如果你也在 怎样代写产业经济学Industrial Economics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
产业经济学是关于公司、行业和市场的研究。它研究各种规模的公司–从当地的角落商店到沃尔玛或乐购这样的跨国巨头。它还考虑了一系列的行业,如发电、汽车生产和餐馆。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写产业经济学Industrial Economics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写产业经济学Industrial Economics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的产业经济学Industrial Economics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等概率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
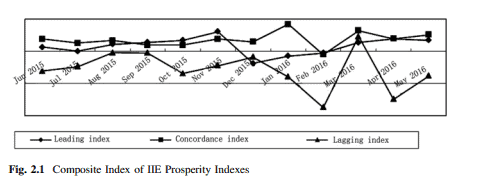
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Analysis of prosperity index in the first half of 2016
It is indicated by the leading index and concordance index that the first half of 2016 greeted a slow pickup trend of prosperity from a low level. In January and February 2016 , the prosperity of leading index fell into the range of negative values under the influence of sluggish prosperity in 2015 but assumed a constant pickup trend, and it further recovered above zero in March 2016 . The concordance index presented a trend ascending year over year and descending month over month. In Fig. 2.1, the prosperity of concordance index ascended for a time to about $0.4$ of that in January and descended afterwards to almost zero, but it picked up in March 2016, generally higher than the prosperity in the same period last year, regardless of a descending
trend that took place later. The lagging index (mainly including export information and price information) indicated some risks in such growth. In 2016, exclusive of March and June, the prosperity of lagging index remained below zero with a greater degree of fluctuation. For some time in the future, there will be increasing uncertainties about growth of industrial economics.
According to prosperity indicators, (1) the fringe market improved greatly; the PMI of American manufacturing industry bounced back over the threshold; the PMI of Eurozone manufacturing industry maintained above the threshold and assumed an uptrend. The economic situation of developed countries would eventually have effect on China’s export trade; despite a substantial decline in China’s general trade export volume in the first quarter of 2016 , the export volume grew $20 \%$ year on year in March; but there had been no substantial growth in the export volume of general trade as the domestic market of China remained in adjustment; (2) the real estate market witnessed brisk trades. In the first half of 2016 , the area sold of real estate grew rapidly. From January to June 2016, it reached $643.02$ million square meters, growing $27.9 \%$ year on year; the sales of real estate amounted to RMB $4.8682$ trillion, growing $42.1 \%$. The investment scale of real estate development maintained a moderate-rapid rate of growth; from January to June 2016, it grew $6.1 \%$ year on year, indicating a limited role of real estate market in driving industrial growth; (3) there was a slowdown in growth of fixed asset investment and a notable decline in industrial fixed asset investment. From January to June 2016 , the fixed asset investment in China amounted to RMB $25.836$ trillion (excluding peasant households), with nominal year-on-year growth of $9 \%$ (it was actually $11 \%$ after adjusting for inflation). The investment in the secondary industry amounted to RMB $10.1702$ trillion, growing $4.4 \%, 16.7$ and $7.7$ percentage points lower than the primary industry the tertiary industry respectively, where the industrial investment amounted to RMB $9.9594$ trillion, growing $4.2 \%$ year on year, and the manufacturing investment amounted to RMB $8.2261$ trillion, growing $3.3 \%$ only; (4) under the influence of overcapacity and inventory adjustment, the outputs of industrial products saw an uneven year-on-year growth, e.g. the outputs of cast iron, crude steel and coke kept sagging while those of ethylene and aluminum products kept growing; and (5) the money supply M1 grew rapidly while M2 slowed down. In response to the downturn risks of industrial economics, Chinese government exercised proactive monetary policy, resulting in a significant growth in money supply; nevertheless, the growth rate of money supply M2 tended to slow down due to the risk of the rising non-performing loan ratio (Table 2.1).
