,还有一个与等距扩展$U{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$相关联的量子通道$\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$,它由
$$
\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}\left(X_A\right)=U X_A U^{\dagger} $$代表$X_A \in \mathcal{L}\left(\mathcal{H}_A\right)$。请注意,$\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$是一个量子信道,具有单个克劳斯算符$U$,假设$U^{\dagger} U=I_A$。
物理代写|量子力学代写quantum mechanics代考|Isometric Extension from Kraus Operators
直接从一组克劳斯算符确定量子信道的等距扩展是可能的。考虑以下克劳斯表示的量子通道$\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$: $$ \mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}\left(\rho_A\right)=\sum_j N_j \rho_A N_j^{\dagger} .
$$
通道$\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$的等距扩展是以下线性映射:$$ U{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}} \equiv \sum_j N_j \otimes|j\rangle_E .
$$
很容易验证上面的图是等距图:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\left(U^{\mathcal{N}}\right)^{\dagger} U^{\mathcal{N}} & =\left(\sum_k N_k^{\dagger} \otimes\left\langle\left. k\right|E\right)\left(\sum_j N_j \otimes|j\rangle_E\right)\right. \ & =\sum{k, j} N_k^{\dagger} N_j\langle k \mid j\rangle \
& =\sum_k N_k^{\dagger} N_k \
& =I_A .
\end{aligned}
$$
最后一个等式由Kraus算子的完备性条件推导出来。因此,我们得到$U^{\mathcal{N}}\left(U^{\mathcal{N}}\right)^{\dagger}$是关节系统$B E$上的投影仪,这与(4.259)中给出的推理相同。最后,我们应该验证$U^{\mathcal{N}}$是$\mathcal{N}$的扩展。将信道$\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}$应用于任意密度算子$\rho_A$,得到以下映射:$$ \begin{aligned} \mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}\left(\rho_A\right) & \equiv U^{\mathcal{N}} \rho_A\left(U^{\mathcal{N}}\right)^{\dagger} \
& =\left(\sum_j N_j \otimes|j\rangle_E\right) \rho_A\left(\sum_k N_k^{\dagger} \otimes\left\langle\left. k\right|E\right)\right. \ & =\sum{j, k} N_j \rho_A N_k^{\dagger} \otimes|j\rangle\left\langle\left. k\right|E,\right. \end{aligned} $$并跟踪环境系统,返回原始量子信道$\mathcal{N}{A \rightarrow B}$:
$$
\operatorname{Tr}E\left{\mathcal{U}{A \rightarrow B E}^{\mathcal{N}}\left(\rho_A\right)\right}=\sum_j N_j \rho_A N_j^{\dagger}=\mathcal{N}_{A \rightarrow B}\left(\rho_A\right)
$$
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。