如果你也在 怎样代写机器学习Machine Learning这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。
机器学习是人工智能(AI)和计算机科学的一个分支,主要是利用数据和算法来模仿人类的学习方式,逐步提高其准确性。
机器学习是不断增长的数据科学领域的一个重要组成部分。通过使用统计方法,算法被训练来进行分类或预测,在数据挖掘项目中发现关键的洞察力。这些洞察力随后推动了应用程序和业务的决策,最好是影响关键的增长指标。随着大数据的不断扩大和增长,市场对数据科学家的需求将增加,需要他们协助确定最相关的业务问题,随后提供数据来回答这些问题。
statistics-lab™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在代写机器学习Machine Learning方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在代写机器学习方面经验极为丰富,各种代写机器学习Machine Learning相关的作业也就用不着说。
我们提供的机器学习Machine Learning及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Statistical Inference 统计推断
- Statistical Computing 统计计算
- Advanced Probability Theory 高等楖率论
- Advanced Mathematical Statistics 高等数理统计学
- (Generalized) Linear Models 广义线性模型
- Statistical Machine Learning 统计机器学习
- Longitudinal Data Analysis 纵向数据分析
- Foundations of Data Science 数据科学基础
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Fundamentals of Risk Management
In 2007, no one would have thought that risk functions could have changed as much as they have in the last eight years. It is a natural temptation to expect that the next decade has to contain less change. However, we believe that the opposite will likely be true.
-Harle et al. (2016)
Risk management is a constantly evolving process. Constant evolution is inevitable due to the fact that long-standing risk management practice cannot keep pace with recent development or be a precursor of unfolding crises. Therefore, it is of importance to monitor and adopt the changes brought by structural breaks in a risk management process. Adoption to the changes implies re-defining the components and tools of risk management and this is what this book is all about.
Traditionally, in finance, empirical research in finance has a strong focus on statistical inference. Econometric has been built upon the rationale of
statistical inference. These types of models concentrate on the structure of underlying data generating process and relationship among variables.
Machine learning models, however, are not assumed to define the underlying data generating process but are considered as a means to an end for the purpose of prediction (Lommers et al. 2021). Thus, machine learning models are tend to be more data-centric and prediction accuracy-oriented.
Moreover, data scarcity and unavailability has always been an issue in finance and it is not hard to guess that the econometric models cannot perform well in this case. Given the solution of machine learning models to the data unavailability via synthetic data generation, machine learning models has been on the top of the agenda in finance and financial risk management is, of course, no exception.
Before going into the detail and discuss these tools, it is worth introducing the main risk management concepts. Thus, this part of the book presents basic concepts of financial risk management, which I will refer throughout the book. These concepts include risk, types of risks, risk management, returns, and some concepts related to risk management.
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|All financial investments
All financial investments are undertaken to gain profit, which is also called return. More formally, return is the gain made on an investment in a given period of time. Thus, return refers to the upside of the risk. Throughout the book, risk and return will refer to downside and upside risk, respectively.
