如果你也在 怎样代写贝叶斯分析Bayesian Analysis 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。贝叶斯分析Bayesian Analysis一种统计推断方法(以英国数学家托马斯-贝叶斯命名),它允许人们将关于人口参数的先验信息与样本中包含的信息证据相结合,以指导统计推断过程。首先指定一个感兴趣的参数的先验概率分布。然后通过应用贝叶斯定理获得并结合证据,为参数提供一个后验概率分布。后验分布为有关该参数的统计推断提供了基础。
贝叶斯分析,一种统计推断方法(以英国数学家托马斯-贝叶斯命名),允许人们将关于人口参数的先验信息与样本所含信息的证据相结合,以指导统计推断过程。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写贝叶斯分析Bayesian Analysis方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写贝叶斯分析Bayesian Analysis代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写贝叶斯分析Bayesian Analysis相关的作业也就用不着说。
统计代写|贝叶斯分析代写Bayesian Analysis代考|Example: estimating the accuracy of record linkage
We emphasize the essentially empirical (not ‘subjective’ or ‘personal’) nature of probabilities with another example in which they are estimated from data.
Record linkage refers to the use of an algorithmic technique to identify records from different databases that correspond to the same individual. Record-linkage techniques are used in a variety of settings. The work described here was formulated and first applied in the context of record linkage between the U.S. Census and a large-scale post-enumeration survey, which is the first step of an extensive matching operation conducted to evaluate census coverage for subgroups of the population. The goal of this first step is to declare as many records as possible ‘matched’ by computer without an excessive rate of error, thereby avoiding the cost of the resulting manual processing for all records not declared ‘matched.’
Existing methods for assigning scores to potential matches
Much attention has been paid in the record-linkage literature to the problem of assigning ‘weights’ to individual fields of information in a multivariate record and obtaining a composite ‘score,’ which we call $y$, that summarizes the closeness of agreement between two records. Here, we assume that this step is complete in the sense that these rules have been chosen. The next step is the assignment of candidate matched pairs, where each pair of records consists of the best potential match for each other from the respective databases. The specified weighting rules then order the candidate matched pairs. In the motivating problem at the Census Bureau, a binary choice is made between the alternatives ‘declare matched’ vs. ‘send to followup,’ where a cutoff score is needed above which records are declared matched. The false-match rate is then defined as the number of falsely matched pairs divided by the number of declared matched pairs.
统计代写|贝叶斯分析代写Bayesian Analysis代考|Estimating match probabilities empirically
We obtain accurate match probabilities using mixture modeling, a topic we discuss in detail in Chapter 22. The distribution of previously obtained scores for the candidate matches is considered a ‘mixture’ of a distribution of scores for true matches and a distribution for non-matches. The parameters of the mixture model are estimated from the data. The estimated parameters allow us to calculate an estimate of the probability of a false match (a pair declared matched that is not a true match) for any given decision threshold on the scores. In the procedure that was actually used, some elements of the mixture model (for example, the optimal transformation required to allow a mixture of normal distributions to apply) were fit using ‘training’ data with known match status (separate from the data to which we apply our calibration procedure), but we do not describe those details here. Instead we focus on how the method would be used with a set of data with unknown match status.
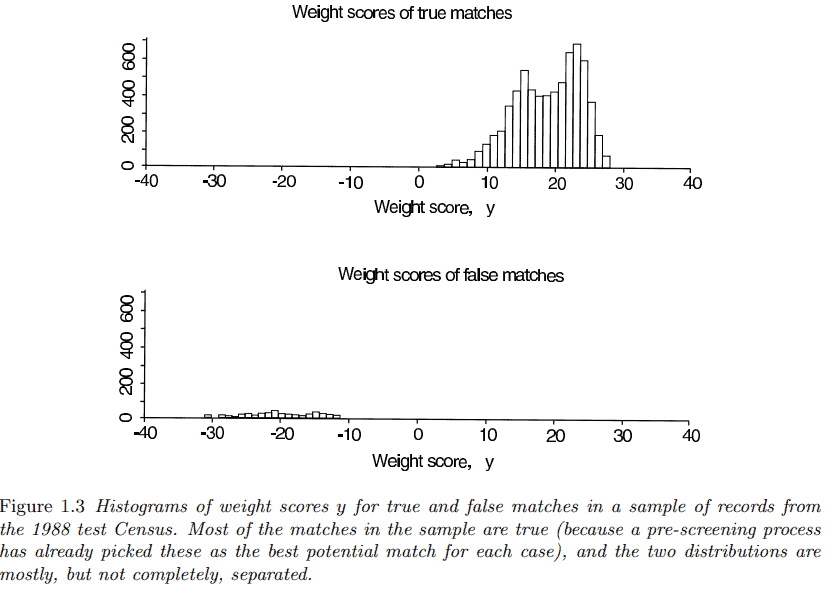
Support for this approach is provided in Figure 1.3, which displays the distribution of scores for the matches and non-matches in a particular dataset obtained from 2300 records from a ‘test Census’ survey conducted in a single local area two years before the 1990 Census. The two distributions, $p(y \mid$ match $)$ and $p(y \mid$ non-match $)$, are mostly distinct-meaning that in most cases it is possible to identify a candidate as a match or not given the score alonebut with some overlap.
