如果你也在 怎样代写机器学习Machine Learning这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
机器学习是人工智能(AI)和计算机科学的一个分支,主要是利用数据和算法来模仿人类的学习方式,逐步提高其准确性。
机器学习是不断增长的数据科学领域的一个重要组成部分。通过使用统计方法,算法被训练来进行分类或预测,在数据挖掘项目中发现关键的洞察力。这些洞察力随后推动了应用程序和业务的决策,最好是影响关键的增长指标。随着大数据的不断扩大和增长,市场对数据科学家的需求将增加,需要他们协助确定最相关的业务问题,随后提供数据来回答这些问题。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写机器学习Machine Learning方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写机器学习方面经验极为丰富,各种代写机器学习Machine Learning相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的机器学习Machine Learning及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Market Risk
Risk is ubiquitous in finance but it is hard to quantify. The first and foremost thing to know is differentiating the sources of financial risks on the grounds that it might not be a wise move to utilize same tools against financial risk arising from different sources.
Thus, treating different sources of financial risk is crucial as the impact of different financial risks as well as tools developed to mitigate risk are completely different. Pretending that firms are subject to large market fluctuations, all assets in the portfolio of the firms are susceptible to risk originating from these fluctuations. However, a different tool should be developed to cope with a risk emanating from customer profile. In addition, it should be kept in mind that different risk factors contribute significantly to the asset prices. All these examples implies that assessing risk factors need careful consideration in finance.
As is briefly discussed previously, these are, mainly, market, credit, liquidity, and operational risks. It is evident that some other types can be added to this list of financial risks but they can be thought of a subset of these
main four risk types. So, these types of risks will be our focus throughout this chapter.
Market risk is the risk arising from changes on financial indicators such as exchange rate, interest rate, inflation and so on. Differently, market risk can be referred to a risk of losses in on and off-balance-sheet positions arising from movements in market prices (BIS, 2020). Let us now see how these factors affect market risk. Suppose that a raise in inflation rate might pose a threat to current profitability of the financial institutions with a view to inflation creates pressure to interest rate. This, in turn, affects borrower’s cost of funds. These instances can be amplified but we should also note the interactions of these financial risk sources. That is, while a single source of financial risk changes, other risk sources cannot stay constant. With that being said, to some extent, financial indicators are interrelated, meaning that interactions of these risks sources should be taken into account.
As you can imagine, there are different tools to measure market risk. Of them, the most prominent and widely acceptable tools are Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Expected Shortfall (ES). The ultimate aim of this chapter is to augment these approaches using recent developments in Machine Learning. At this juncture, it would be tempting to ask: Does the traditional model fail in finance? And what makes the ML-based model different?
I will start tackling the first question. The first and foremost challenge that traditional models unable to address is the complexity of the financial system. Due either to the some strong assumptions or simply inahility to capture the complexity introduced by the data, long-standing traditional models has been started to be replaced by ML-based models.
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Value-at-Risk
The emergence of VaR model rests upon a request for a JP Morgan executive who wanted to have a summary report showing possible losses as well as risks in one day that JP Morgan is exposed to. In this report, executives are informed about the risk assumed by the institution in an aggregated manner. The method by which market risk is computed is known as VaR. So, it is the starting point of VaR and, now, it has become so widespread that its adoption has been forced by regulators.
The adoption of VaR dates back to 1990 s and despite numerous extensions to VaR and new proposed models, it is still in use. So, what makes it so appealing? maybe the question to be addressed. The answer comes from Kevin Dowd:
The VaR figure has two important characteristics. The first is that it provides a common consistent measure of risk across different positions and risk factors. It enables us to measure the risk associated with a fixed-income position, say, in a way that is comparable to and consistent with a measure of the risk associated with equity positions. VaR provides us with a common risk yardstick, and this yardstick makes it possible for institutions to manage their risks in new ways that were not possible before. The other characteristic of VaR is that it takes account of the correlations between different risk factors. If two risks offset each other, the VaR allows for this offset and tells us that the overall risk is fairly low.
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Variance-Covariance Method
Variance-Covariance Method is also known as parametric method, because the data is assumed to be normally distributed. Variance-Covariance method is commonplace due to this assumption, however it is worth noting that returns are not normal distributed. Parametric form assumption makes the application of Variance-Covariance method practical and easy-to-apply.
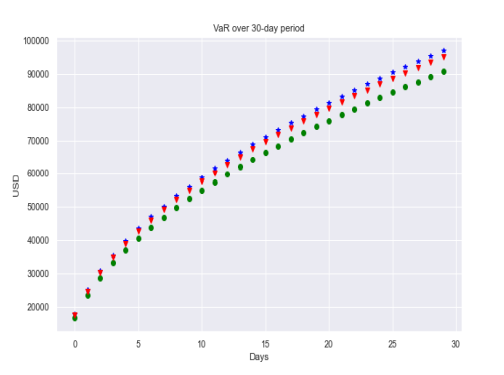
As in all VaR approaches, we can either work with single asset or a portfolio. However, working with portfolio requires careful treatment in the sense that correlation structure and portfolio variance need to be estimated. Exactly at this point, correlation comes into the picture and historical data is used to calculate correlation, mean, and standard deviation. While augmenting this with MI -based approach, correlation structure will he our main focus.