As you can imagine, there is a trade-off between risk and return, the higher risk assumed, the greater the return realized. As it is a formidable task to come up with a optimum solution, this trade-off is one of the most controversial issues in finance. However, Markowitz (1952) proposes an intuitive and appealing solution to this long-standing issue. The way he defined risk, which was until then ambiguous, is nice and clean and led to a shift in landscape in financial research. Markowitz (1952) used standard deviation $\sigma_{R_{i}}$ to quantify risk. This intuitive definition allows researchers to use mathematics and statistics in finance. The standard deviation can be mathematically defined as (Hull, 2012):
$$
\sigma=\sqrt{\mathbb{E}\left(R^{2}\right)-[\mathbb{E}(R)]^{2}}
$$
where $\mathrm{R}$ and $\mathbb{E}$ symbols refer to annual return and expectation, respectively. The book uses the symbol $\mathbb{E}$ numerous times as expected return represent the return of interest. This is because it is probability we are talking about in defining risk. When it comes to portfolio variance, covariance comes into the picture and the formula turns out to be:
$$
\sigma_{p}^{2}=w_{a}^{2} \sigma_{a}^{2}+w_{b}^{2} \sigma_{b}^{2}+2 w_{a} w_{b} \operatorname{Cov}\left(r_{a}, r_{b}\right)
$$
where w denotes weight, $\sigma^{2}$ is variance, and $\operatorname{Cov}$ is covariance matrix. Taking square root of the variance obtained above gives us the portfolio standard deviation:
$$
\sigma_{p}=\sqrt{\sigma_{p}^{2}}
$$
In other words, portfolio expected return is a weighted average of the individual returns and can be shown as:
$$
\mathbb{E}(R)=\sum_{i}^{n} w_{i} R_{i}=w_{1} R_{1}+w_{2} R_{2} \cdots+w_{n} R_{n}
$$
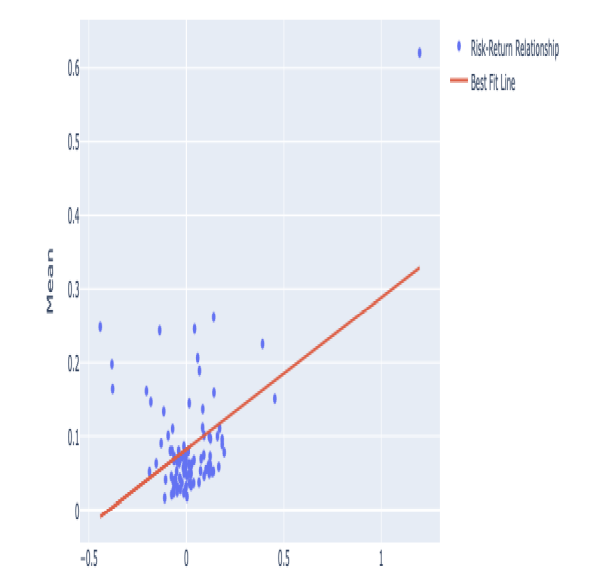
Let us explore the risk-return relationship by visualization. To do that, an hypothetical portfolio is constructed to calculate necessary statistics with Python.
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Risk Management
Financial risk management is a process to deal with the uncertainties resulting from financial markets. It involves assessing the financial risks facing an organization and developing management strategies consistent with internal priorities and policies (Horcher, 2011).
According to this definition, as every organization faces different type of risks, the way that a company deals with it is completely unique. Every company should properly assess and take necessary action against risk. It, however, does not necessarily mean that once a risk is identified, it needs to be mitigated as much as a company can do.
Risk management is, therefore, not about mitigating risk at all costs. Mitigating risk may require sacrificing return and it can be tolerable up to certain level as companies are searching for higher return as much as lowering risk. Thus, to maximize profit while lowering the risk should be delicate and well-defined task.
Managing risk is a delicate task as it comes with a cost and even though dealing with it requires specific company policies, there exists a general framework for possible risk strategies. These are:
- Ignore: In this strategy, companies accept all risks and their consequences and prefer to do nothing.
- Transfer: This strategy involves transferring the risks to a thirdparty by hedging or some other ways.
- Mitigate: Companies develop a strategy to mitigate risk partly because its harmful effect might be considered too much to bear and/or supprass the benefit attached to it.
- Accept risk: If companies embrace the strategy of accepting the risk, they properly identify risks and acknowledge the benefit of them. In other words, when assuming certain risks arising from some activities bring values to shareholder, this strategy can be picked.
