如果你也在 怎样代写机器学习Machine Learning这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
机器学习是人工智能(AI)和计算机科学的一个分支,主要是利用数据和算法来模仿人类的学习方式,逐步提高其准确性。
机器学习是不断增长的数据科学领域的一个重要组成部分。通过使用统计方法,算法被训练来进行分类或预测,在数据挖掘项目中发现关键的洞察力。这些洞察力随后推动了应用程序和业务的决策,最好是影响关键的增长指标。随着大数据的不断扩大和增长,市场对数据科学家的需求将增加,需要他们协助确定最相关的业务问题,随后提供数据来回答这些问题。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写机器学习Machine Learning方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写机器学习方面经验极为丰富,各种代写机器学习Machine Learning相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的机器学习Machine Learning及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Generative and discriminative models
Predictive algorithms are often categorized into generative and discriminative models. This distinction presumes a probabilistic perspective on machine learning algorithms. Generally speaking, a generative model learns the joint probability distribution $p(x, y)$, whereas a discriminative model learns the conditional probability distribution $p(y \mid x)$, in other words, the probability of $y$ given $x$. A generative algorithm models how the data was generated in order to categorize a signal. It is called generative since sampling can generate synthetic data points. Generative models ask the question: Based on my generation assumptions, which category is most likely to generate this signal? Generative models include naïve Bayes, Bayesian networks, Hidden Markov models (HMM) and Markov random fields (MRF).
A discriminative algorithm does not care about how the data was generated, it simply categorizes a given signal. It directly estimates posterior probabilities, they do not attempt to model the underlying probability distributions. Logistic regression, support vector machines (SVM), traditional neural networks and nearest neighbor models fall into this category. Discriminative models tend to perform better since they solve the problem directly, whereas generative models require an intermediate step. However, generative models tend to converge a lot faster.
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Evaluation of learner
In order to evaluate the quality of a trained model, we need to evaluate how well the predictions match the observed data. In other words, we need to measure the quality of the fit. The quality is measured using a loss function or objective function. The goal of all loss functions is to measure how well an algorithm is doing against a given data set.
The loss function quantifies the extend to which the model fits the data [14], in other words, it measures the goodness of fit. During training, the machine learning algorithm tries to minimize the loss function, a process called loss minimization. We are minimizing the training loss, or training error, which is the average loss over all the training samples. A loss function calculates the price, the loss, paid for inaccuracies in a classification problem. It is, thus, also called the cost function.
There are many different loss functions. We have already seen the mean absolute error in equation 2.8. Another popular loss function is the mean squared error (MSE) since it is easy to understand and implement. The mean squared error simply takes the difference between the predictions and the ground truth, squares it, and averages it out across the whole data set. The mean squared error is always positive and the closer to zero the better. The mean squared error is computed as shown in equation $2.9$.
$$
M S E=\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(y_{i}-f\left(x_{i}\right)\right)^{2}
$$
where
$$
\begin{array}{ll}
y & =\text { Vector of n predictions } \
n & =\text { Number of predictions } \
f\left(x_{i}\right) & =\text { Prediction for the } i \text { th observation }
\end{array}
$$
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考| Stochastic gradient descent
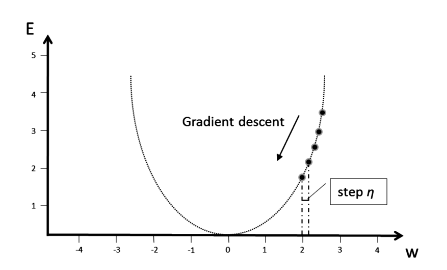
During training we try to minimize a loss function. So we need to make sure we learn into the right “direction” and not getting worse. For a simple loss function, we could use calculus to find the optimal parameters that minimize the loss function. However, for a more complex loss function, calculus might not be feasible anymore. One approach is to iteratively optimize the objective function by using the gradient of the function. This iterative optimization process is called gradient descent where the gradient tells us which direction to move to decrease the loss function. Figure $2.9$ shows gradient descent with a hypothetical objective function $w^{2}$ and the derivative $2 w$ that gives us the slope. If the derivative is positive, it slopes downwards to the left as shown in Figure $2.9$, if it is negative, it slopes to the right. The value of the derivative is multiplied by the constant step size $\eta$, called the learning rate, and subtracted from the current value. Once the change of the parameter value becomes too small, in Figure $2.9$ when it approaches zero, the process stops. The hyperparameter $\eta$ is the step size, which defines how fast we move to the minimum.
