如果你也在 怎样代写金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics是使用统计方法来发展理论或检验经济学或金融学的现有假设。计量经济学依靠的是回归模型和无效假设检验等技术。计量经济学也可用于尝试预测未来的经济或金融趋势。
金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics的一个基本工具是多元线性回归模型。计量经济学理论使用统计理论和数理统计来评估和发展计量经济学方法。计量经济学家试图找到具有理想统计特性的估计器,包括无偏性、效率和一致性。应用计量经济学使用理论计量经济学和现实世界的数据来评估经济理论,开发计量经济学模型,分析经济历史和预测。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写计量经济学Econometrics方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写计量经济学Econometrics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种代写计量经济学Econometrics相关的作业也就用不着说。
经济代写|计量经济学代写Econometrics代考|Autoregressive Conditional Betas
An alternative to the state space model presented above that also allows a direct specification of dynamic conditional betas has recently been proposed by Darolles et al. (2018). Their model, called CHAR, is a multivariate GARCH model based on the Cholesky decomposition of the $m \times m$ (with $m=N+1$ ) conditional covariance matrix $\Sigma_t$ of $\left(\mathbf{x}_t, y_t\right)^{\prime}$.
As Pourahmadi (1999), let us consider the Cholesky decomposition of $\Sigma_t$, i.e.,
$$
\boldsymbol{\Sigma}t=\boldsymbol{L}_t \boldsymbol{G}_t \boldsymbol{L}_t^{\prime}, $$ where $\boldsymbol{G}_t=\operatorname{diag}\left(g{11, t}, \ldots, g_{m m, t}\right)$ and $\boldsymbol{L}t$ is a lower unitriangular matrix (i.e., triangular with 1 ‘s on the diagonal and 0 ‘s above the diagonal) with element $\ell{i j, t}$ at the row $i$ and column $j$ for $i>j$.
Let us now illustrate this decomposition for $m=3$.
$$
\boldsymbol{L}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 0 & 0 \
l_{21, t} & 1 & 0 \
l_{31, t} & l_{32, t} & 1
\end{array}\right] \quad \boldsymbol{G}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
g_{11, t} & 0 & 0 \
0 & g_{22, t} & 0 \
0 & 0 & g_{33, t}
\end{array}\right]
$$
and
$$
\boldsymbol{\Sigma}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
g_{11, t} & l_{21, t} g_{11, t} & l_{31, t} g_{11, t} \
l_{21, t} g_{11, t} & l_{21, t}^2 g_{11, t}+g_{22, t} & l_{21, t} l_{31, t} g_{11, t}+l_{32, t} g_{22, t} \
l_{31, t} g_{11, t} & l_{21, t} h_{31, t} g_{11, t}+l_{32, t} g_{22, t} & l_{31, t}^2 g_{11, t}+l_{32, t}^2 g_{22, t}+g_{33, t}
\end{array}\right] .
$$
Darolles et al. (2018) show that if $\boldsymbol{w}t \equiv\left(\mathbf{x}_t, y_t\right)^{\prime}$ has mean $\mathbf{0}$, $$ \begin{aligned} w{i, t} & =\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} \ell_{i j, t} \varepsilon_{j, t}+\varepsilon_{i, t}=\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} \ell_{i j, t}\left(w_{j, t}-\sum_{k=1}^{j-1} \ell_{j k, t} v_{k, t}\right)+\varepsilon_{i, t} \
& =\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} \beta_{i j, t} w_{j, t}+\varepsilon_{i, t} .
\end{aligned}
$$
Interestingly, for $i=m$, the $m$ th equation of the CHAR model is
$$
y_t=\sum_{j=1}^{m-1} \beta_{i j, t} x_{j, t}+\varepsilon_{i, t}
$$
which corresponds to Eq. (35) when $\alpha_t=0, N=m-1$ and $\varepsilon_t=\varepsilon_{i, t}$.