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|The steady rise in leading indexes predicted
The steady rise in leading indexes predicted a quarter-long slow growth of the industrial economics for some time in the future, but the industrial economics would be under big downward pressure as it remained in growing pains of rebalance. Specifically, firstly, the ex-factory price index of industrial products remained within a negative range, the industrial overcapacity failed to improve in real sense, and the main industrial products trading market was not as active as expected; secondly, this round of growth of industrial economics was still dependent heavily on pickup of real estate market, and there would be limited space for growth in the future as the real estate market entered the period of adjustment; thirdly, the fixed asset investment remained a main force in supporting this round of slow growth of industrial economics, and the main sectors that could drive growth of fixed asset investment were infrastructure investment and real estate market investment while the manufacturing fixed asset investment remained at a low level; and fourthly, the loose monetary policy played a positive role in promoting pickup of real estate market, but the exit of the loose monetary policy would inevitably restrain the growing trend of the real estate market and further compromise demands of industrial products. Generally, this round of industrial economics growth as a continuity of the old investment-driven development pattern failed to result in any new growth points. Considering the transition of China’s economic development from the industry-driven pattem to the service-driven pattern, there would be an irresistible trend of rapid growth of the service industry and slowdown of industrial growth.
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Factors Influencing the Trend Variation of Industrial Economics
The decline of fixed asset investment in industrial sectors would inevitably lead to a slowing growth rate of capital stock and usher in a falling trend of industrial sectors. The innovative development strategy and global technological revolution initiated by Chinese Government would be a strong support for growth of industrial economics.
(1) Lower and lower investment return of industrial enterprises and continuous downsizing of the fixed asset investment
Since reform and opening up in 1979 , the profit scale of Chinese industrial sectors had expanded constantly; especially since the year of 2002 , it grew at a rate up to $20 \%$ and made it possible for industrial investment return to maintain a high level. Since the year of 2011 , however, the profit growth rate of industrial sectors slowed down even to a negative rate. As the profit growth rate remained low, the
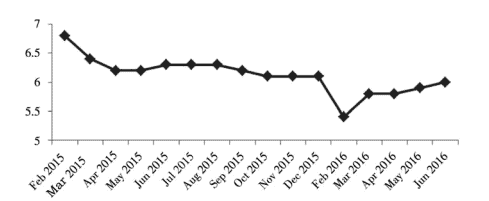
investment return receded gradually. Bai Chong’en and Zhang Qiong (2014) ${ }^{1}$ pointed out that since the year 2011 China’s return on invested capital presented a constantly declining trend, i.e. $21.1,16.6$ and $14.7 \%$ respectively from 2011 to 2013. The return on invested capital of industrial sectors stayed basically consistent with that of the whole society. The former’s decline would result in transfer of investment into other industries and into overseas market. Data showed that from 2005 to 2013 , the fixed asset investment of industrial sectors took up all the time over $40 \%$ of the total fixed assets investment; however, since the year of 2014 , the fixed asset fell back to $39.9 \%$ and presented a trend of continuous decline (Fig. 2.2).
The growth of private fixed asset investment ushered in this round of the declining trend in fixed asset investment. Over years, the growth of private fixed asset investment in the secondary industry has all the time outnumbered the growth of total fixed asset investment and thus become the main force of fixed asset investment in the secondary industry. In March 2016 , however, the private fixed asset investment in the secondary industry began to present a declining trend and became a leading force to bring down the growth of fixed asset investment (Fig. 2.3).
