如果你也在 怎样代写神经网络neural networks这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
神经网络,也被称为人工神经网络(ANN)或模拟神经网络(SNN),是机器学习的一个子集,是深度学习算法的核心。它们的名称和结构受到人脑的启发,模仿了生物神经元相互之间的信号方式。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写神经网络neural networks方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写神经网络neural networks代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写神经网络neural networks相关的作业也就用不着说。
计算机代写|神经网络代写neural networks代考|Introduction and Role of Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks are, as their name indicates, computational networks which attempt to simulate, in a gross manner, the networks of nerve cell (neurons) of the biological (human or animal) central nervous system. This simulation is a gross cell-by-cell (neuron-by-neuron, element-by-element) simulation. It borrows from the neurophysiological knowledge of biological neurons and of networks of such biological neurons. It thus differs from conventional (digital or analog) computing machines that serve to replace, enhance or speed-up human brain computation without regard to organization of the computing elements and of their networking. Still, we emphasize that the simulation afforded by neural networks is very gross.
Why then should we view artificial neural networks (denoted below as neural networks or ANNs) as more than an exercise in simulation? We must ask this question especially since, computationally (at least), a conventional digital computer can do everything that an artificial neural network can do.
The answer lies in two aspects of major importance. The neural network, by its simulating a biological neural network, is in fact a novel computer architecture and a novel algorithmization architecture relative to conventional computers. It allows using very simple computational operations (additions, multiplication and fundamental logic elements) to solve complex, mathematically ill-defined problems, nonlinear problems or stochastic problems. A conventional algorithm will employ complex sets of equations, and will apply to only a given problem and exactly to it. The ANN will be (a) computationally and algorithmically very simple and (b) it will have a self-organizing feature to allow it to hold for a wide range of problems.
For example, if a house fly avoids an obstacle or if a mouse avoids a cat, it certainly solves no differential equations on trajectories, nor does it employ complex pattern recognition algorithms. Its brain is very simple, yet it employs a few basic neuronal cells that fundamentally obey the structure of such cells in advanced animals and in man. The artificial neural network’s solution will also aim at such (most likely not the same) simplicity. Albert Einstein stated that a solution or a model must be as simple as possible to fit the problem at hand. Biological systems, in order to be as efficient and as versatile as they certainly are despite their inherent slowness (their basic computational step takes about a millisecond versus less than a nanosecond in today’s electronic computers), can only do so by converging to the simplest algorithmic architecture that is possible. Whereas high level mathematics and logic can yield a broad general frame for solutions and can be reduced to specific but complicated algorithmization, the neural network’s design aims at utmost simplicity and utmost self-organization. A very simple base algorithmic structure lies behind a neural network, but it is one which is highly adaptable to a broad range of problems. We note that at the present state of neural networks their range of adaptability is limited. However, their design is guided to achieve this simplicity and self-organization by its gross simulation of the biological network that is (must be) guided by the same principles.
计算机代写|神经网络代写neural networks代考|Fundamentals of Biological Neural Networks
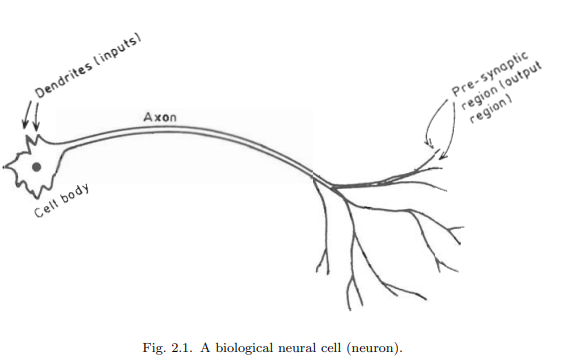
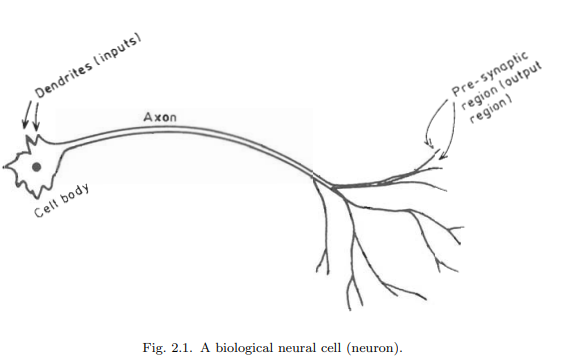
The biological neural network consists of nerve cells (neurons) as in Fig. 2.1, which are interconnected as in Fig. 2.2. The cell body of the neuron, which includes the neuron’s nucleus is where most of the neural “computation” takes place. Neural activity passes from one neuron to another in terms of electrical triggers which travel from one cell to the other down the neuron’s axon, by means of an electrochemical process of voltage-gated ion exchange along the axon and of diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules through the membrane over the synaptic gap (Fig. 2.3). The axon can be viewed as a connection wire. However, the mechanism of signal flow is not via electrical conduction but via charge exchange that is transported by diffusion of ions. This transportation process moves along the neuron’s cell, down the axon and then through synaptic junctions at the end of the axon via a very narrow synaptic space to the dendrites and/or soma of the next neuron at an average rate of $3 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$., as in Fig. 2.3 .