经济代写|计量经济学代写Econometrics代考|Empirical Application on REITs
Real Estate Investment Trusts ${ }^{23}$ (REITs), which are publicly traded real estate companies that own and manage commercial or residential real estate, are attractive alternatives to the mainstream investment choice (e.g., stocks and bonds) since they allow investors to easily access real estate investments without directly owning or managing the underlying assets. ${ }^{24}$ Moreover, the literature on real estate has shown that the inclusion of REITs within one’s portfolio improves the risk-return profile of the portfolio. Compared to other asset classes such as bonds and stocks, they have the characteristics of offering more stable returns and a lower volatility historically. For the purpose of portfolio diversification, it is important to know how the level of exposure of REITs to both the bond market risk and to the stock market risk varies over time. The aim of this section is thus to perform a comparative analysis of the three most advanced modeling techniques (state space, DCB, and ACB) used in estimating the sensitivity of REIT indices to changes in both the bond market and the stock market. Van Nieuwerburgh (2019) argues that a model with a bond market and stock market factor is both the most basic and most natural model of risk for REITs as the bond market beta measures how sensitive REITs are to changes in interest rates and the stock market beta measures how sensitive REITs are to changes in economic activity. ${ }^{25}$ A similar model is used by Allen et al. (2000). Moreover, we note that the addition of three Fama-French risk factors (size, value, and momentum) to the original two-factor model in the study of Van Nieuwerburgh (2019) leaves the bond and stock market betas almost unchanged. As a consequence, we follow Van Nieuwerburgh (2019) and choose to perform our analysis on the following parsimonious two-factor model:
$$
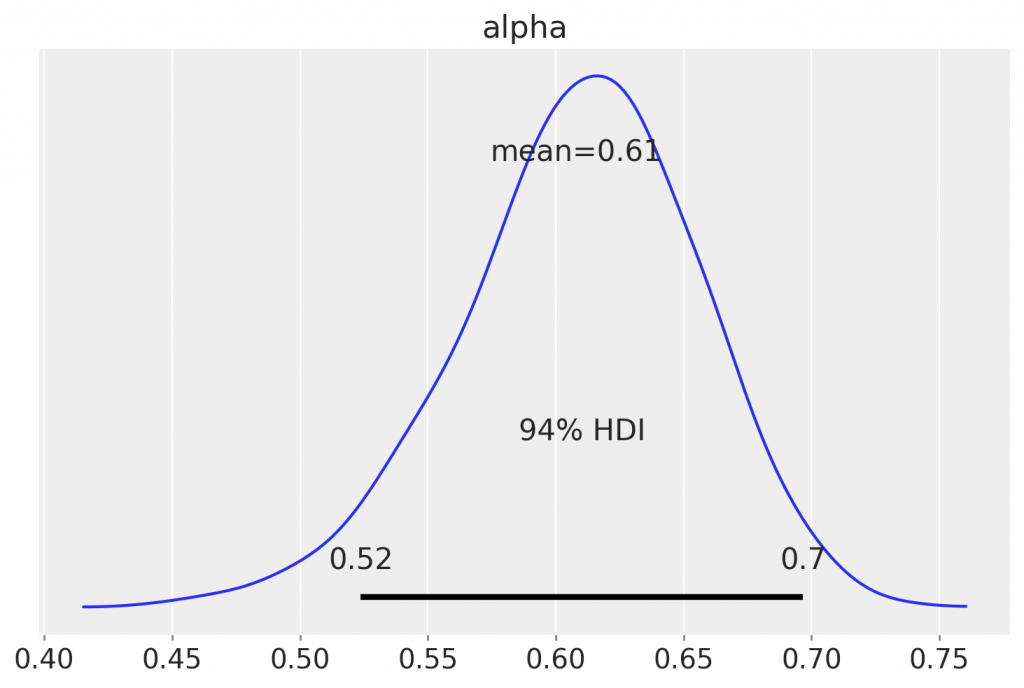
\tilde{r}{\mathrm{REIT}, t}=\alpha_t+\beta{B, t} \tilde{r}{B, t}+\beta{M, t} \widetilde{r}{M, t}+\varepsilon_t, $$ where $\widetilde{r}{\text {REIT }}$ is the excess return on the REIT market, measured by the daily excess return on the FTSE EPRA Nareit index, $\widetilde{r}B$ is the excess return on the bond market, measured by the daily excess return on the sovereign bond index and $\widetilde{r}_M$ is the excess return on the stock market, measured by the daily excess return on the stock market index. Equation (66) corresponds to the conditional risk factor model that we use to estimate conditional betas on day $t$ from a regression of the daily excess REIT index returns on the excess stock market and bond market returns. In the special case where $\boldsymbol{\beta}_t=\left(\beta{B, t}, \beta_{M, t}\right)^{\prime}=\boldsymbol{\beta}$, the betas are restricted to be constant. Note also that for some models, the alpha is allowed to be time-varying as well. However, empirical results (not reported here to save space) suggest that $\alpha_t=\alpha(\forall t)$ once allowing the conditional betas of this two-factor model to be time-varying.
