如果你也在 怎样代写产业经济学Industrial Economics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
产业经济学是关于公司、行业和市场的研究。它研究各种规模的公司–从当地的角落商店到沃尔玛或乐购这样的跨国巨头。它还考虑了一系列的行业,如发电、汽车生产和餐馆。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写产业经济学Industrial Economics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的产业经济学Industrial Economics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
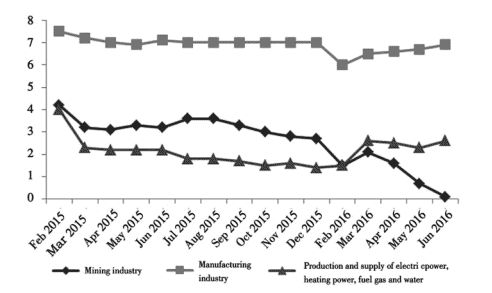
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Analysis of the Industrial Economics Prosperity in 2016
To get an intuitive understanding of the industrial economics development, this report has synthesized the available original data including industrial economics development to derive a composite indicator that reflects the situation of industrial economics, i.e. the composite index. According to the composite index, the industrial economics grew significantly in the first quarter of 2016 , unlike the trend that remained lower last year. According to the prosperity index, the first quarter of 2016 witnessed a significant rise in prosperity index of industrial economics as compared to the previous year, but the lagging index indicates that this high trend seems feeble and the leading index indicates that this trend will continue.
(1) Formation of the composite index
Processing of original data: the composite index needs to eliminate the “redundant” information (or information irrelative to our purpose) from the original data. To eliminate this “redundant” information, it can be differentiated from original data. Firstly, the original data include high-frequency and low-frequency data, and the former contains daily, weekly and monthly data. What is needed in this report is the monthly data, so daily and weekly data are “redundant” to us and all data are necessarily subject to de-frequency processing. Secondly, the original data contain output data and value quantity data, and the value quantity data may lead to incomparability inside data sequence under the influence of changing prices; therefore, the incomparable data caused by changing prices need to be removed in order to accurately describe the trend of industrial economics development. Thirdly, it is the influence of movable holiday effect. Unlike the statistical data that are calculated in accordance with the solar calendar, the traditional Chinese Spring is always celebrated in accordance with the lunar calendar, so the Spring Festival usually takes place in different solar months. As a public holiday in China, the Spring Festival has strong holiday effects: suspended production, additional leisure time, sharp rise in consumption, and abnormality in all economic activities. As a result, some “redundant” information such as “holiday effect” is included in monthly data. When the data are relevant to growth rate, the above three kinds of information are redundant information that needs to be removed in this report. Thanks to coincidence between seasonal information and holiday information, however, the movable holiday information is usually eliminated earlier than is the seasonable information. In this report, the three kinds of redundant information will be eliminated by de-frequency adjustment, price adjustment and movable holiday adjustment methods.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Correlation analysis is a statistical
Correlation analysis is a statistical method commonly used in research on closeness among various variables and in research on the degree of correlation between two or more variables and the mutual relation of phenomena with certain functions. The correlative relation means the stochastic relation of change in two phenomena values that are not completely determined, or a kind of dependence relation that is not yet completely determined, often abbreviated as correlative relation, which is the object of study in correlation analysis. The closeness of correlative relation describes the degree of association among variables through calculation of correlation coefficient, i.e. the correlation coefficient is the statistical magnitude that describes the degree and direction of linear relation between two variables, usually expressed as $r$, without unit, value of which ranges between $-1$ and $+1$. The closer to $r$ the absolute value is, the greater the degree of linear correlation between two variables will be. If $r$ is greater than 0 , it is a positive correlation and variable $\mathrm{Y}$ will increase as variable $\mathrm{X}$ increases; if $\mathrm{r}$ is less than 0 , it is a negative correlation and variable $\mathrm{Y}$ will decrease as variable $\mathrm{x}$ increases.
Based on the principle of correlation coefficient, the cross correlation coefficient method has broken the sequence of two variables’ correlation coefficient arranged by time limit according to time variable. This sequence may give the mutual relation between two variables at different times; accordingly, the maximum cross correlation coefficient is used to determine whether this index is a leading index, concordance index or a lagging index.
