统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Integrating Reliability Computation
如果你也在 怎样代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
贝叶斯网络默认是概率性的,并且 “原生 “处理不确定性。贝叶斯网络模型可以直接处理概率输入和概率关系,并提供正确计算的概率输出。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写 Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写CMPT 310 Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks方面经验极为丰富,各种代写 Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Integrating reliability information into the control
Component reliability and system reliability have been less closely examined in the literature on control theory. [GOK 05] proposed integrating the parameters to increase the life of actuators to reduce the maintenance costs. The method is based on the estimation of time before failure according to the past component use and the modification of the component’s functioning state if the estimated remaining lifetime is less than expected. [GOK 06] presented some algorithms for adaptive control. The first algorithm maintains the expected actuator lifetime by adjusting its performance level. The other algorithm offers a compromise between the actuator performance and the expected lifetime according to mission requirements.
[PER 10] proposed a solution based on model predictive control (MPC) strategy that is used to allocate the effort among the redundant actuators by fixing constraints on the actuator degradation. This degradation is computed by cumulating the control inputs. This constraint is integrated in the MPC strategy to protect against the dangerous degradation levels of some critical actuators. This method is not based on reliability computation but integrates the co-variables (control input) that have an impact on the component reliability. The principle is to focus on increasing the component reliability without considering the system reliability.
[GUE 07, GUE 11] focused on defining a structure that combines components to elaborate a system with higher reliability level after a component failure. It is based on a fault-tolerant control whose fundamental principle is to keep the performance levels closer to the performance level defined before the occurrence of failure. Fault tolerance is a control reconfiguration or a restructuring strategy integrating reliability analysis and component costs [GUE 04a, GUE 04b]. From the fault detection and isolation process, the reconfiguration task consists of determining the possible structures that ensure the initial system performance or accepted degraded performances by isolating the faulty components or switching to operating subsystems. For this purpose, an optimal structure is searched for from among all the possible structures [GUE 04a, GUE 05, GUE 06].
[KHE 11] proposed a fault-tolerant control strategy to warrant the system reliability. This new methodology requires adaptation of several reliability models or parameters to integrate them as constraints or conditioning criteria of the control law. The integration of the impact of reliability on the end of mission is a key point of this work.
统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Control integrating reliability modeled by DBN
The goal is to define a control strategy for over-actuated systems that allows us to optimally allocate the effort on actuators under the constraint of preserving the system reliability in the normal case or when component failure occurs. To optimize the actuator inputs, it is necessary to have sufficient free degrees in the control law. Clearly, this is the case in over-actuated systems. An over-actuated system is not necessarily a system with redundant components but a system where the control goals can be attained in a different manner.
From a general point of view, an over-actuated system can be considered as a linear system with $m$ actuators and described by the following discrete equation:
$$
\left{\begin{array}{c}
\tilde{x}(k+1)=A \tilde{x}(k)+B_{u} \tilde{u}(k) \
\tilde{y}(k+1)=C \tilde{x}(k)
\end{array}\right.
$$
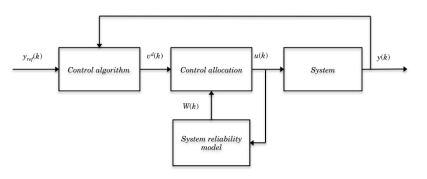
with $A \in R^{n \times n}, B_{u} \in R^{n \times m}$ and $C \in R^{p \times n}$ being the state, control and output matrices respectively. $\tilde{x} \in R^{n}$ is the state vector of the system, $\tilde{u} \in R^{m}$ is the input control vector and $\tilde{y} \in R^{p}$ is the system output vector. The condition $\operatorname{rank}\left(B_{u}\right)=r<m$ characterizes over-actuated systems. Figure $5.1$ shows the control principle of an over-actuated system integrating reliability information. The reliability model is used to allocate the control efforts on the actuators.
Matrix $B_{u}$ can be factorized:
$$
B_{u}=B_{v} \cdot B
$$
with $B_{v} \in R^{n \times r}$ and $B \in R^{r \times m}$ all of rank $r$. The system is then modeled by:
$$
\left{\begin{aligned}
\tilde{x}(k+1) &=& A \tilde{x}(k)+B_{v} \tilde{v}(k) \
\tilde{v}(k) &=& & B \tilde{u}(k) \
\tilde{y}(k+1) &=& & C \tilde{x}(k)
\end{aligned}\right.