计量经济学代考
经济代写|计量经济学代写Econometrics代考|Autoregressive Conditional Betas
Darolles等人(2018)最近提出了上述状态空间模型的替代方案,该模型也允许直接规范动态条件beta。他们的模型称为CHAR,是一个基于$\left(\mathbf{x}_t, y_t\right)^{\prime}$的$m \times m$(与$m=N+1$)条件协方差矩阵$\Sigma_t$的Cholesky分解的多元GARCH模型。
正如Pourahmadi(1999),让我们考虑$\Sigma_t$的Cholesky分解,即:
$$
\boldsymbol{\Sigma}t=\boldsymbol{L}t \boldsymbol{G}_t \boldsymbol{L}_t^{\prime}, $$,其中$\boldsymbol{G}_t=\operatorname{diag}\left(g{11, t}, \ldots, g{m m, t}\right)$和$\boldsymbol{L}t$是一个较低的单角矩阵(即三角形,对角线上有1,对角线上有0),元素$\ell{i j, t}$位于行$i$,列$j$为$i>j$。
现在我们来说明$m=3$的分解。
$$
\boldsymbol{L}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 0 & 0 \
l_{21, t} & 1 & 0 \
l_{31, t} & l_{32, t} & 1
\end{array}\right] \quad \boldsymbol{G}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
g_{11, t} & 0 & 0 \
0 & g_{22, t} & 0 \
0 & 0 & g_{33, t}
\end{array}\right]
$$
和
$$
\boldsymbol{\Sigma}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
g_{11, t} & l_{21, t} g_{11, t} & l_{31, t} g_{11, t} \
l_{21, t} g_{11, t} & l_{21, t}^2 g_{11, t}+g_{22, t} & l_{21, t} l_{31, t} g_{11, t}+l_{32, t} g_{22, t} \
l_{31, t} g_{11, t} & l_{21, t} h_{31, t} g_{11, t}+l_{32, t} g_{22, t} & l_{31, t}^2 g_{11, t}+l_{32, t}^2 g_{22, t}+g_{33, t}
\end{array}\right] .
$$
Darolles et al.(2018)表明,如果$\boldsymbol{w}t \equiv\left(\mathbf{x}t, y_t\right)^{\prime}$有平均$\mathbf{0}$, $$ \begin{aligned} w{i, t} & =\sum{j=1}^{i-1} \ell_{i j, t} \varepsilon_{j, t}+\varepsilon_{i, t}=\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} \ell_{i j, t}\left(w_{j, t}-\sum_{k=1}^{j-1} \ell_{j k, t} v_{k, t}\right)+\varepsilon_{i, t} \
& =\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} \beta_{i j, t} w_{j, t}+\varepsilon_{i, t} .
\end{aligned}
$$
有趣的是,对于$i=m$, CHAR模型的$m$第1方程为
$$
y_t=\sum_{j=1}^{m-1} \beta_{i j, t} x_{j, t}+\varepsilon_{i, t}
$$
当$\alpha_t=0, N=m-1$和$\varepsilon_t=\varepsilon_{i, t}$时对应式(35)。
经济代写|计量经济学代写Econometrics代考|Empirical Application on REITs
房地产投资信托${ }^{23}$ (REITs)是拥有和管理商业或住宅房地产的上市房地产公司,是主流投资选择(例如股票和债券)的有吸引力的替代品,因为它们允许投资者轻松获得房地产投资,而无需直接拥有或管理相关资产。${ }^{24}$此外,有关房地产的文献表明,在投资组合中纳入REITs可以改善投资组合的风险收益状况。与债券和股票等其他资产类别相比,它们具有更稳定的回报和更低的历史波动性的特点。为了使投资组合多样化,了解房地产投资信托基金对债券市场风险和股票市场风险的敞口水平如何随时间变化是很重要的。因此,本节的目的是对用于估计REIT指数对债券市场和股票市场变化的敏感性的三种最先进的建模技术(状态空间,DCB和ACB)进行比较分析。Van Nieuwerburgh(2019)认为,具有债券市场和股票市场因素的模型是REITs最基本和最自然的风险模型,因为债券市场beta衡量REITs对利率变化的敏感程度,股票市场beta衡量REITs对经济活动变化的敏感程度。${ }^{25}$ Allen等人(2000)使用了一个类似的模型。此外,我们注意到,在Van Nieuwerburgh(2019)的研究中,将三个Fama-French风险因素(规模、价值和动量)添加到原始的双因素模型中,债券和股票市场的贝塔系数几乎没有变化。因此,我们遵循Van Nieuwerburgh(2019),选择对以下简约的双因素模型进行分析:
$$
\tilde{r}{\mathrm{REIT}, t}=\alpha_t+\beta{B, t} \tilde{r}{B, t}+\beta{M, t} \widetilde{r}{M, t}+\varepsilon_t, $$其中$\widetilde{r}{\text {REIT }}$为房地产投资信托基金市场的超额收益,以富时EPRA Nareit指数的每日超额收益衡量;$\widetilde{r}B$为债券市场的超额收益,以主权债券指数的每日超额收益衡量;$\widetilde{r}M$为股票市场的超额收益,以股票市场指数的每日超额收益衡量。式(66)对应于条件风险因子模型,我们使用该模型从超额股票市场和债券市场回报的每日超额REIT指数回报的回归中估计day $t$的条件贝塔。在$\boldsymbol{\beta}_t=\left(\beta{B, t}, \beta{M, t}\right)^{\prime}=\boldsymbol{\beta}$的特殊情况下,beta被限制为常数。还要注意,对于某些模型,alpha也允许时变。然而,实证结果(为了节省篇幅,这里没有报道)表明$\alpha_t=\alpha(\forall t)$一旦允许这个双因素模型的条件贝塔是时变的。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。