Synthesis of index: the composite index may be coded in different ways, e.g. the composite index method of the US Department of Commerce, the composite index method introduced by the Economic Planning Agency of Japan, and the composite index method of the UN Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). The Japanese Economic Planning Agency’s composite index method agrees with the US Department of Commerce in basic idea but differs slightly in method while the OECD’s composite index method is developed specific to the leading composite index and seems simpler than the former two methods. In this report, the US Department of Commerce’s composite index method is adopted as an internationally common method. It is basically used in the literature of Chinese development of prosperity index.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Determine and standardize the symmetrical change rate of index
Step 1: Determine and standardize the symmetrical change rate of index
(i) Let index $Y_{i j t}$ be the value of $j$ index in $i$ index group at $t$ time, where $i=1,2,3$, representing the leading, concordance and lagging index groups respectively, $j=1,2,3, \ldots, k_{i}$, representing indexes in three groups, and $k_{i}$ means the number of indexes in $i$ index group. First determine symmetrical change $C_{i j i t}$ of $Y_{i j t}$, where $t=2,3, \ldots, n$.
(ii) To prevent greatly variable indexes from producing significant impact on composite index, the symmetrical change rate $C_{i j t}$ of each index is standardized to make its average absolute value equal to 1 . First determine the normalized factor $A_{i j}$ and then standardize $C_{i j t}$ with $A_{i j}$ to obtain standardized change rate $S_{i j t}$, where $t=2,3, \ldots, n$.
Step 2: Determine standardized average change rate of each index group
(i) Determine average change rates of the leading index, concordance index and lagging index group, with $R_{i, t}$ of $i=1,2,3$ and $t=2,3$, $\ldots, n$.
Where $W_{i j}$ is the weight of $j$ index in $i$ index group. The equal weight is usually used to set weight in composite index. The scoring system may be used to determine weight so that each index is given a score according to its economic importance, statistical adequacy, historical concordance and publishing timeliness, and then each index is weighted. If this step is not followed, the weight will be not as desirable as equal weight due to its strong arbitrariness and subjectivity. In order to keep consistent the numerical values of composite index in three index group, the standardized average change rates of all three index groups need to be calculated by dividing the average change rates of all index groups by normalized factor among index groups.
(ii) Work out the normalized factor $F_{i}$, where $i=1,2,3$.
(iii) Figure out the standardized average change rate $V_{i, t}$, where $t=2,3$, $\ldots, n$.
Step 3: Calculate composite index
(i) Let $I_{i}(1)=100$, then $i=1,2,3$ and $t=2,3, \ldots, n$.
(ii) Synthesize a composite index with 100 as benchmark year, where $I_{i}$ is the average value of $I_{i, t}$ in the benchmark year.
Follow above step in aggregating and synthesizing indexes of three index groups, and then figure out the composite index of the leading index, concordance index and lagging index.
