如果你也在 怎样代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
宏观经济学是经济学的一个分支,涉及整个经济或总体经济的结构、绩效、行为和决策。宏观经济研究的两个主要领域是长期经济增长和短期商业周期。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写宏观经济学Macroeconomics相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的宏观经济学Macroeconomics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|The Relationship between Production and Employment
The production function is the level of production that a company (or group of companies) achieves with given levels of available capital, labor, and technology. The capital of a company is formed by the plant, the equipment, and the quantity of primary, semiprocessed, and finished goods owned by the company (called stocks or inventories). The labor component is related to the total number of employees and the number of hours they work, and
technology is the way capital and labor are combined in the production process.
When we study the short term (a period of one year or less), it is possible to assume that the capital stock and the level of technological knowledge of the economy are fixed. Therefore, large output fluctuations typically reflect changes in labor inputs and changes in transitory factors, such as strikes, civil unrest, or other shocks to production. Over longer periods, variations in production also reflect changes in the capital stock and technology.
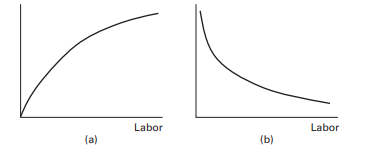
The production function has two important characteristics. First, an increase in the amount of any inputcapital, labor, or technology-increases production. The term marginal productivity is used to measure the increase in production that results from increasing any input by a single unit and is almost always positive. Second, the marginal productivity of each factor decreases when more of that factor is used and the other factors are fixed.
Let’s consider, for example, an automobile assembly plant. Suppose a machine can normally be used by ten workers, although only five workers are available to operate each machine. Under these conditions, if an additional worker is hired, production will increase substantially. However, if more workers are hired without an increase in the number of machines, the increase in total production generated by each new worker will decline. If ten workers are needed to oversee the operation of a single machine, the eleventh worker hired will add little or almost nothing to total production. The production function and marginal productivity are represented graphically in figure $2 .$
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|Labor Supply and Equilibrium in the Labor Market
The next step in understanding how employment and output are determined in the economy is to define the amount of work that families are willing to offer to businesses. This starts with a simple decision of work supply, whereby a person must choose between working or enjoying leisure time. A day has only twenty-four hours, so each additional hour dedicated to work is one hour less available for leisure. Leisure is understood as recreational activities, such as reading for pleasure, listening to $\mathrm{mu}$ sic, playing sports, going to the theater, or even sleeping. However, the economic measurement of leisure is less precise and includes almost any other activity that has not been accounted for in the national production, such as household chores. This last definition has implications when one considers differences in labor force participation by gender, insofar as the fraction of people who are engaged in household chores is still higher among women, especially in developing countries.
In real life, the decision to offer labor to a business is, of course, much more complex. Individuals are subject to many more limitations and needs, along with personal long-term goals and aspirations, that play an important role in their work-supply decision. This is the case with many other decisions or real-life situations that economic models intend to portray. The fact that economic models simplify reality helps explain why they do not provide exact predictions for real outcomes. This is especially relevant when we consider the role of models in the making of macroeconomic policy. However, one should keep in mind that models, although often inexact, tend to provide the closest mathematical approach to reality and facilitate decision-making.
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|The fact that economic
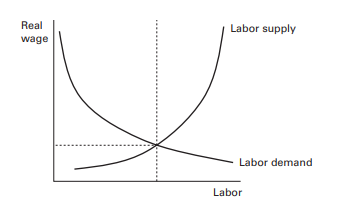
Now that we have determined labor demand and supply, the next step is to observe how they interact and how equilibrium is obtained in the labor market. Equilibrium is the point at which the demand for labor is met by the supply of labor: in other words, every job opening has been filled and the unemployment rate is 0 percent. True equilibrium is generally possible only in economic models. In the real world, there is often some level of unemployment, which we discuss in the next section. The simplest version of the labor market equilibrium is the classical approach, which assumes that real wages are flexible and adjust to keep the supply of and demand for labor in equilibrium. In this context, work is fully employed, since companies want to hire exactly the amount of work that people are offering, and the real wage is determined by the market.
