如果你也在 怎样代写回归分析Regression Analysis 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。回归分析Regression Analysis回归中的概率观点具体体现在给定X数据的特定固定值的Y数据的可变性模型中。这种可变性是用条件分布建模的;因此,副标题是:“条件分布方法”。回归的整个主题都是用条件分布来表达的;这种观点统一了不同的方法,如经典回归、方差分析、泊松回归、逻辑回归、异方差回归、分位数回归、名义Y数据模型、因果模型、神经网络回归和树回归。所有这些都可以方便地用给定特定X值的Y条件分布模型来看待。
回归分析Regression Analysis条件分布是回归数据的正确模型。它们告诉你,对于变量X的给定值,可能存在可观察到的变量Y的分布。如果你碰巧知道这个分布,那么你就知道了你可能知道的关于响应变量Y的所有信息,因为它与预测变量X的给定值有关。与基于R^2统计量的典型回归方法不同,该模型解释了100%的潜在可观察到的Y数据,后者只解释了Y数据的一小部分,而且在假设几乎总是被违反的情况下也是不正确的。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写回归分析Regression Analysis方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写回归分析Regression Analysis代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写回归分析Regression Analysis相关的作业也就用不着说。
统计代写|回归分析作业代写Regression Analysis代考|The Quadratic Model in Two or More $X$ Variables
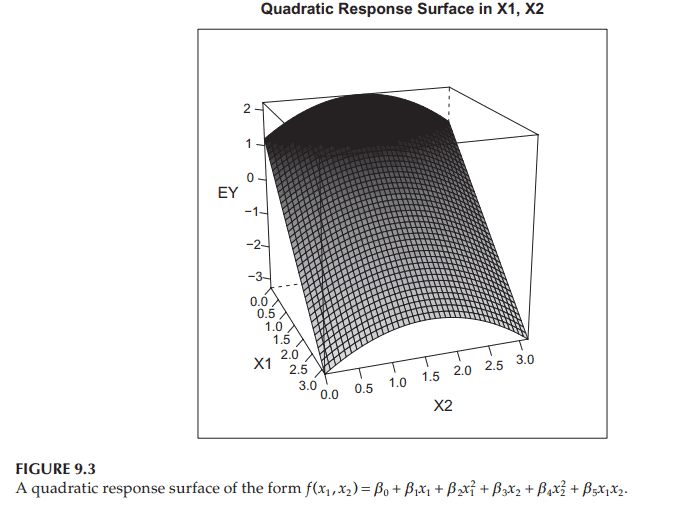
The general quadratic response surface as given in the introduction to this chapter is $f\left(x_1, x_2\right)=\beta_0+\beta_1 x_1+\beta_2 x_1^2+\beta_3 x_2+\beta_4 x_2^2+\beta_5 x_1 x_2$. An example for particular choices of the coefficients $\beta$ is shown in Figure 9.3. Notice that the response function is curved, not planar, and is, therefore, more realistic. The term “response surface” is sometimes used instead of “response function” in the case of two or more $X$ variables; the “surface” term is explained by the appearance of the graph of the function in Figure 9.3.
In addition to modeling and testing for curvature in higher dimensional space, quadratic models are also useful for identifying an optimal combination of $X$ values that maximizes or minimizes the response function; see the “rsm” package of $\mathrm{R}$ for more information. While quadratic models are more flexible (and therefore more realistic) than planar models, they can have poor extrapolation properties and are often less realistic than the similarly flexible, curved class of response surfaces known as neural network regression models. In Chapter 17, we compare polynomial regression models with neural network regression models.
统计代写|回归分析作业代写Regression Analysis代考|Interaction (or Moderator) Analysis
The commonly-used interaction model is a special case of the general quadratic model, involving the interaction term but no quadratic terms. When performing interaction analysis, you typically will assume the following conditional mean function:
$$
\mathrm{E}\left(Y \mid X_1=x_1, X_2=x_2\right)=\beta_0+\beta_1 x_1+\beta_2 x_2+\beta_3 x_1 x_2
$$
A slight modification of the Product Complexity example provides a case study in which interaction is needed. Suppose you measure $Y=$ Intent to Purchase a Luxury Product, say expensive jewelry, using a survey of consumers. You also measure the attractiveness $\left(X_1\right)$ of a web design used to display and promote the product, say measured in a scale from 1 to 10 , with $10=$ most attractive design, and the person’s income $\left(X_2\right)$ in a scale from 1 to 5 , with $5=$ most wealthy.
