计算机代写|操作系统代写operating systems代考|CS140
如果你也在 怎样代写操作系统operating systems这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
操作系统是在计算机上运行的最重要的软件。它管理着计算机的内存和进程,以及所有的软件和硬件。它还允许你在不知道如何讲计算机语言的情况下与计算机进行交流。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写操作系统operating systems方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写操作系统operating systems代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写操作系统operating systems相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的操作系统operating systems及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
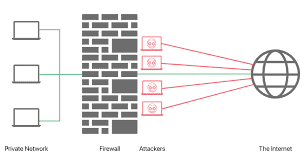
计算机代写|操作系统代写operating systems代考|Network-Based Firewalls
A network-based firewall is a hardware device designed to protect you against the dangers of having an unprotected connection to the Internet. It sits between a private network and the Internet (or other network) and examines all traffic in and out of the network it is protecting. It will block any traffic it recognizes as a potential threat, using a variety of techniques. Table $2-1$ lists some of the most common technologies normally included in a firewall, although some of these are not strictly firewall technologies. Your ISP and most corporations employ hardware firewalls, expensive and specialized computers manufactured by companies such as Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, and others, and these sophisticated firewalls require highly trained people to manage them. Such a firewall probably protects the network at work or at school.
At home or in a small office, most people have a consumer-grade hardware firewall that comes in a small device that performs many of the same functions performed by a more professional-grade firewall. The most common name for these devices is broadband router or cable/DSL router. They combine the function of a firewall, a router (a device that “routes” traffic from one network to another), an Ethernet switch, and even a wireless access point all in one tiny box. These inexpensive devices can handle the traffic of just a few computers, while the more serious devices employed by ISPs and large organizations can handle thousands of simultaneous high-speed transmissions. These consumer-grade devices now come with the “one button” configuration that automatically configures a simple connection to the Internet, with the latest security turned on. You can also access the built-in Web page to make manual changes to the settings. Figure 2-7 shows the security page of a Cisco Wireless Router, which includes support for all the technologies listed in Table $2-1$ and many more features, including support for the $802.11 \mathrm{~N}$ standard for Wi-Fi communications and security. The setting labeled “Firewall” is just one option for securing your home network. Even with this device, you would need to research the impact of the various settings before changing from the default settings.
The firewall administrator configures a firewall to allow traffic into the private network or prohibit traffic from entering the private network based on the types of computers residing within the private network, and how they will interact with the Internet. If all the computers on a private network are desktop computers that connect to the Internet to browse Web pages and access FTP sites, the firewall protecting the network has a simple job. It simply blocks all in-bound traffic that is not the result of a request from a computer on the internal network; it matches incoming traffic with previous outgoing traffic that made requests that would result in incoming traffic. Then, when you connect to a website, outgoing traffic from your computer to the website requests to see a page. That page comes to you as incoming traffic and a firewall will allow it through based on your initial request.
But if the private network includes servers that offer services on the Internet, then the firewall must allow initiating traffic to come through, but it does not allow all incoming traffic through. In this case, an administrator configures a firewall to allow incoming traffic of the type that can only communicate with the internally based servers. The various types of traffic include email, Web, FTP, and others. Each type of traffic has a certain characteristic the firewall can recognize. Figure 2-8 shows a firewall protecting a network containing both servers and desktop computers (shown as clients).
计算机代写|操作系统代写operating systems代考|Antispam Software
A spam filter is software designed to combat spam by examining incoming email messages and filtering out those that have characteristics of spam, including certain identified keywords. In an organization with centralized network and computer management, spam filter software installed on central mail servers can remove spam before it gets to a user’s desktop. Network administrators may use Internet=based spam filtering services that block spam before it reaches the corporate network.
Individuals connected to the Internet from home or in small businesses are often on their own when it comes to eliminating spam. Luckily, many email clients, such as Microsoft Outlook, offer spam filtering. Without a spam filter you must sort through your own email to find and delete the spam. Spam filters are not perfect-they can filter out legitimate messages, while allowing some spam messages through. For this reason, most spam filters require some configuration on the part of the user using rules or filters that will automate the process of removing spam from known sources. And the user will still often need to review a list of suspected spam messages. Figure 2-12 shows the Microsoft Outlook Junk Email Options dialog box with several tabbed pages of settings that allow you to configure the spam filter.
An antivirus program can examine the contents of a storage device or RAM looking for hidden viruses and files that may act as hosts for virus code. Effective antivirus products not only detect and remove viruses, but they also help you recover data that has been lost because of a virus. To remain current, they require frequent updating as to the virus threats to watch for. An antivirus program includes an antivirus engine (the main program) and a set of patterns of recognized viruses. usually contained in files called definition files. Retailers of antivirus software commonly charge an annual fee for updates to the antivirus engine and the definition files. There are excellent free services for home users. One example is AVG antivirus from GRIsoft. Software companies that offer free security software usually also offer a feature-rich commercial version to which you can upgrade for a fee. The free version gives you a chance to see if you like using it before you put out any money. Once installed, most antivirus programs will automatically connect to the manufacturer’s website and check for these updates.