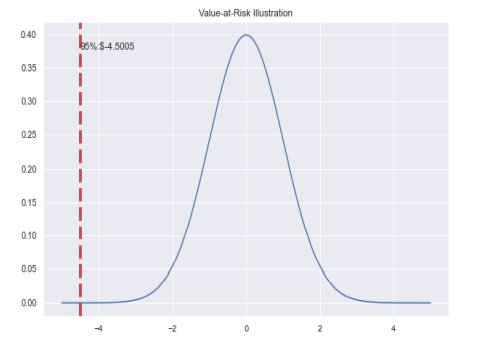
Suppose that we have a single asset, in Figure 5-1, it is shown that the mean of this asset is zero and standard deviation is 1 and if the holding period is 1 , the corresponding VaR value can be computed the value of the asset by corresponding Z-value and standard deviation. Hence, normality assumption makes things easier but it is a strong assumption because there is no guarantee that asset returns are normally distributed rather most of the asset returns do not follow normal distribution. Moreover, due to the normality
assumption, potential risk in tail might not be captured. Therefore normality assumption comes with a cost.
机器学习代写
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Market Risk
风险在金融中无处不在,但很难量化。首先要知道的是区分金融风险的来源,因为使用相同的工具来应对来自不同来源的金融风险可能不是明智之举。
因此,处理不同来源的金融风险至关重要,因为不同金融风险的影响以及为降低风险而开发的工具是完全不同的。假设公司受到大的市场波动的影响,公司投资组合中的所有资产都容易受到来自这些波动的风险的影响。但是,应该开发一种不同的工具来应对来自客户档案的风险。此外,应该记住,不同的风险因素对资产价格的影响很大。所有这些例子都意味着在金融领域评估风险因素需要仔细考虑。
如前所述,这些主要是市场、信用、流动性和操作风险。很明显,可以将一些其他类型添加到此金融风险列表中,但可以将它们视为其中的一个子集
主要四种风险类型。因此,这些类型的风险将是我们在本章中的重点。
市场风险是指汇率、利率、通货膨胀等金融指标变化产生的风险。不同的是,市场风险可以指因市场价格变动而导致表内和表外头寸损失的风险(BIS,2020)。现在让我们看看这些因素如何影响市场风险。假设通货膨胀率上升可能会对金融机构当前的盈利能力构成威胁,以期通货膨胀会对利率造成压力。这反过来又会影响借款人的资金成本。这些例子可以放大,但我们也应该注意这些金融风险来源的相互作用。也就是说,当单一的金融风险来源发生变化时,其他风险来源不能保持不变。话虽如此,在某种程度上,财务指标是相互关联的,
可以想象,有不同的工具来衡量市场风险。其中,最突出和被广泛接受的工具是风险价值(VaR)和预期短缺(ES)。本章的最终目的是利用机器学习的最新发展来增强这些方法。在这个关头,不禁要问:传统模式在金融上会失败吗?是什么让基于 ML 的模型与众不同?
我将开始解决第一个问题。传统模型无法解决的首要挑战是金融系统的复杂性。由于一些强有力的假设或根本无法捕捉数据引入的复杂性,长期存在的传统模型已开始被基于 ML 的模型所取代。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Value-at-Risk
VaR 模型的出现取决于摩根大通高管的要求,他希望获得一份总结报告,显示摩根大通在一天内可能面临的损失和风险。在本报告中,高管以汇总的方式了解机构承担的风险。计算市场风险的方法称为 VaR。因此,它是 VaR 的起点,现在它已经变得如此普遍,以至于监管机构强制采用它。
VaR 的采用可以追溯到 1990 年代,尽管对 VaR 进行了大量扩展并提出了新的模型,但它仍在使用中。那么,是什么让它如此吸引人呢?也许是要解决的问题。答案来自凯文·多德:
VaR 数字有两个重要特征。首先是它提供了一种通用的、一致的跨不同头寸和风险因素的风险度量。它使我们能够衡量与固定收益头寸相关的风险,例如,以一种与股票头寸相关风险的衡量标准可比和一致的方式。VaR 为我们提供了一个共同的风险衡量标准,而这个衡量标准使机构能够以前所未有的新方式管理风险。VaR 的另一个特点是它考虑了不同风险因素之间的相关性。如果两个风险相互抵消,VaR 允许这种抵消,并告诉我们整体风险相当低。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Variance-Covariance Method
方差-协方差法也称为参数法,因为假设数据是正态分布的。由于这种假设,方差-协方差方法很常见,但值得注意的是,收益不是正态分布的。参数形式假设使方差-协方差法的应用具有实用性和易于应用性。
与所有 VaR 方法一样,我们可以使用单一资产或投资组合。然而,使用投资组合需要仔细处理,因为需要估计相关结构和投资组合方差。正是在这一点上,相关性出现了,历史数据用于计算相关性、均值和标准差。在使用基于 MI 的方法增强这一点的同时,相关结构将是我们的主要关注点。
假设我们有一个资产,如图 5-1 所示,该资产的均值为零,标准差为 1,如果持有期限为 1,则可以计算出对应的 VaR 值该资产的价值通过相应的 Z 值和标准偏差。因此,正态假设使事情变得更容易,但这是一个强有力的假设,因为不能保证资产收益是正态分布的,而是大多数资产收益不服从正态分布。此外,由于正态
假设,可能无法捕捉到尾部的潜在风险。因此,正态假设是有代价的。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