In our application dataset, we do not know the match status. Thus we are faced with a single combined histogram from which we estimate the two component distributions and the proportion of the population of scores that belong to each component. Under the mixture model, the distribution of scores can be written as,
$$
p(y)=\operatorname{Pr}(\text { match }) p(y \mid \text { match })+\operatorname{Pr}(\text { non-match }) p(y \mid \text { non-match })
$$
The mixture probability ( $\operatorname{Pr}($ match $))$ and the parameters of the distributions of matches $(p(y \mid$ match $))$ and non-matches $(p(y \mid$ non-match $))$ are estimated using the mixture model approach (as described in Chapter 22) applied to the combined histogram from the data with unknown match status.
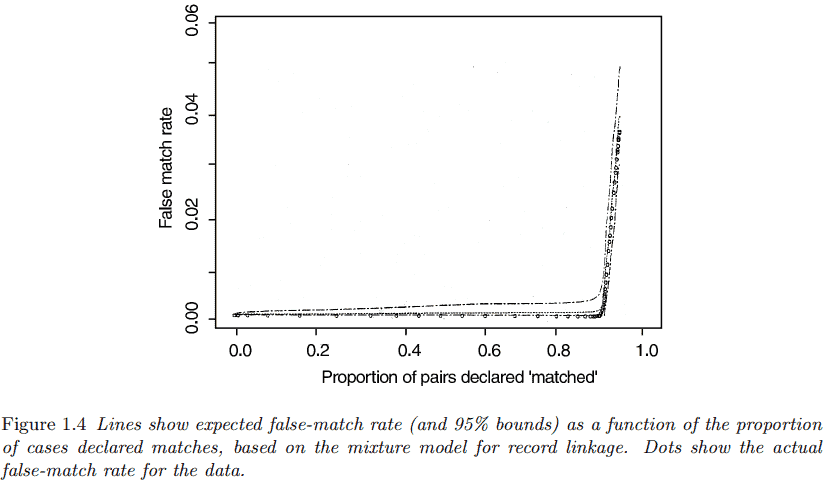
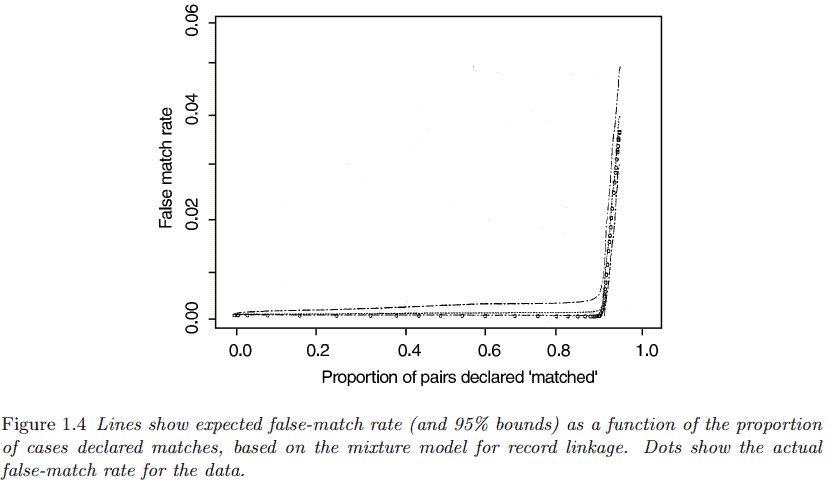
To use the method to make record-linkage decisions, we construct a curve giving the false-match rate as a function of the decision threshold, the score above which pairs will be ‘declared’ a match. For a given decision threshold, the probability distributions in (1.7) can be used to estimate the probability of a false match, a score $y$ above the threshold originating from the distribution $p(y \mid$ non-match $)$. The lower the threshold, the more pairs we will declare as matches. As we declare more matches, the proportion of errors increases. The approach described here should provide an objective error estimate for each threshold. (See the validation in the next paragraph.) Then a decision maker can determine the threshold that provides an acceptable balance between the goals of declaring more matches automatically (thus reducing the clerical labor) and making fewer mistakes.