The problem with gradient descent is that it is slow since every iteration has to go through all the training instances, the batch, which is expensive, especially if the training set is large. The training loss is the sum over all the training data, which means, the algorithm has to go through all training instances to move one step down.
机器学习代写
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Generative and discriminative models
预测算法通常分为生成模型和判别模型。这种区别假定了机器学习算法的概率观点。一般来说,生成模型学习联合概率分布p(X,是),而判别模型学习条件概率分布p(是∣X),换句话说,概率是给定X. 生成算法对如何生成数据进行建模,以便对信号进行分类。它被称为生成,因为采样可以生成合成数据点。生成模型提出了一个问题:根据我的生成假设,哪个类别最有可能生成这个信号?生成模型包括朴素贝叶斯、贝叶斯网络、隐马尔可夫模型 (HMM) 和马尔可夫随机场 (MRF)。
判别算法不关心数据是如何生成的,它只是对给定的信号进行分类。它直接估计后验概率,它们不尝试对潜在的概率分布进行建模。逻辑回归、支持向量机 (SVM)、传统神经网络和最近邻模型都属于这一类。判别模型往往表现更好,因为它们直接解决问题,而生成模型需要一个中间步骤。然而,生成模型往往收敛得更快。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Evaluation of learner
为了评估训练模型的质量,我们需要评估预测与观察数据的匹配程度。换句话说,我们需要衡量拟合的质量。使用损失函数或目标函数来衡量质量。所有损失函数的目标是衡量算法在给定数据集上的表现。
损失函数量化了模型拟合数据的范围[14],换句话说,它衡量了拟合优度。在训练过程中,机器学习算法试图最小化损失函数,这个过程称为损失最小化。我们正在最小化训练损失或训练误差,这是所有训练样本的平均损失。损失函数计算为分类问题中的不准确所付出的代价,即损失。因此,它也称为成本函数。
有许多不同的损失函数。我们已经在方程 2.8 中看到了平均绝对误差。另一个流行的损失函数是均方误差 (MSE),因为它易于理解和实现。均方误差只是取预测值和基本事实之间的差异,对其进行平方,然后在整个数据集中取平均值。均方误差始终为正,越接近零越好。均方误差的计算如等式所示2.9.
米小号和=1n∑一世=1n(是一世−F(X一世))2
在哪里
是= n 个预测的向量 n= 预测数 F(X一世)= 预测为 一世 观察
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考| Stochastic gradient descent
在训练期间,我们尝试最小化损失函数。所以我们需要确保我们学习到正确的“方向”而不是变得更糟。对于一个简单的损失函数,我们可以使用微积分来找到最小化损失函数的最佳参数。但是,对于更复杂的损失函数,微积分可能不再可行。一种方法是通过使用函数的梯度来迭代优化目标函数。这种迭代优化过程称为梯度下降,其中梯度告诉我们向哪个方向移动以减少损失函数。数字2.9显示具有假设目标函数的梯度下降在2和导数2在这给了我们斜率。如果导数为正,则向左向下倾斜,如图所示2.9,如果为负,则向右倾斜。导数的值乘以恒定步长这,称为学习率,并从当前值中减去。一旦参数值的变化变得太小,如图2.9当它接近零时,该过程停止。超参数这是步长,它定义了我们移动到最小值的速度。
梯度下降的问题在于它很慢,因为每次迭代都必须经过所有训练实例,即批次,这很昂贵,尤其是在训练集很大的情况下。训练损失是所有训练数据的总和,这意味着算法必须遍历所有训练实例才能向下移动一步。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