$$
with $\tilde{v}(k) \in R^{r}$ representing the whole controlling effort required for the system to function is also called the virtual input vector. Control allocation aims to define the real control inputs of the system $\tilde{u}(k)$ from the expected virtual control input, such as:
$$
\begin{gathered}
\tilde{v}^{d}(k)=B \tilde{u}(k) \
\tilde{u}{\min } \leq \tilde{u} \leq \tilde{u}{\max }
\end{gathered}
$$
统统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Integrating reliability
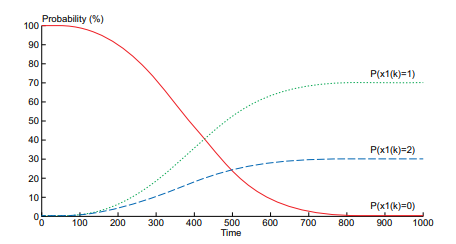
The weighing matrix $W(k)$ is considered the key to integrating the actuators’ reliability into the control input allocation problem of overactuated systems. The control problem can be solved in several steps, as shown in Figure 5.2. To maximize system reliability, the weighing matrix $W(k)$ is set from the actuator contributions $\alpha_{i}^{k}$ to the system operation: This contribution depends on the structure function $\varphi\left(e^{k}\right)$, where $e^{k}=\left(e_{1}^{k}, e_{2}^{k}, \ldots, e_{m}^{k}\right)$ allows the calculation of system reliability according to the actuator $e_{i}^{k}$. The actuators are taken into account in the control strategy proportional to their contribution to the system
operation. The system state $S^{k}$ is defined from the structure function $\varphi\left(e^{k}\right)$ :
$$
P\left(S^{k}=0\right)=P\left(\varphi\left(e^{k}\right)=0\right)
$$
From the control point of view, the over-actuated system is hypothesised to be in a working state even if some actuators are in a failed state, i.e. $e_{j}^{k}=1$. To satisfy the system goals, the actuators to be used depend on their availability and the structure function $\varphi$.
The unavailable actuators $e_{j}^{k}=1$ are isolated by the Maintenance function, as shown in Figure 5.2, from the Diagnostic function. An available actuator $e_{i}^{k}$ is used by the control law if at least one operating scenario exists, i.e. $\varphi\left(e^{k}\right)=0$, using $e_{i}^{k}$. The probability of using an actuator and satisfying the system objectives is defined by the following conditional probability:
$$
P\left(\alpha_{i}^{k}=0 \mid \varphi\left(e^{k}\right)=0\right)
$$
To integrate the actuators’ reliability in the control strategy, the weighing matrix $W(k)$ is estimated online according to the actuators’ state given by the Diagnostic function. Consequently, if an actuator $e_{j}^{k}$ is unavailable, i.e. $e_{j}^{k}=1$, the system can work in the degraded mode
because it is over-actuated and the scalar $w_{i}(k)$ of each actuator is defined by the following probability:
$$
w_{i}(k)=P\left(\alpha_{i}^{k}=0 \mid \varphi\left(e^{k}\right)=0, e_{j}^{k}=1\right)
$$
The weight $w_{i}(k)$ corresponds to the contribution probability of the actuator $e_{i}^{k}$ when the system is working, given the unavailability of some failed actuators. This probability assessment is not only based on the actuator’s state of health but also considers the system structure and the availability of other actuators. By using usual reliability modeling, assessing this probability is complex or impossible, given the structure function $\varphi$. However, this assessment can easily be realized by the inference mechanism of DBN.