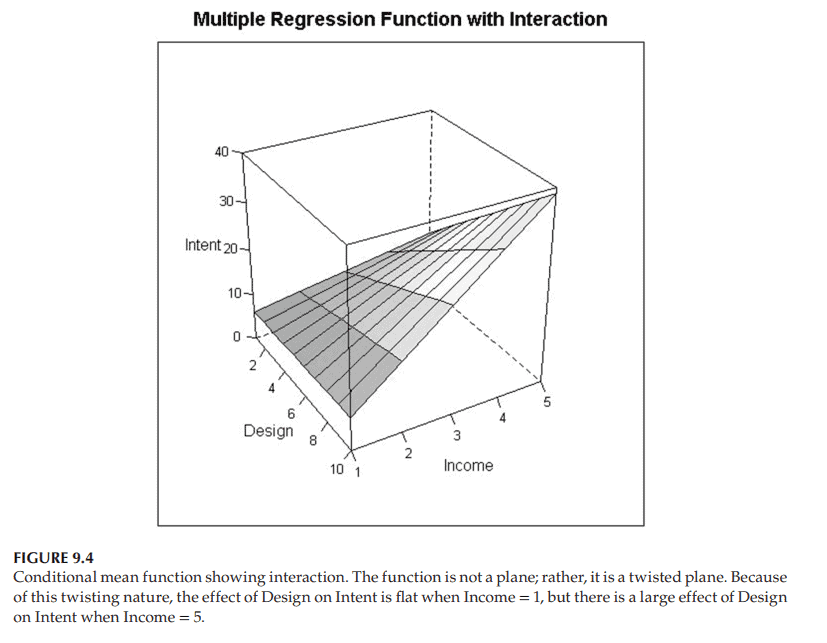
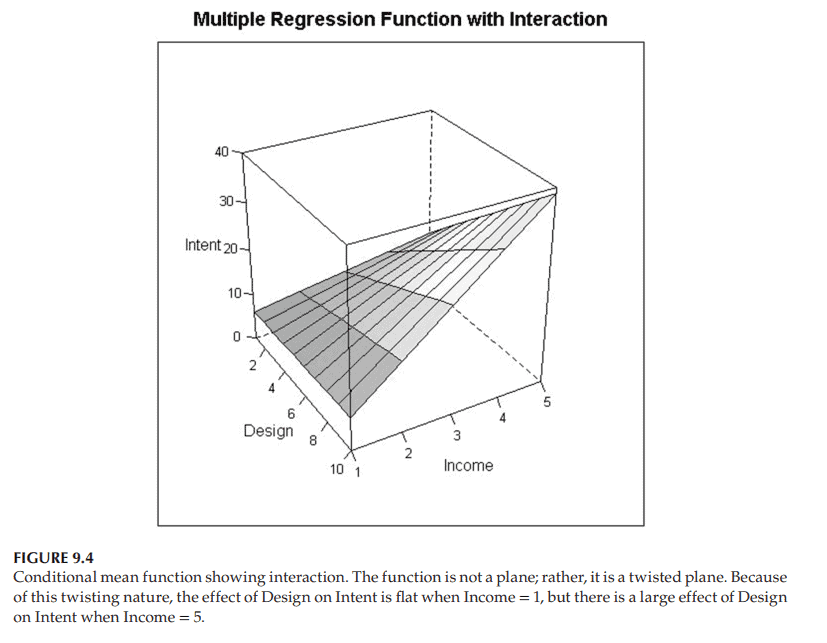
Figure 9.4 shows an example of how this conditional mean function might look. Like the quadratic response surface, it is a curved function in space, not a plane. But note in particular that the effect of $X_1$, Attractiveness of Web Design, on $Y=$ Intent to Purchase, depends on the value of $X_2$, Income: For consumers with the lowest income, $X_2=1$, the slice of the surface corresponding to $X_2=1$ is nearly flat as a function of $X_1=$ Attractiveness of Web Design. That is to say, for people with the lowest income, Attractiveness of Web Design has little effect on Intent to Purchase this luxury product. No surprise! They do not have enough money to purchase luxury items, so the web design is mostly irrelevant to them. On the other hand, for people with the highest income $\left(X_2=5\right)$, the slice of the surface corresponding to $X_2=5$ increases substantially as a function of $X_1=$ Attractiveness of Web Design. Thus, this single model states both (i) that Attractiveness of Web Design $\left(X_1\right)$ has little effect on Intention to Purchase a Luxury Product for people with little money, and (ii) that Attractiveness of Web Design $\left(X_1\right)$ has a substantial effect on Intention to Purchase a Luxury Product for people with lots of money.