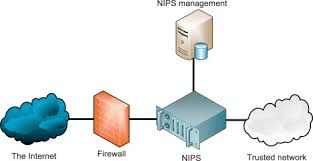
操作系统代考
计算机代写|操作系统代写operating systems代考|Network-Based firewall
. sh
基于网络的防火墙是一种硬件设备,旨在保护你免受未受保护的互联网连接的危险。它位于私有网络和Internet(或其他网络)之间,检查所有进出它所保护的网络的流量。它将使用各种技术阻止它认为是潜在威胁的任何流量。表$2-1$列出了防火墙中通常包含的一些最常见的技术,尽管其中一些严格来说并不是防火墙技术。您的ISP和大多数公司使用硬件防火墙,由思科、Palo Alto Networks、Fortinet等公司生产的昂贵的专用计算机,这些复杂的防火墙需要受过高度训练的人员来管理。这样的防火墙可能会保护工作或学校的网络
在家里或小办公室里,大多数人都有一个消费级硬件防火墙,它装在一个小设备里,执行许多由更专业级防火墙执行的相同功能。这些设备最常见的名称是宽带路由器或电缆/DSL路由器。它们将防火墙、路由器(一种将流量从一个网络“路由”到另一个网络的设备)、以太网交换机甚至无线接入点的功能都集中在一个小盒子里。这些便宜的设备只能处理几台计算机的流量,而isp和大型组织使用的更严肃的设备可以同时处理数千个高速传输。这些消费级设备现在都有“一键”配置,可以自动配置一个简单的互联网连接,并开启了最新的安全措施。您还可以访问内置的Web页面来手动更改设置。图2-7显示了Cisco无线路由器的安全页面,它包括对表$2-1$中列出的所有技术的支持,以及更多的功能,包括对Wi-Fi通信和安全的$802.11 \mathrm{~N}$标准的支持。标记为“防火墙”的设置只是保护家庭网络的一个选项。即使使用这种设备,在更改默认设置之前,您也需要研究各种设置的影响
防火墙管理员根据驻留在私有网络中的计算机的类型以及它们与Internet的交互方式来配置防火墙,允许流量进入私有网络或禁止流量进入私有网络。如果私有网络中的所有计算机都是连接到Internet上浏览网页和访问FTP站点的台式计算机,那么保护网络的防火墙的工作就很简单了。它只是阻止所有传入的流量,不是来自内部网络上的计算机的请求的结果;它将传入的流量与先前发出请求并导致传入流量的传出流量进行匹配。然后,当您连接到一个网站时,从您的计算机到该网站的输出流量要求查看一个页面。该页面作为传入流量来到您面前,防火墙将根据您的初始请求允许它通过
但是如果私有网络包括在Internet上提供服务的服务器,那么防火墙必须允许发起的流量通过,但不允许所有传入的流量通过。在这种情况下,管理员配置防火墙,以允许只能与内部服务器通信的类型的传入流量。各种类型的流量包括电子邮件、Web、FTP和其他。每种类型的流量都有防火墙能够识别的特定特征。图2-8所示为保护包含服务器和桌面计算机(如客户端所示)的网络的防火墙
计算机代写|操作系统代写operating systems代考|Antispam Software
. sh
垃圾邮件过滤器是一种用来对抗垃圾邮件的软件,它通过检查传入的电子邮件信息,过滤掉那些具有垃圾邮件特征的信息,包括某些已识别的关键字。在具有集中网络和计算机管理的组织中,安装在中央邮件服务器上的垃圾邮件过滤软件可以在垃圾邮件到达用户桌面之前将其删除。网络管理员可以使用基于Internet=的垃圾邮件过滤服务,在垃圾邮件到达公司网络之前阻止垃圾邮件
当涉及到消除垃圾邮件时,从家里或小企业连接到互联网的个人通常是自己的。幸运的是,许多电子邮件客户端,如Microsoft Outlook,都提供垃圾邮件过滤功能。如果没有垃圾邮件过滤器,你必须通过自己的电子邮件来查找和删除垃圾邮件。垃圾邮件过滤器并不完美——它们可以过滤掉合法的邮件,同时允许一些垃圾邮件通过。由于这个原因,大多数垃圾邮件过滤器需要用户使用规则或过滤器进行一些配置,这些规则或过滤器将自动从已知来源删除垃圾邮件。而且用户仍然经常需要查看可疑的垃圾邮件列表。如图2-12所示,“Microsoft Outlook垃圾邮件选项”对话框中有几个选项卡页面,允许您配置垃圾邮件过滤器
反病毒程序可以检查存储设备或RAM的内容,寻找隐藏的病毒和文件,这些病毒代码可能作为宿主。有效的反病毒产品不仅可以检测和清除病毒,还可以帮助您恢复因病毒而丢失的数据。为了保持最新,它们需要经常更新要观察的病毒威胁。一个防病毒程序包括一个防病毒引擎(主程序)和一组可识别的病毒模式。通常包含在称为定义文件的文件中。杀毒软件的零售商通常对杀毒引擎和定义文件的更新收取年费。为家庭用户提供优质的免费服务。GRIsoft的AVG杀毒软件就是一个例子。提供免费安全软件的软件公司通常也提供功能丰富的商业版本,你可以付费升级到该版本。免费版让你有机会在掏钱之前看看自己是否喜欢使用。一旦安装,大多数防病毒程序将自动连接到制造商的网站,并检查这些更新
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。