机器学习代写
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Fundamentals of Risk Management
在 2007 年,没有人会想到风险职能会发生像过去八年那样大的变化。期望下一个十年必须包含更少的变化是一种自然的诱惑。然而,我们认为情况可能正好相反。
-Harle 等人。(2016)
风险管理是一个不断发展的过程。由于长期的风险管理实践无法跟上最近的发展步伐或成为危机蔓延的前兆,因此不断演变是不可避免的。因此,在风险管理过程中监控和采用结构性中断带来的变化非常重要。采用这些变化意味着重新定义风险管理的组件和工具,这就是本书的全部内容。
传统上,在金融领域,金融领域的实证研究非常关注统计推断。计量经济学建立在以下基本原理之上
统计推断。这些类型的模型专注于底层数据生成过程的结构和变量之间的关系。
然而,机器学习模型并未被假定为定义基础数据生成过程,而是被视为达到预测目的的一种手段(Lommers 等人,2021 年)。因此,机器学习模型往往更加以数据为中心和以预测准确性为导向。
此外,数据稀缺和不可用一直是金融领域的一个问题,不难猜测,计量经济学模型在这种情况下表现不佳。鉴于机器学习模型通过合成数据生成来解决数据不可用的问题,机器学习模型一直是金融领域的首要任务,金融风险管理当然也不例外。
在深入讨论这些工具之前,有必要介绍一下主要的风险管理概念。因此,本书的这一部分介绍了金融风险管理的基本概念,我将在整本书中提及这些概念。这些概念包括风险、风险类型、风险管理、收益以及与风险管理相关的一些概念。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|All financial investments
所有的金融投资都是为了获得利润,也叫回报。更正式地说,回报是在给定时间段内投资所获得的收益。因此,回报是指风险的上升。在整本书中,风险和回报将分别指下行风险和上行风险。
可以想象,风险和回报之间存在权衡,承担的风险越高,实现的回报就越大。由于提出最佳解决方案是一项艰巨的任务,因此这种权衡是金融界最具争议的问题之一。然而,Markowitz (1952) 为这个长期存在的问题提出了一个直观且有吸引力的解决方案。他定义风险的方式,在此之前是模棱两可的,但它很好而且很干净,并导致了金融研究领域的转变。Markowitz (1952) 使用标准差 $\sigma_{R_{i}}$ 来量化风险。这个直观的定义允许研究人员在金融中使用数学和统计学。标准差可以在数学上定义为 (Hull, 2012):
$$
\sigma=\sqrt{\mathbb{E}\left(R^{2}\right)-[\mathbb{E}(R)]^ {2}}
$$
其中 $\mathrm{R}$ 和 $\mathbb{E}$ 符号分别表示年回报率和期望值。本书多次使用符号$\mathbb{E}$,因为预期回报代表利息回报。这是因为我们在定义风险时谈论的是概率。当谈到投资组合方差时,协方差就出现了,公式结果是:
$$
\sigma_{p}^{2}=w_{a}^{2} \sigma_{a}^{2}+w_{b}^{2} \sigma_{b}^{2}+2 w_ {a} w_{b} \operatorname{Cov}\left(r_{a}, r_{b}\right)
$$
其中 w 表示权重,$\sigma^{2}$ 是方差,$\operatorname{ Cov}$ 是协方差矩阵。取上面获得的方差的平方根,我们得到了投资组合标准差:
$$
\sigma_{p}=\sqrt{\sigma_{p}^{2}}
$$
换句话说,投资组合预期收益是个人的回报可以表示为:
$$
\mathbb{E}(R)=\sum_{i}^{n} w_{i} R_{i}=w_{1} R_{1}+w_{2 } R_{2} \cdots+w_{n} R_{n}
$$
让我们通过可视化来探索风险回报关系。为此,构建了一个假设的投资组合以使用 Python 计算必要的统计数据。
统计代写|机器学习作业代写Machine Learning代考|Risk Management
金融风险管理是应对金融市场带来的不确定性的过程。它涉及评估组织面临的财务风险并制定与内部优先事项和政策一致的管理战略(Horcher,2011 年)。
根据这个定义,由于每个组织都面临不同类型的风险,因此公司处理风险的方式是完全不同的。每家公司都应正确评估风险并采取必要的措施来应对风险。然而,这并不一定意味着一旦确定了风险,就需要尽可能地减轻风险。
因此,风险管理并不是不惜一切代价降低风险。降低风险可能需要牺牲回报,并且在一定程度上是可以容忍的,因为公司正在寻求更高的回报以及降低风险。因此,在降低风险的同时最大化利润应该是一项微妙而明确的任务。