回归分析代写
统计代写|回归分析作业代写Regression Analysis代考|The Quadratic Model in Two or More $X$ Variables
本章导言中给出的一般二次响应面是$f\left(x_1, x_2\right)=\beta_0+\beta_1 x_1+\beta_2 x_1^2+\beta_3 x_2+\beta_4 x_2^2+\beta_5 x_1 x_2$。图9.3显示了系数$\beta$的特定选择示例。请注意,响应函数是弯曲的,而不是平面的,因此更真实。在两个或多个$X$变量的情况下,有时使用术语“响应面”代替“响应函数”;“面”一词由图9.3所示的函数图来解释。
除了对高维空间中的曲率进行建模和测试外,二次模型还可用于识别使响应函数最大化或最小化的$X$值的最佳组合;有关更多信息,请参阅$\mathrm{R}$的“rsm”包。虽然二次模型比平面模型更灵活(因此也更现实),但它们的外推特性很差,而且往往不如类似灵活的曲线响应面(即神经网络回归模型)真实。在第17章中,我们比较了多项式回归模型和神经网络回归模型。
统计代写|回归分析作业代写Regression Analysis代考|Interaction (or Moderator) Analysis
常用的交互模型是一般二次模型的一种特殊情况,只涉及交互项而不涉及二次项。在进行交互分析时,您通常会假设以下条件平均函数:
$$
\mathrm{E}\left(Y \mid X_1=x_1, X_2=x_2\right)=\beta_0+\beta_1 x_1+\beta_2 x_2+\beta_3 x_1 x_2
$$
对Product Complexity示例稍加修改,提供了一个需要交互的案例研究。假设你通过对消费者的调查来衡量$Y=$购买奢侈品的意向,比如昂贵的珠宝。你还测量了用于展示和推广产品的网页设计的吸引力$\left(X_1\right)$,比如用1到10的等级来衡量,$10=$是最吸引人的设计,而这个人的收入$\left(X_2\right)$用1到5的等级来衡量,$5=$是最富有的。
图9.4显示了这个条件平均函数的示例。和二次响应曲面一样,它是空间中的一个曲线函数,而不是一个平面。但要特别注意的是,$X_1$网页设计吸引力对$Y=$购买意愿的影响取决于$X_2$收入的值:对于收入最低的$X_2=1$消费者来说,$X_2=1$对应的表面片几乎是平坦的,作为$X_1=$网页设计吸引力的函数。也就是说,对于收入最低的人群来说,网页设计的吸引力对购买这一奢侈品的意愿影响不大。一点也不奇怪!他们没有足够的钱去购买奢侈品,所以网页设计基本上与他们无关。另一方面,对于收入最高的人$\left(X_2=5\right)$,对应于$X_2=5$的表面的切片作为$X_1=$的函数显著增加。因此,这个单一的模型表明(i)网页设计的吸引力$\left(X_1\right)$对没有钱的人购买奢侈品的意愿影响很小,(ii)网页设计的吸引力$\left(X_1\right)$对有钱的人购买奢侈品的意愿有实质性的影响。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。