产业经济学代考
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Analysis of prosperity index in the first half of 2016
领先指数和和谐指数显示,2016年上半年景气度由低位缓慢回升。2016年1、2月,领先指数景气度在2015年景气度低迷的影响下跌入负值区间,但呈现持续回升趋势,2016年3月进一步回升至零上方。一致性指数呈现逐年上升、逐月下降的趋势。在图 2.1 中,一致性指数的繁荣度一度上升到大约0.41 月后回落至几乎为零,但 2016 年 3 月有所回升,总体高于去年同期景气度,无论跌至多少
后来出现的趋势。滞后指数(主要包括出口信息和价格信息)表明这种增长存在一定风险。2016年,剔除3月和6月,景气度滞后指数保持在零以下,波动幅度较大。未来一段时间,产业经济增长的不确定性将增加。
从景气指标看,(1)边缘市场明显好转;美国制造业采购经理人指数反弹突破门槛;欧元区制造业PMI维持在关口上方并呈上升趋势。发达国家的经济形势最终会对中国的出口贸易产生影响;尽管2016年一季度我国一般贸易出口量大幅下降,但出口量增长20%3月同比;但中国国内市场仍在调整中,一般贸易出口额没有大幅增长;(二)房地产市场交易活跃。2016年上半年,房地产销售面积快速增长。2016 年 1 月至 6 月,达到643.02万平方米,不断增长27.9%比去年同期; 房地产销售额达人民币4.8682万亿,增长中42.1%. 房地产开发投资规模保持中速增长;2016 年 1 月至 6 月,增长6.1%同比,表明房地产市场对工业增长的拉动作用有限;(三)固定资产投资增速放缓,工业固定资产投资下降明显。2016年1-6月,我国固定资产投资额为人民币25.836万亿元(不含农户),名义同比增长9%(实际上是11%通货膨胀调整后)。第二产业投资达人民币10.1702万亿,增长中4.4%,16.7和7.7分别低于第一产业和第三产业,其中工业投资达人民币9.9594万亿,增长中4.2%同比,制造业投资达人民币8.2261万亿,增长中3.3%只要; (四)受产能过剩和库存调整影响,工业产品产量同比增长不均衡,如铸铁、粗钢、焦炭产量持续低迷,乙烯、铝制品产量持续增长。(5)货币供应量M1快速增长,M2放缓。为应对产业经济下行风险,中国政府实施积极的货币政策,货币供应量大幅增长;然而,由于不良贷款率上升的风险,货币供应量 M2 的增速趋于放缓(表 2.1)。
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|The steady rise in leading indexes predicted
领先指数的稳步上升预示着未来一段时间工业经济将出现一个季度的缓慢增长,但工业经济仍将面临较大的下行压力,因为它仍处于再平衡的阵痛之中。具体来看,一是工业品出厂价格指数维持在负值区间,工业产能过剩未有实质改善,主要工业品交易市场不如预期活跃;二是产业经济本轮增长仍严重依赖房地产市场回暖,随着房地产市场进入调整期,未来增长空间有限。三是固定资产投资仍是支撑本轮产业经济低速增长的主力军。带动固定资产投资增长的主要行业是基础设施投资和房地产市场投资,制造业固定资产投资仍处于低位。四是宽松货币政策对房地产市场回暖起到了积极的推动作用,但宽松货币政策的退出势必会抑制房地产市场的上涨趋势,进一步损害工业品需求。总体来看,本轮产业经济增长延续了原有的投资驱动发展模式,并未产生新的增长点。考虑到中国经济发展由产业驱动型向服务业驱动型转变,
经济代写|产业经济学代写Industrial Economics代考|Factors Influencing the Trend Variation of Industrial Economics
工业部门固定资产投资下降,必然导致资本存量增速放缓,工业部门将迎来下行趋势。中国政府发起的创新发展战略和全球科技革命,将成为产业经济发展的有力支撑。
(一)工业企业投资回报率越来越低,固定资产投资规模不断缩小
1979年改革开放以来,中国工业部门利润规模不断扩大;尤其是2002年以来,增长速度高达20%使工业投资回报率保持较高水平。但2011年以来,工业部门利润增速放缓,甚至出现负增长。由于利润增长率保持低位,
投资回报逐渐回落。白崇恩、张琼 (2014)1指出,2011年以来我国投资资本回报率呈现持续下降趋势,即21.1,16.6和14.7%2011年至2013年,各行业投资资本回报率与全社会基本持平。前者的下降将导致投资转移到其他行业和海外市场。数据显示,从2005年到2013年,工业部门固定资产投资占比一直居高不下。40%占固定资产投资总额;但自 2014 年以来,固定资产回落至39.9%并呈现持续下降的趋势(图2.2)。
民间固定资产投资增长迎来本轮固定资产投资回落趋势。多年来,民间第二产业固定资产投资增速始终超过固定资产投资总额增速,成为第二产业固定资产投资的主力军。但2016年3月,第二产业民间固定资产投资开始呈现下降趋势,成为拉低固定资产投资增速的主导力量(图2.3)。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