产业经济学代考
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Analysis of the Industrial Economics Prosperity in 2016
为直观了解产业经济发展情况,本报告综合包括产业经济发展在内的现有原始数据,推导出反映产业经济状况的综合指标,即综合指数。综合指数显示,2016年一季度工业经济增速明显,不同于去年持续走低的趋势。从景气指数看,2016年一季度工业经济景气指数较上年有明显上升,但滞后指数表明这一高位走势微弱,领先指数表明这一趋势将持续。
(一)综合指数的形成
原始数据的处理:综合索引需要从原始数据中剔除“冗余”信息(或与我们的目的无关的信息)。为了消除这种“冗余”信息,可以将其与原始数据区分开来。首先,原始数据包括高频数据和低频数据,前者包含日、周和月数据。这份报告需要的是月度数据,所以每天和每周的数据对我们来说是“多余的”,所有数据都必须经过去频率处理。其次,原始数据包含输出数据和价值量数据,价值量数据在价格变动的影响下可能导致内部数据序列的不可比性;所以,需要剔除价格变动造成的不可比数据,才能准确描述产业经济发展趋势。三是活动假期效应的影响。与按照阳历计算的统计数据不同,中国传统的春节总是按照农历庆祝,因此春节通常发生在不同的太阳月。春节作为中国的公共假期,具有强烈的节日效应:停产、闲暇时间增加、消费大幅上升、各项经济活动异常。因此,月度数据中包含了一些“冗余”信息,例如“假期效应”。当数据与增长率相关时,以上三类信息为本报告需要剔除的冗余信息。然而,由于季节信息和节假日信息之间的重合,可移动节假日信息通常比节假日信息更早地被消除。本报告将通过去频率调整、价格调整和移动节假日调整等方式剔除三种冗余信息。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Correlation analysis is a statistical
相关性分析是一种统计方法,常用于研究各种变量之间的接近程度,研究两个或多个变量之间的相关程度以及现象与某些函数之间的相互关系。相关关系是指两个未完全确定的现象值变化的随机关系,或一种尚未完全确定的依赖关系,常简称为相关关系,是相关分析研究的对象。相关关系的密切程度通过计算相关系数来描述变量之间的关联程度,即相关系数是描述两个变量之间线性关系程度和方向的统计量级,通常表示为r, 无单位,其值介于−1和+1. 越接近r绝对值越大,两个变量之间的线性相关程度越大。如果r大于 0 是正相关且变量是将随着变量增加X增加;如果r小于 0 ,是负相关和变量是将随着变量减少X增加。
互相关系数法基于相关系数原理,打破了两个变量相关系数按照时间变量按时限排列的顺序。这个序列可以给出两个变量在不同时间的相互关系;因此,使用最大互相关系数来确定该指数是领先指数、一致性指数还是滞后指数。
综合指数:综合指数可以有不同的编码方式,例如美国商务部的综合指数法、日本经济计划厅引入的综合指数法、联合国经济合作组织的综合指数法等。合作与发展(经合组织)。日本经济计划厅的综合指数法在基本思想上与美国商务部一致,但在方法上略有不同,而经合组织的综合指数法是专门针对领先综合指数开发的,似乎比前两种方法简单。本报告采用美国商务部综合指数法作为国际通用方法。它主要用于中国发展繁荣指数的文献中。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Determine and standardize the symmetrical change rate of index
步骤 1:确定和标准化指数的对称变化率
(i) 让指数是一世j吨成为j索引一世索引组在吨时间,地点一世=1,2,3,分别代表领先、一致和落后指数组,j=1,2,3,…,ķ一世,代表三组中的索引,以及ķ一世表示索引的数量一世指数组。首先确定对称变化C一世j一世吨的是一世j吨, 在哪里吨=2,3,…,n.
(ii) 为防止大变动指数对综合指数产生重大影响,对称变化率C一世j吨对每个指标进行标准化,使其平均绝对值等于 1 。首先确定归一化因子一个一世j然后标准化C一世j吨和一个一世j获得标准化的变化率小号一世j吨, 在哪里吨=2,3,…,n.
步骤 2:确定每个指数组的标准化平均变化率
(i) 确定领先指数、一致性指数和滞后指数组的平均变化率,用R一世,吨的一世=1,2,3和吨=2,3, …,n.
在哪里在一世j是重量j索引一世指数组。等权重通常用于在综合指数中设定权重。评分系统可用于确定权重,使每个指标根据其经济重要性、统计充分性、历史一致性和发布及时性进行评分,然后对每个指标进行加权。如果不遵循这一步,权重将不如等权重,因为它具有很强的任意性和主观性。为了使三个指标组中综合指标的数值保持一致,需要将所有指标组的平均变化率除以指标组间的标准化因子,计算出所有三个指标组的标准化平均变化率。
(ii) 计算出归一化因子F一世, 在哪里一世=1,2,3.
(iii) 计算出标准化的平均变化率在一世,吨, 在哪里吨=2,3, …,n.
第 3 步:计算综合指数
(i) 让我一世(1)=100, 然后一世=1,2,3和吨=2,3,…,n.
(ii) 以 100 为基准年合成一个综合指数,其中我一世是平均值我一世,吨在基准年。
按照上述步骤对三个指标组的指标进行聚合和综合,然后计算出领先指标、一致性指标和滞后指标的综合指标。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