Figure 3 shows how the labor market is balanced at the intersection of labor demand and supply. However, this relationship between output and employment could be broken temporarily. For example, in Chile, the year 2000 was quite contradictory in economic terms. While the Chilean GDP increased by $4.5$ percent, 23,000 jobs were lost. This is paradoxical since historically, for every percentage point increase in Chile’s GDP, employment grew by approximately $0.7$ percent per year. This means that in the year 2000 more than 100,000 jobs should have been created.
宏观经济学代考
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|The Relationship between Production and Employment
生产函数是公司(或公司集团)在给定的可用资本、劳动力和技术水平下所达到的生产水平。公司的资本由工厂、设备以及公司拥有的初级产品、半加工产品和制成品的数量(称为库存或存货)构成。劳动力部分与员工总数和他们工作的小时数有关,并且
技术是资本和劳动力在生产过程中结合的方式。
当我们研究短期(一年或更短的时间)时,可以假设经济的资本存量和技术知识水平是固定的。因此,巨大的产出波动通常反映了劳动力投入的变化和临时因素的变化,例如罢工、内乱或其他生产冲击。在较长时期内,生产的变化也反映了资本存量和技术的变化。
生产函数有两个重要特征。首先,任何投入资本、劳动力或技术数量的增加都会增加生产。边际生产率一词用于衡量因将任何投入增加一个单位而导致的产量增加,并且几乎总是正数。其次,当使用更多该要素且其他要素固定时,每个要素的边际生产率会降低。
例如,让我们考虑一个汽车装配厂。假设一台机器通常可供十名工人使用,尽管每台机器只有五名工人可以操作。在这种情况下,如果雇用额外的工人,产量将大幅增加。但是,如果在不增加机器数量的情况下雇用更多工人,则每个新工人所产生的总产量的增加将下降。如果需要 10 名工人来监督一台机器的运行,那么雇用的第 11 名工人将很少或几乎不会增加总产量。生产函数和边际生产率用图形表示在图中2.
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|Labor Supply and Equilibrium in the Labor Market
了解经济中就业和产出如何决定的下一步是确定家庭愿意为企业提供的工作量。这从一个简单的工作供应决定开始,一个人必须在工作或享受休闲时间之间做出选择。一天只有 24 小时,因此每多用于工作的一小时,用于休闲的时间就会减少一小时。休闲被理解为娱乐活动,例如阅读以消遣,听米在sic,做运动,去剧院,甚至睡觉。然而,休闲的经济测量不太精确,几乎包括了国家生产中没有考虑到的任何其他活动,例如家务活。最后一个定义在考虑劳动力参与性别差异时会产生影响,因为女性从事家务劳动的比例仍然较高,尤其是在发展中国家。
在现实生活中,为企业提供劳动力的决定当然要复杂得多。个人受到更多的限制和需求,以及个人的长期目标和愿望,这在他们的工作供应决策中起着重要作用。经济模型打算描绘的许多其他决策或现实生活情况就是这种情况。经济模型简化现实这一事实有助于解释为什么它们不能为实际结果提供准确的预测。当我们考虑模型在制定宏观经济政策中的作用时,这一点尤其重要。但是,应该记住,模型虽然通常不精确,但往往会提供最接近现实的数学方法并有助于决策制定。
经济代写|宏观经济学作业代写Macroeconomics代考|The fact that economic
既然我们已经确定了劳动力的需求和供给,下一步就是观察它们如何相互作用以及如何在劳动力市场中获得均衡。均衡是劳动力供给满足劳动力需求的点:换句话说,每个职位空缺都已填补,失业率为 0%。真正的均衡通常只有在经济模型中才有可能。在现实世界中,通常存在一定程度的失业,我们将在下一节讨论。劳动力市场均衡的最简单版本是经典方法,它假设实际工资是灵活的并且可以调整以保持劳动力的供需平衡。在这种情况下,工作是充分就业的,因为公司希望准确地雇用人们提供的工作量,而实际工资是由市场决定的。
图 3 显示了劳动力市场如何在劳动力需求和供给的交叉点达到平衡。然而,产出和就业之间的这种关系可能会暂时被打破。例如,在智利,2000 年在经济方面是非常矛盾的。虽然智利国内生产总值增长4.5%,失去了 23,000 个工作岗位。这是自相矛盾的,因为从历史上看,智利国内生产总值每增加一个百分点,就业人数就会增加大约0.7每年百分之几。这意味着在 2000 年应该创造超过 100,000 个工作岗位。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