贝叶斯分析代考
统计代写|贝叶斯分析代写Bayesian Analysis代考|Example: estimating the accuracy of record linkage
我们用另一个从数据中估计概率的例子来强调概率本质上是经验的(而不是“主观的”或“个人的”)性质。
记录链接是指使用一种算法技术来识别来自不同数据库的记录,这些记录对应于同一个人。记录链接技术用于各种设置。本文所描述的工作是在美国人口普查和大规模普查后调查之间的记录联系的背景下制定和首次应用的,这是进行广泛匹配操作的第一步,以评估人口子群体的人口普查覆盖范围。第一步的目标是在不产生过高错误率的情况下,声明尽可能多的记录由计算机“匹配”,从而避免对所有未声明“匹配”的记录进行人工处理的成本。
为潜在的匹配分配分数的现有方法
在记录链接文献中,对多变量记录中的单个信息字段分配“权重”并获得综合“分数”的问题给予了大量关注,我们称之为$y$,它总结了两个记录之间的一致程度。在这里,我们假设这个步骤已经完成,因为已经选择了这些规则。下一步是分配候选匹配对,其中每对记录由各自数据库中彼此的最佳潜在匹配组成。然后指定的加权规则对候选匹配对排序。在人口普查局的激励问题中,在“宣布匹配”和“宣布匹配”之间做出了二选一的选择。’send to follow – up ‘,在这里需要一个截止分数,高于这个分数的记录被声明为匹配。然后将错误匹配率定义为错误匹配对的数量除以声明的匹配对的数量。
统计代写|贝叶斯分析代写Bayesian Analysis代考|Estimating match probabilities empirically
我们使用混合建模获得准确的匹配概率,我们将在第22章详细讨论这个主题。先前获得的候选匹配分数的分布被认为是真实匹配分数分布和非匹配分数分布的“混合”。根据数据估计了混合模型的参数。估计的参数允许我们对分数上任何给定的决策阈值计算假匹配(一对声明匹配但不是真匹配的配对)的概率估计。在实际使用的过程中,混合模型的一些元素(例如,允许应用混合正态分布所需的最佳转换)使用具有已知匹配状态的“训练”数据(与我们应用校准程序的数据分开)进行拟合,但我们在这里不描述这些细节。相反,我们关注的是如何将该方法用于一组匹配状态未知的数据。
图1.3提供了对这种方法的支持,图1.3显示了从1990年人口普查前两年在单个地区进行的“测试普查”调查中获得的2300条记录中获得的特定数据集中匹配和不匹配的分数分布。这两个分布,$p(y \mid$匹配$)$和$p(y \mid$不匹配$)$,大多是不同的,这意味着在大多数情况下,可以确定一个候选人是匹配的,或者不是单独给出分数,但有一些重叠。
在我们的应用程序数据集中,我们不知道匹配状态。因此,我们面临着一个单一的组合直方图,从中我们估计两个分量的分布和属于每个分量的分数的总体比例。在混合模型下,分数的分布可以写成:
$$
p(y)=\operatorname{Pr}(\text { match }) p(y \mid \text { match })+\operatorname{Pr}(\text { non-match }) p(y \mid \text { non-match })
$$
混合概率($\operatorname{Pr}($ match $))$)和匹配$(p(y \mid$ match $))$和不匹配$(p(y \mid$ non-match $))$的分布参数使用混合模型方法(如第22章所述)对未知匹配状态数据的组合直方图进行估计。
为了使用该方法做出记录链接决策,我们构建了一条曲线,将错误匹配率作为决策阈值的函数,高于该阈值的分数将被“声明”为匹配。对于给定的决策阈值,可以使用(1.7)中的概率分布来估计错误匹配的概率,即高于阈值的分数$y$来自分布$p(y \mid$ non-match $)$。阈值越低,我们将声明为匹配的对就越多。当我们声明更多的匹配时,错误的比例就会增加。这里描述的方法应该为每个阈值提供客观的误差估计。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
金融工程代写
金融工程是使用数学技术来解决金融问题。金融工程使用计算机科学、统计学、经济学和应用数学领域的工具和知识来解决当前的金融问题,以及设计新的和创新的金融产品。
非参数统计代写
非参数统计指的是一种统计方法,其中不假设数据来自于由少数参数决定的规定模型;这种模型的例子包括正态分布模型和线性回归模型。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
术语 广义线性模型(GLM)通常是指给定连续和/或分类预测因素的连续响应变量的常规线性回归模型。它包括多元线性回归,以及方差分析和方差分析(仅含固定效应)。
有限元方法代写
有限元方法(FEM)是一种流行的方法,用于数值解决工程和数学建模中出现的微分方程。典型的问题领域包括结构分析、传热、流体流动、质量运输和电磁势等传统领域。
有限元是一种通用的数值方法,用于解决两个或三个空间变量的偏微分方程(即一些边界值问题)。为了解决一个问题,有限元将一个大系统细分为更小、更简单的部分,称为有限元。这是通过在空间维度上的特定空间离散化来实现的,它是通过构建对象的网格来实现的:用于求解的数值域,它有有限数量的点。边界值问题的有限元方法表述最终导致一个代数方程组。该方法在域上对未知函数进行逼近。[1] 然后将模拟这些有限元的简单方程组合成一个更大的方程系统,以模拟整个问题。然后,有限元通过变化微积分使相关的误差函数最小化来逼近一个解决方案。
tatistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
随机分析代写
随机微积分是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。