管理风险是一项微妙的任务,因为它伴随着成本,尽管处理它需要特定的公司政策,但存在可能的风险策略的一般框架。这些都是:
- 忽略:在这种策略中,公司接受所有风险及其后果,宁愿什么也不做。
- 转移:该策略涉及通过对冲或其他方式将风险转移给第三方。
- 缓解:公司制定降低风险的战略,部分原因是其有害影响可能被认为太多,无法承担和/或超过它所带来的好处。
- 接受风险:如果公司采用接受风险的策略,他们就会正确识别风险并承认风险的好处。换句话说,当假设某些活动产生的某些风险为股东带来价值时,可以选择这种策略。
统计代写请认准statistics-lab™. statistics-lab™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。统计代写|python代写代考
随机过程代考
在概率论概念中,随机过程是随机变量的集合。 若一随机系统的样本点是随机函数,则称此函数为样本函数,这一随机系统全部样本函数的集合是一个随机过程。 实际应用中,样本函数的一般定义在时间域或者空间域。 随机过程的实例如股票和汇率的波动、语音信号、视频信号、体温的变化,随机运动如布朗运动、随机徘徊等等。
贝叶斯方法代考
贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析表示使用概率陈述回答有关未知参数的研究问题以及统计范式。后验分布包括关于参数的先验分布,和基于观测数据提供关于参数的信息似然模型。根据选择的先验分布和似然模型,后验分布可以解析或近似,例如,马尔科夫链蒙特卡罗 (MCMC) 方法之一。贝叶斯统计概念及数据分析使用后验分布来形成模型参数的各种摘要,包括点估计,如后验平均值、中位数、百分位数和称为可信区间的区间估计。此外,所有关于模型参数的统计检验都可以表示为基于估计后验分布的概率报表。
广义线性模型代考
广义线性模型(GLM)归属统计学领域,是一种应用灵活的线性回归模型。该模型允许因变量的偏差分布有除了正态分布之外的其它分布。
statistics-lab作为专业的留学生服务机构,多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于Essay代写,Assignment代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,小组作业代写,Proposal代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,计算机作业代写,论文修改和润色,网课代做,exam代考等等。写作范围涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学全阶段,辐射金融,经济学,会计学,审计学,管理学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
机器学习代写
随着AI的大潮到来,Machine Learning逐渐成为一个新的学习热点。同时与传统CS相比,Machine Learning在其他领域也有着广泛的应用,因此这门学科成为不仅折磨CS专业同学的“小恶魔”,也是折磨生物、化学、统计等其他学科留学生的“大魔王”。学习Machine learning的一大绊脚石在于使用语言众多,跨学科范围广,所以学习起来尤其困难。但是不管你在学习Machine Learning时遇到任何难题,StudyGate专业导师团队都能为你轻松解决。
多元统计分析代考
基础数据: $N$ 个样本, $P$ 个变量数的单样本,组成的横列的数据表
变量定性: 分类和顺序;变量定量:数值
数学公式的角度分为: 因变量与自变量
时间序列分析代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其时间序列是一组按照时间发生先后顺序进行排列的数据点序列。通常一组时间序列的时间间隔为一恒定值(如1秒,5分钟,12小时,7天,1年),因此时间序列可以作为离散时间数据进行分析处理。研究时间序列数据的意义在于现实中,往往需要研究某个事物其随时间发展变化的规律。这就需要通过研究该事物过去发展的历史记录,以得到其自身发展的规律。
回归分析代写
多元回归分析渐进(Multiple Regression Analysis Asymptotics)属于计量经济学领域,主要是一种数学上的统计分析方法,可以分析复杂情况下各影响因素的数学关系,在自然科学、社会和经济学等多个领域内应用广泛。
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。