Figures 2.1 and 2.2 indicate that since a given neuron may have several (hundreds of) synapses, a neuron can connect (pass its message/signal) to many (hundreds of) other neurons. Similarly, since there are many dendrites per each neuron, a single
neuron can receive messages (neural signals) from many other neurons. In this manner, the biological neural network interconnects [Ganong, 1973].
It is important to note that not all interconnections, are equally weighted. Some have a higher priority (a higher weight) than others. Also some are excitory and some are inhibitory (serving to block transmission of a message). These differences are effected by differences in chemistry and by the existence of chemical transmitter and modulating substances inside and near the neurons, the axons and in the synaptic junction. This nature of interconnection between neurons and weighting of messages is also fundamental to artificial neural networks (ANNs).
神经网络代写
计算机代写|神经网络代写neural networks代考|Introduction and Role of Artificial Neural Networks
人工神经网络,顾名思义,是试图以粗略的方式模拟生物(人类或动物)中枢神经系统的神经细胞(神经元)网络的计算网络。这个模拟是一个细胞对细胞(神经元对神经元,元素对元素)的模拟。它借鉴了生物神经元和这种生物神经元网络的神经生理学知识。因此,它与传统的(数字或模拟)计算机器不同,传统的计算机器用来取代、增强或加速人脑的计算,而不考虑计算元素的组织和它们的网络。不过,我们要强调的是,神经网络提供的模拟是非常粗糙的。
那么,为什么我们要将人工神经网络(下文表示为神经网络或ANNs)视为不仅仅是模拟练习呢?我们必须问这个问题,特别是因为,在计算上(至少),传统的数字计算机可以做人工神经网络能做的一切。
答案在于两个重要的方面。神经网络通过模拟生物神经网络,实际上是一种相对于传统计算机而言的新型计算机体系结构和算法体系结构。它允许使用非常简单的计算操作(加法、乘法和基本逻辑元素)来解决复杂的、数学上不明确的问题、非线性问题或随机问题。传统的算法会使用复杂的方程组,只适用于一个给定的问题,并且完全适用于这个问题。人工神经网络将(a)在计算和算法上非常简单,(b)它将具有自组织特征,使其能够适用于广泛的问题。
例如,如果一只家蝇避开了一个障碍物,或者一只老鼠避开了一只猫,它当然不会求解轨迹上的微分方程,也不会使用复杂的模式识别算法。它的大脑非常简单,但它使用了一些基本的神经细胞,这些细胞从根本上服从于高级动物和人类的神经细胞结构。人工神经网络的解决方案也将以这种(很可能不是同样的)简单性为目标。阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦说,一个解决方案或模型必须尽可能简单,以适应手头的问题。尽管生物系统固有的速度很慢(它们的基本计算步骤大约需要一毫秒,而在今天的电子计算机中不到一纳秒),但为了像它们一样高效和通用,它们只能通过收敛到尽可能简单的算法架构来实现。高水平的数学和逻辑可以为解决方案提供一个广泛的通用框架,并可以简化为具体但复杂的算法,而神经网络的设计旨在最大限度地简单和最大限度地自组织。神经网络的基础算法结构非常简单,但它是一个高度适应广泛问题的算法结构。我们注意到,在目前的状态下,神经网络的自适应范围是有限的。然而,它们的设计是通过对生物网络的总体模拟来实现这种简单性和自组织的,而生物网络是(必须)由相同的原则指导的。
计算机代写|神经网络代写neural networks代考|Fundamentals of Biological Neural Networks
生物神经网络由神经细胞(神经元)组成,如图2.1所示,神经元之间相互连接,如图2.2所示。神经元的细胞体,包括神经元的细胞核,是大多数神经“计算”发生的地方。神经活动通过电触发器从一个神经元传递到另一个神经元,电触发器沿着神经元的轴突从一个细胞传递到另一个细胞,通过沿轴突电压门控离子交换的电化学过程和神经递质分子通过突触间隙上的膜扩散(图2.3)。轴突可以看作是一根连接线。然而,信号流动的机制不是通过电传导,而是通过离子扩散传递的电荷交换。这个运输过程沿着神经元的细胞,沿着轴突向下,然后通过轴突末端的突触连接,通过一个非常狭窄的突触空间,以平均$3 \ mathm {~m} / \ mathm {sec}$的速度到达下一个神经元的树突和/或体细胞。,如图2.3所示。
图2.1和2.2表明,由于一个给定的神经元可能有几个(数百个)突触,一个神经元可以连接(传递其信息/信号)到许多(数百个)其他神经元。同样的,因为每个神经元有很多树突,一个
一个神经元可以接收来自许多其他神经元的信息(神经信号)。以这种方式,生物神经网络相互连接[Ganong, 1973]。
重要的是要注意,并非所有的互连都具有相同的权重。有些优先级更高(权重更高)。还有一些是兴奋性的,一些是抑制性的(用于阻止信息的传递)。这些差异是由化学成分的差异以及神经元、轴突和突触连接处的化学递质和调节物质的存在所影响的。神经元之间的互连和信息加权的本质也是人工神经网络(ann)的基础。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。