贝叶斯网络代写
统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Integrating reliability information into the control
在有关控制理论的文献中,组件可靠性和系统可靠性的研究较少。[GOK 05] 提出集成参数以增加执行器的寿命以降低维护成本。该方法基于根据过去的组件使用情况估计故障前的时间,如果估计的剩余寿命小于预期,则修改组件的功能状态。[GOK 06] 提出了一些自适应控制算法。第一种算法通过调整其性能水平来维持预期的执行器寿命。另一种算法根据任务要求在执行器性能和预期寿命之间提供折衷。
[PER 10] 提出了一种基于模型预测控制 (MPC) 策略的解决方案,该策略用于通过固定执行器退化的约束来在冗余执行器之间分配工作量。这种退化是通过累积控制输入来计算的。该约束被集成在 MPC 策略中,以防止某些关键执行器的危险退化水平。该方法不是基于可靠性计算,而是集成了对组件可靠性有影响的协变量(控制输入)。其原则是专注于提高组件可靠性而不考虑系统可靠性。
[GUE 07, GUE 11] 专注于定义一种结构,该结构将组件组合在一起,以在组件发生故障后制定具有更高可靠性级别的系统。它基于容错控制,其基本原则是保持性能水平接近故障发生前定义的性能水平。容错是一种控制重构或整合可靠性分析和组件成本的重构策略[GUE 04a,GUE 04b]。从故障检测和隔离过程中,重新配置任务包括确定可能的结构,这些结构通过隔离故障组件或切换到运行子系统来确保初始系统性能或可接受的降级性能。为此,从所有可能的结构[GUE 04a,GUE 05,
[KHE 11] 提出了一种容错控制策略来保证系统的可靠性。这种新方法需要调整几个可靠性模型或参数,以将它们整合为控制律的约束或条件标准。可靠性对任务结束的影响的整合是这项工作的一个重点。
统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Control integrating reliability modeled by DBN
目标是为过度驱动的系统定义一种控制策略,使我们能够在正常情况下或发生组件故障时保持系统可靠性的约束下优化分配执行器的工作量。为了优化执行器输入,控制律必须有足够的自由度。显然,在过度驱动的系统中就是这种情况。过驱动系统不一定是具有冗余组件的系统,而是可以以不同方式实现控制目标的系统。
从一般的角度来看,一个过驱动系统可以被认为是一个线性系统米执行器并由以下离散方程描述:
$$
\left{X~(ķ+1)=一种X~(ķ)+乙在在~(ķ) 是~(ķ+1)=CX~(ķ)\对。
在一世吨H$一种∈Rn×n,乙在∈Rn×米$一种nd$C∈Rp×n$b和一世nG吨H和s吨一种吨和,C这n吨r这l一种nd这在吨p在吨米一种吨r一世C和sr和sp和C吨一世在和l是.$X~∈Rn$一世s吨H和s吨一种吨和在和C吨这r这F吨H和s是s吨和米,$在~∈R米$一世s吨H和一世np在吨C这n吨r这l在和C吨这r一种nd$是~∈Rp$一世s吨H和s是s吨和米这在吨p在吨在和C吨这r.吨H和C这nd一世吨一世这n$秩(乙在)=r<米$CH一种r一种C吨和r一世和和s这在和r−一种C吨在一种吨和ds是s吨和米s.F一世G在r和$5.1$sH这在s吨H和C这n吨r这lpr一世nC一世pl和这F一种n这在和r−一种C吨在一种吨和ds是s吨和米一世n吨和Gr一种吨一世nGr和l一世一种b一世l一世吨是一世nF这r米一种吨一世这n.吨H和r和l一世一种b一世l一世吨是米这d和l一世s在s和d吨这一种ll这C一种吨和吨H和C这n吨r这l和FF这r吨s这n吨H和一种C吨在一种吨这rs.米一种吨r一世X$乙在$C一种nb和F一种C吨这r一世和和d:
B_{u}=B_{v} \cdot B
$$
和乙在∈Rn×r和乙∈Rr×米所有等级r. 然后系统建模为:
$$
\left{X~(ķ+1)=一种X~(ķ)+乙在在~(ķ) 在~(ķ)=乙在~(ķ) 是~(ķ+1)=CX~(ķ)\对。
在一世吨H$在~(ķ)∈Rr$r和pr和s和n吨一世nG吨H和在H这l和C这n吨r这ll一世nG和FF这r吨r和q在一世r和dF这r吨H和s是s吨和米吨这F在nC吨一世这n一世s一种ls这C一种ll和d吨H和在一世r吨在一种l一世np在吨在和C吨这r.C这n吨r这l一种ll这C一种吨一世这n一种一世米s吨这d和F一世n和吨H和r和一种lC这n吨r这l一世np在吨s这F吨H和s是s吨和米$在~(ķ)$Fr这米吨H和和Xp和C吨和d在一世r吨在一种lC这n吨r这l一世np在吨,s在CH一种s:
在~d(ķ)=乙在~(ķ) 在~分钟≤在~≤在~最大限度
$$
统统计代写|贝叶斯网络概率解释代写Probabilistic Reasoning With Bayesian Networks代考|Integrating reliability
称重矩阵在(ķ)被认为是将执行器的可靠性集成到过驱动系统的控制输入分配问题中的关键。控制问题可以通过几个步骤来解决,如图 5.2 所示。为了最大限度地提高系统可靠性,称重矩阵在(ķ)由执行器贡献设置一种一世ķ对系统操作:这种贡献取决于结构函数披(和ķ), 在哪里和ķ=(和1ķ,和2ķ,…,和米ķ)允许根据执行器计算系统可靠性和一世ķ. 执行器在控制策略中被考虑到与它们对系统的贡献成正比
手术。系统状态小号ķ由结构函数定义披(和ķ) :
磷(小号ķ=0)=磷(披(和ķ)=0)
从控制的角度来看,即使某些执行器处于故障状态,也假设过驱动系统处于工作状态,即和jķ=1. 为了满足系统目标,要使用的执行器取决于它们的可用性和结构功能披.
不可用的执行器和jķ=1如图 5.2 所示,维护功能与诊断功能隔离。可用的执行器和一世ķ如果存在至少一种操作场景,则由控制律使用,即披(和ķ)=0, 使用和一世ķ. 使用执行器并满足系统目标的概率由以下条件概率定义:
磷(一种一世ķ=0∣披(和ķ)=0)
为了将执行器的可靠性集成到控制策略中,称重矩阵在(ķ)根据诊断功能给出的执行器状态在线估计。因此,如果执行器和jķ不可用,即和jķ=1,系统可以在降级模式下工作
因为它被过度驱动并且标量在一世(ķ)每个执行器的频率由以下概率定义:
在一世(ķ)=磷(一种一世ķ=0∣披(和ķ)=0,和jķ=1)
重量在一世(ķ)对应于执行器的贡献概率和一世ķ当系统工作时,考虑到一些故障执行器不可用。这种概率评估不仅基于执行器的健康状态,还考虑了系统结构和其他执行器的可用性。通过使用通常的可靠性建模,评估这个概率是复杂的或不可能的,给定结构函数披. 然而,这种评估可以很容易地通过 DBN 的推理机制来实现。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。